Products
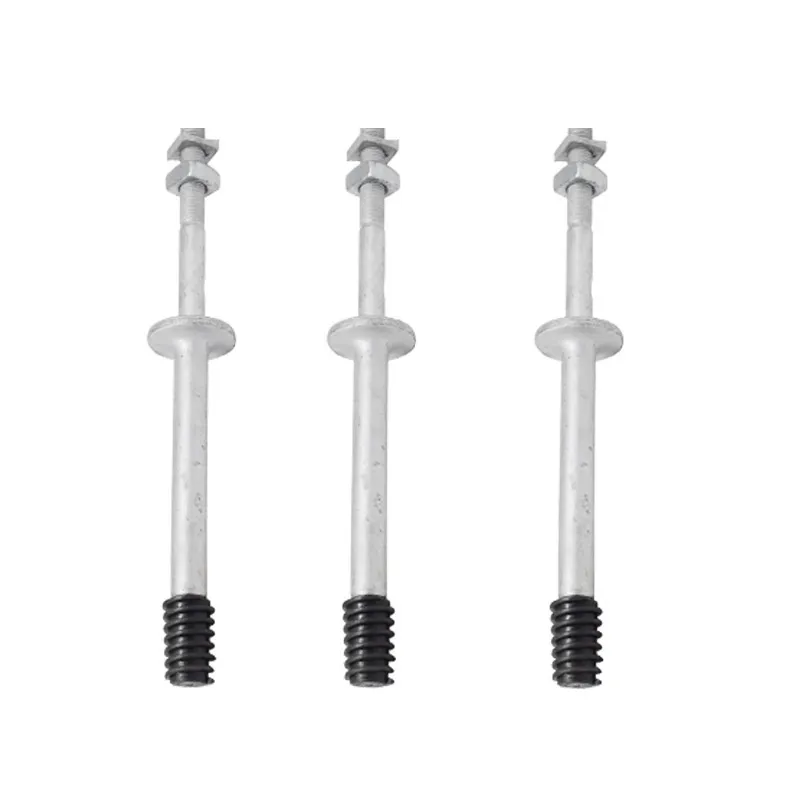
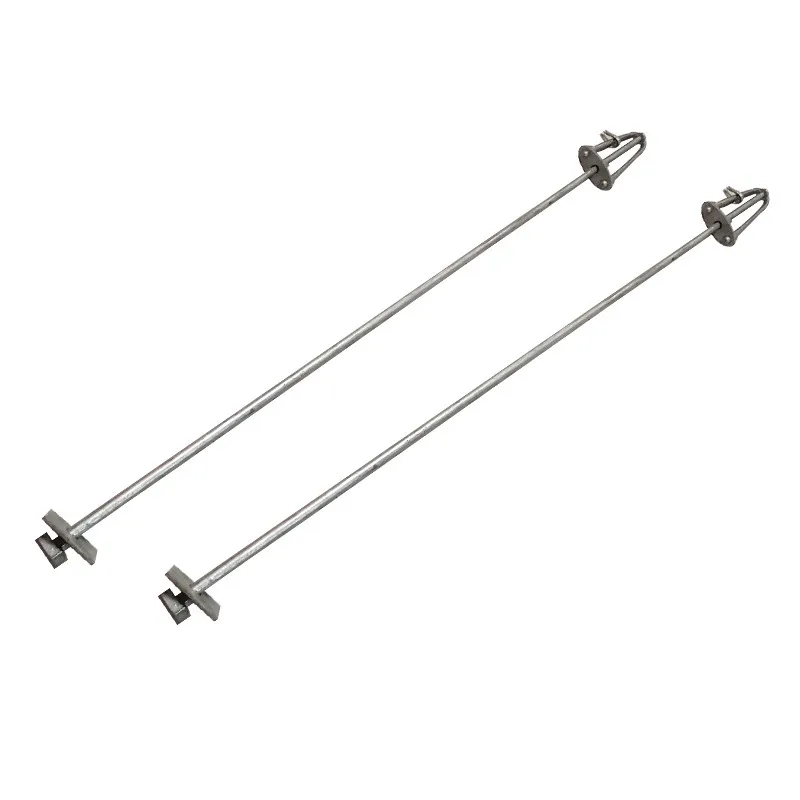
Arched rods
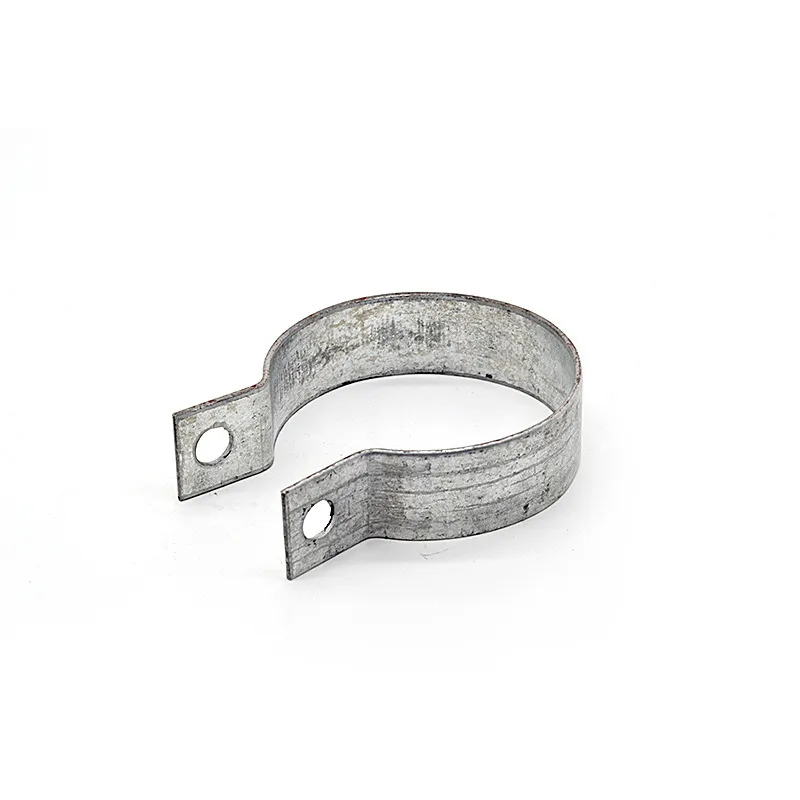
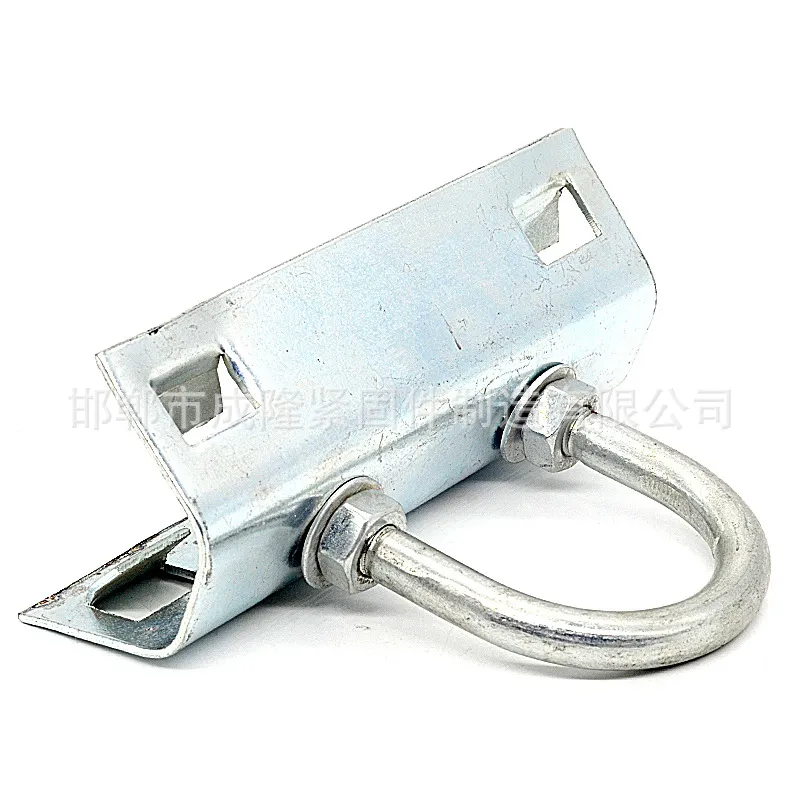
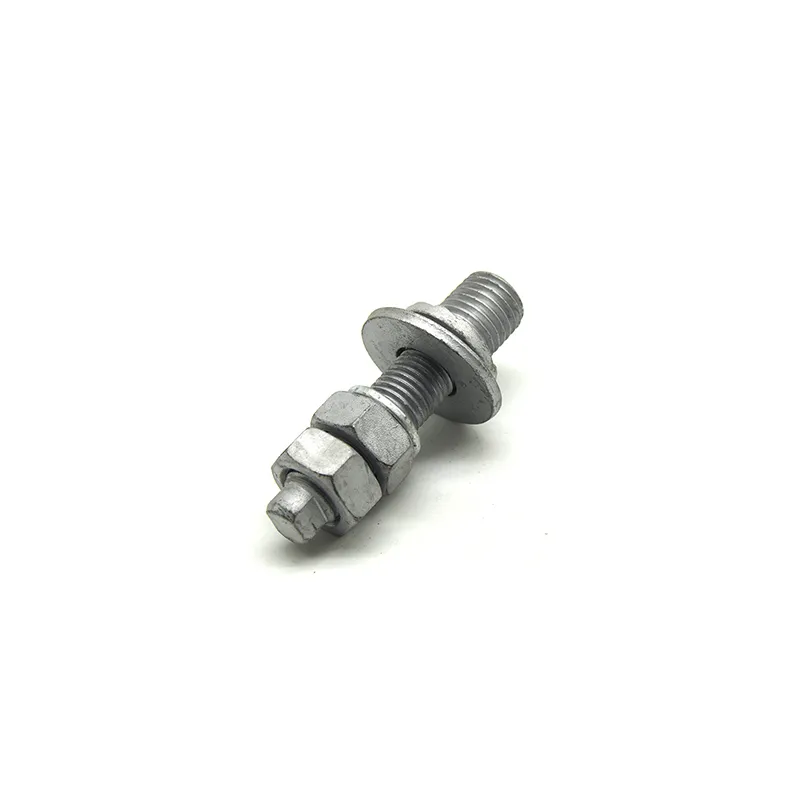
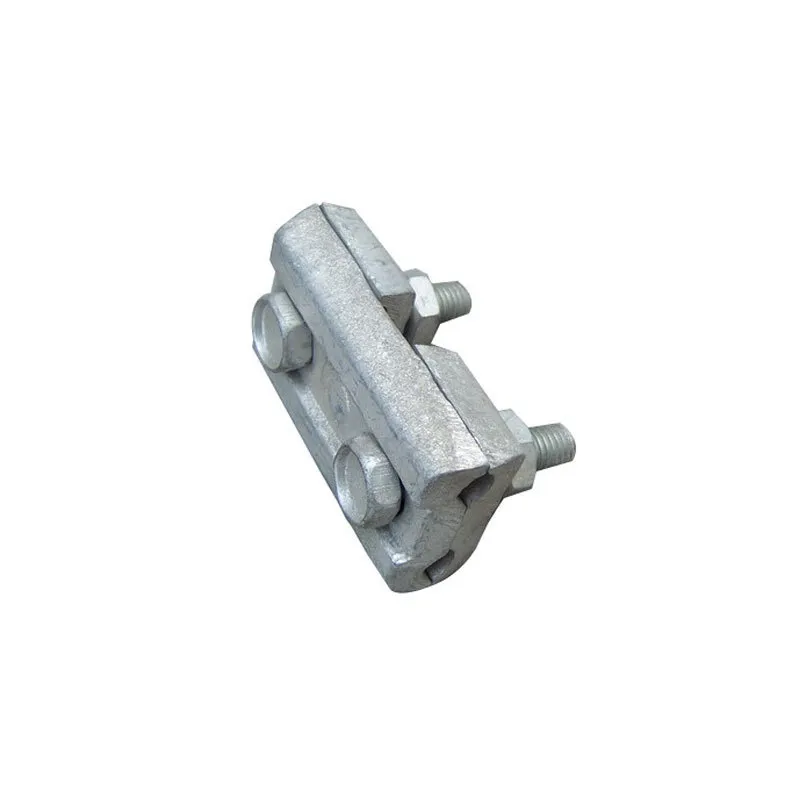
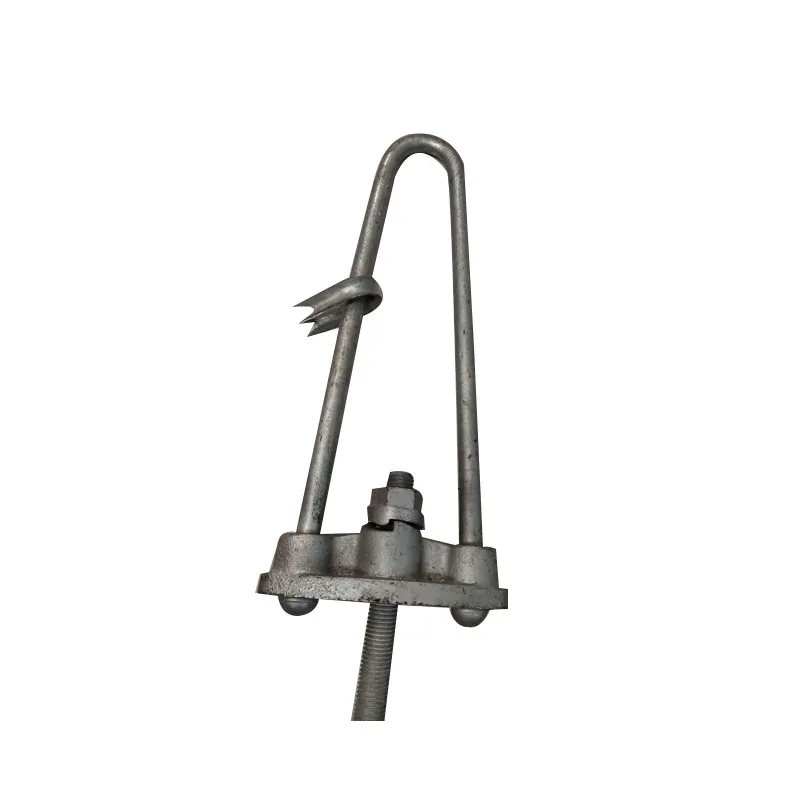
Product Description: The “butterfly-type cable tie” is a fastener with a special shape and function, widely used in various fields. Its design and working principle enable efficient force transmission and load-bearing capacity. Below is a detailed description of the butterfly-t...
Description
marker
Product Description:
The "butterfly-type cable tie" is a fastener with a special shape and function, widely used in various fields. Its design and working principle enable efficient force transmission and load-bearing capacity. Below is a detailed description of the butterfly-type cable tie:
Design Features:
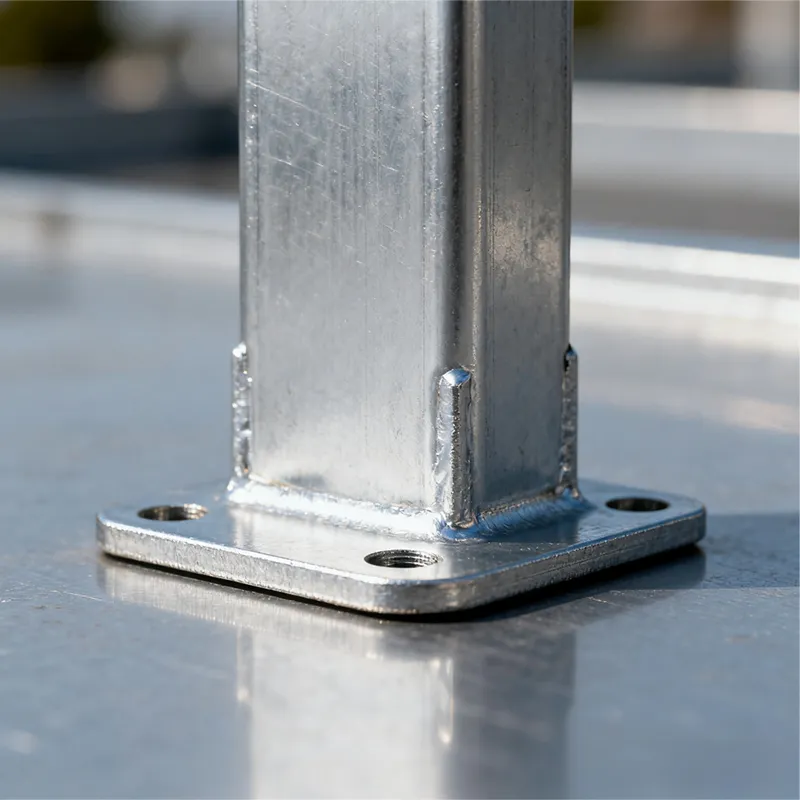
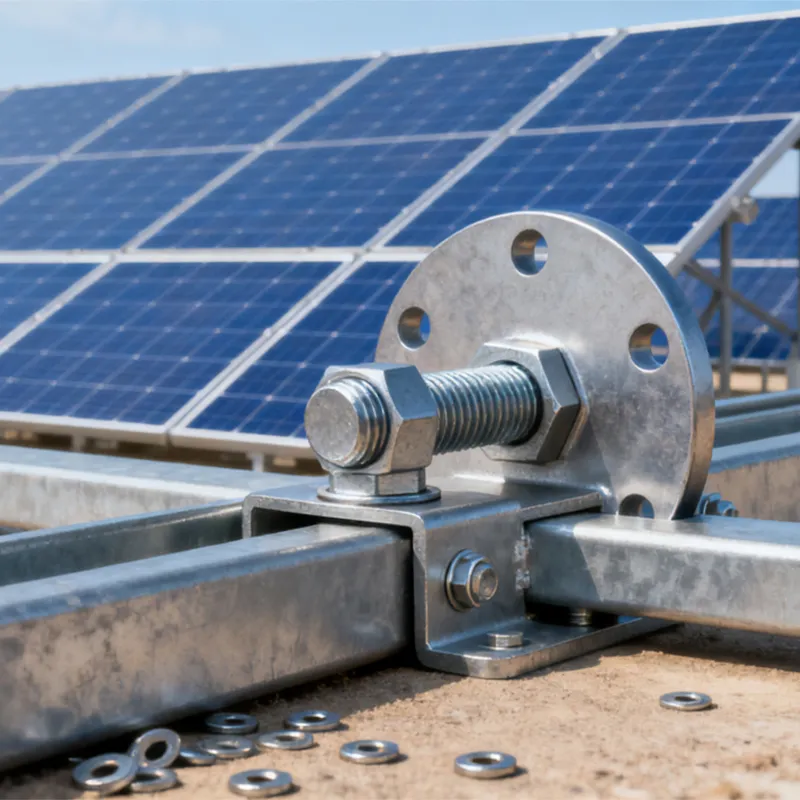
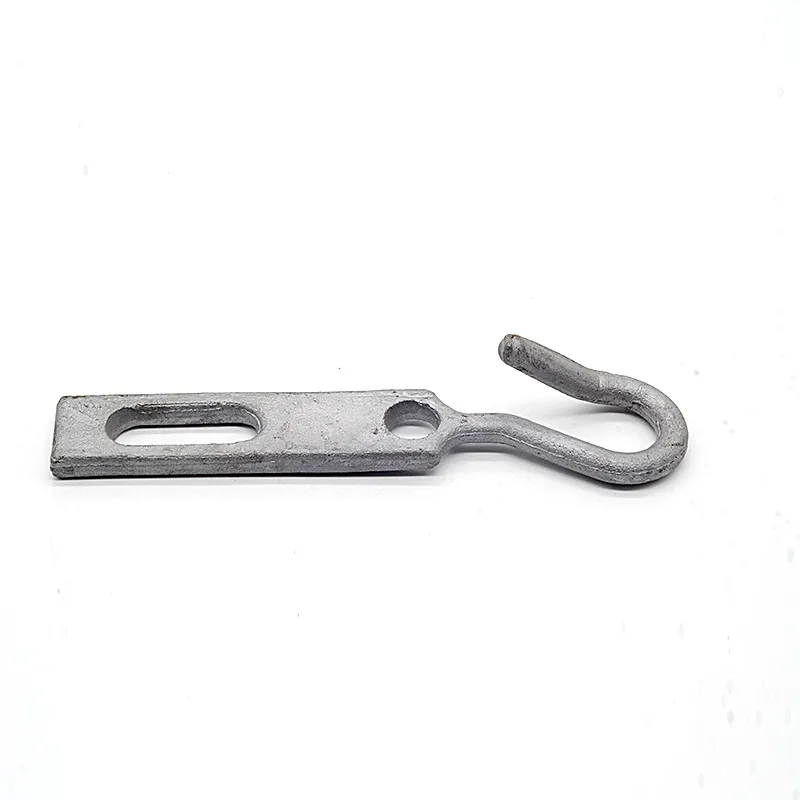
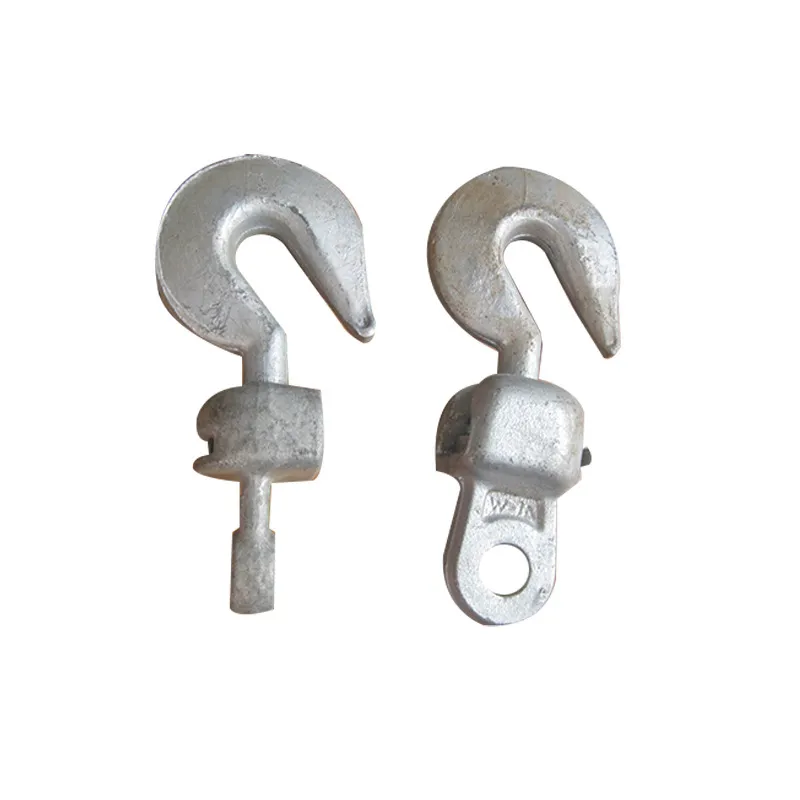
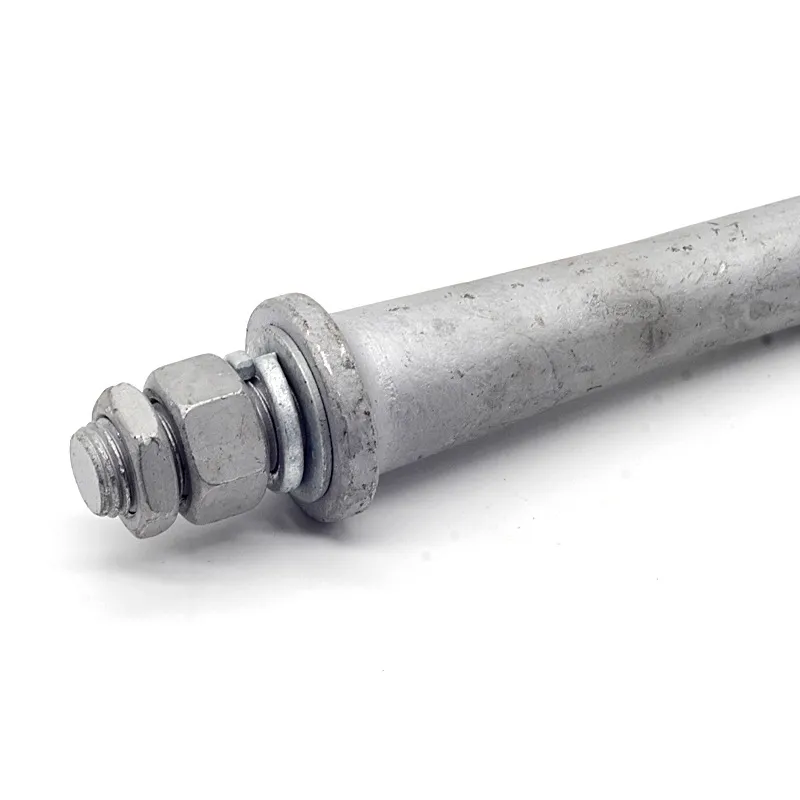
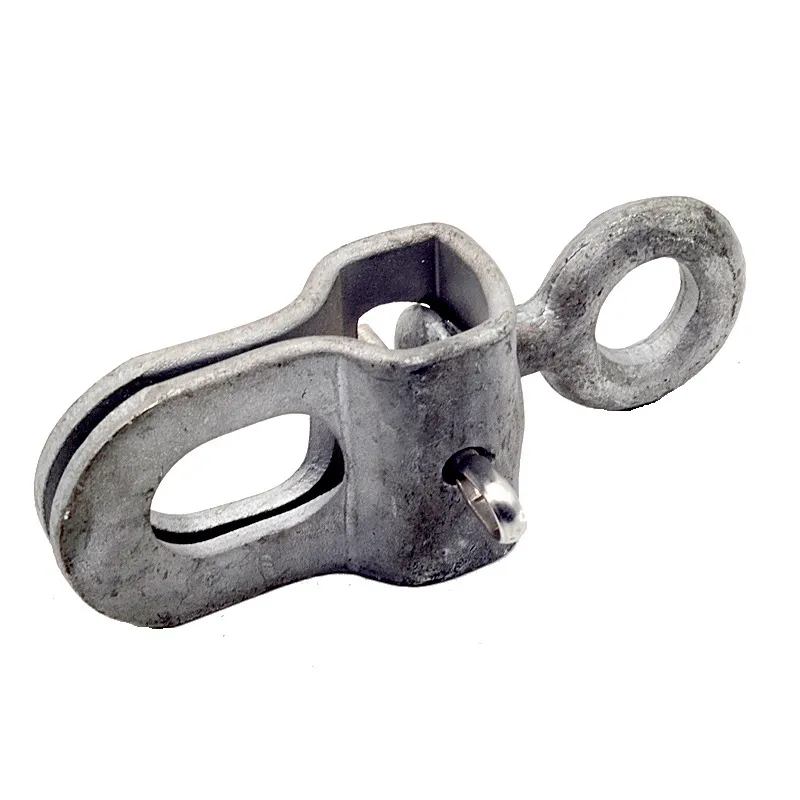
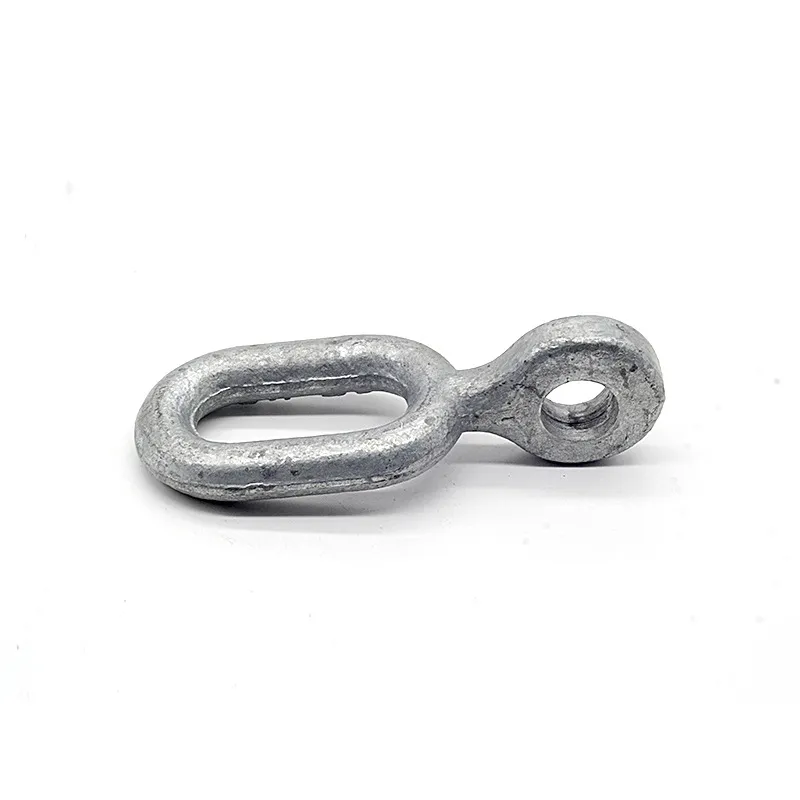
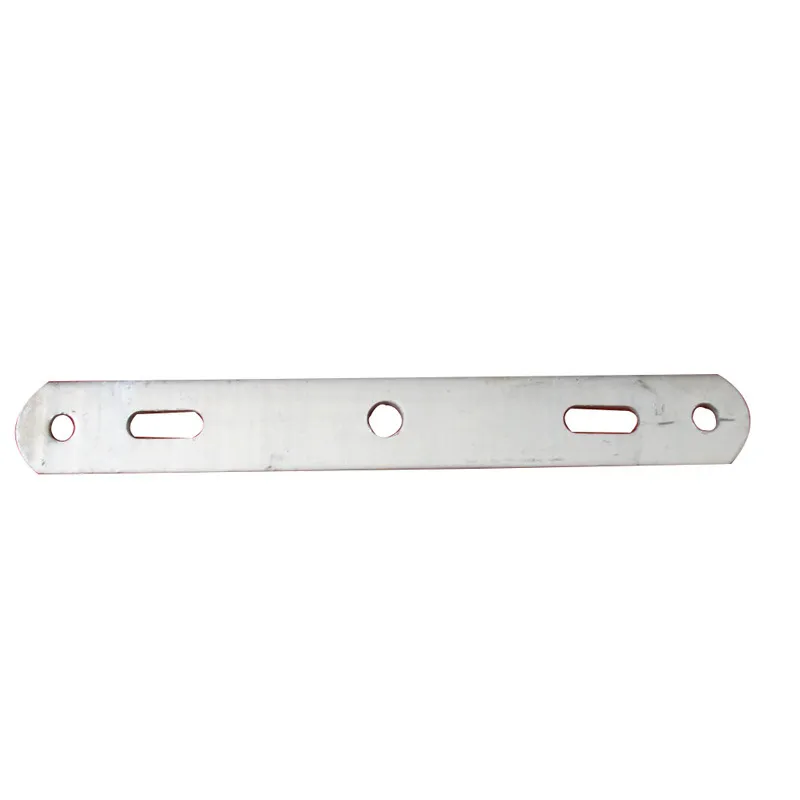
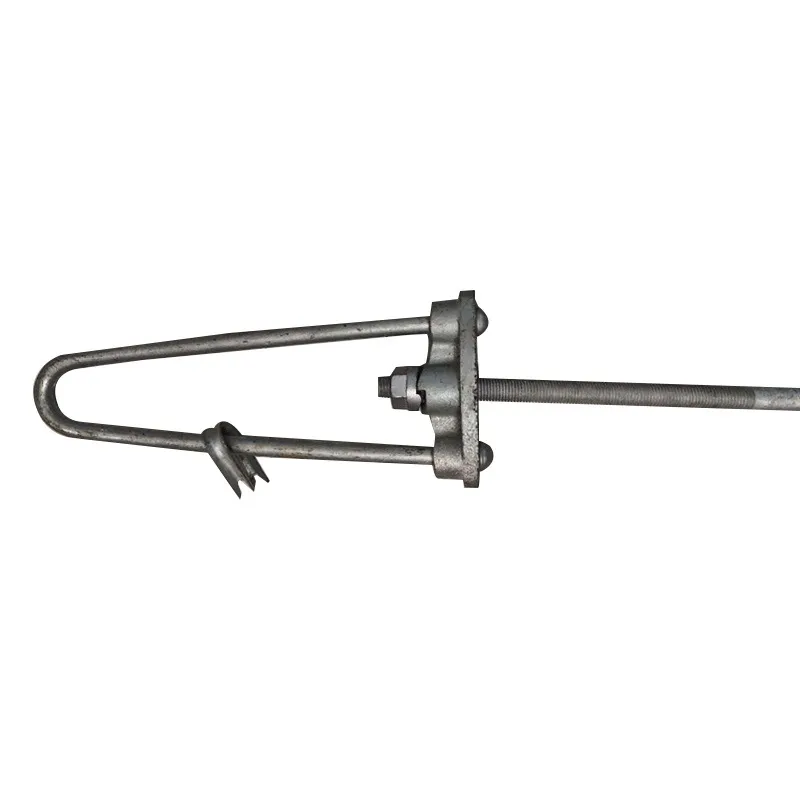
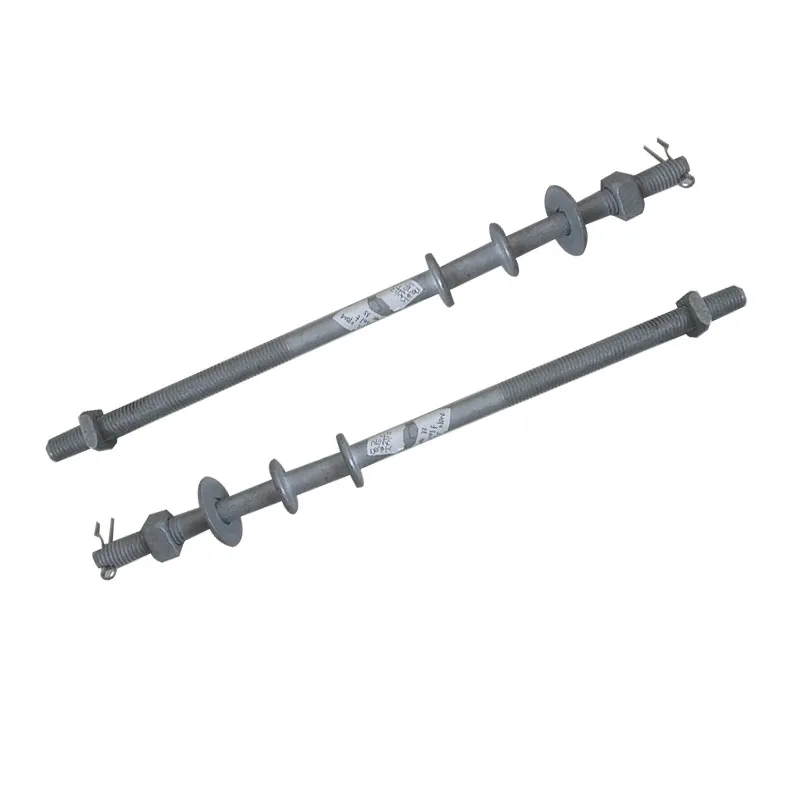
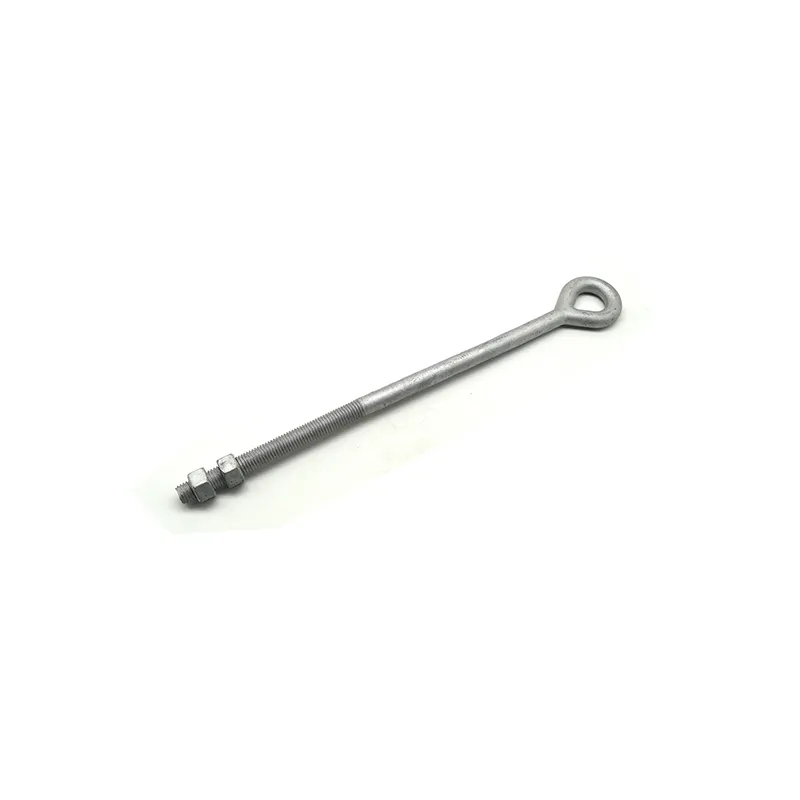
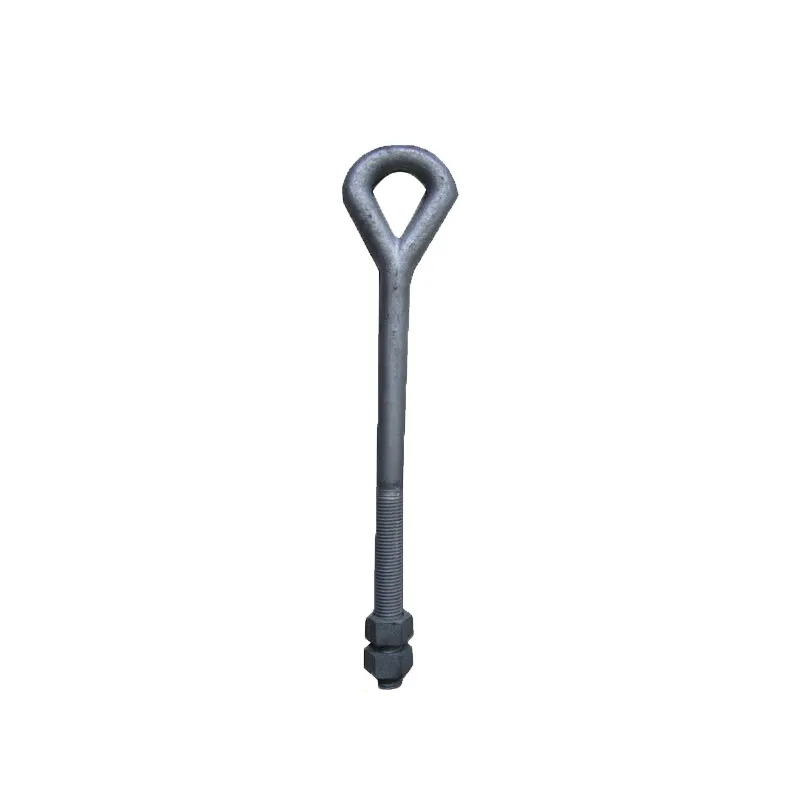
Main Structure: An arched rod typically consists of a curved arched section and connecting elements at both ends. The arched section serves as the main load-bearing structure and is usually arc-shaped. This shape ensures uniform distribution of tensile forces along the entire length of the rod, enhancing its load-bearing capacity. The end connections facilitate attachment to other components, typically via bolted joints or pin connections.
Material Selection: To ensure sufficient strength and durability, arched rods are usually made of high-strength steels such as alloy steels. These materials undergo appropriate heat treatment, including quenching and tempering, to improve strength, toughness, and wear resistance, enabling them to meet the requirements of various operating conditions and loads.
Operating Principle:
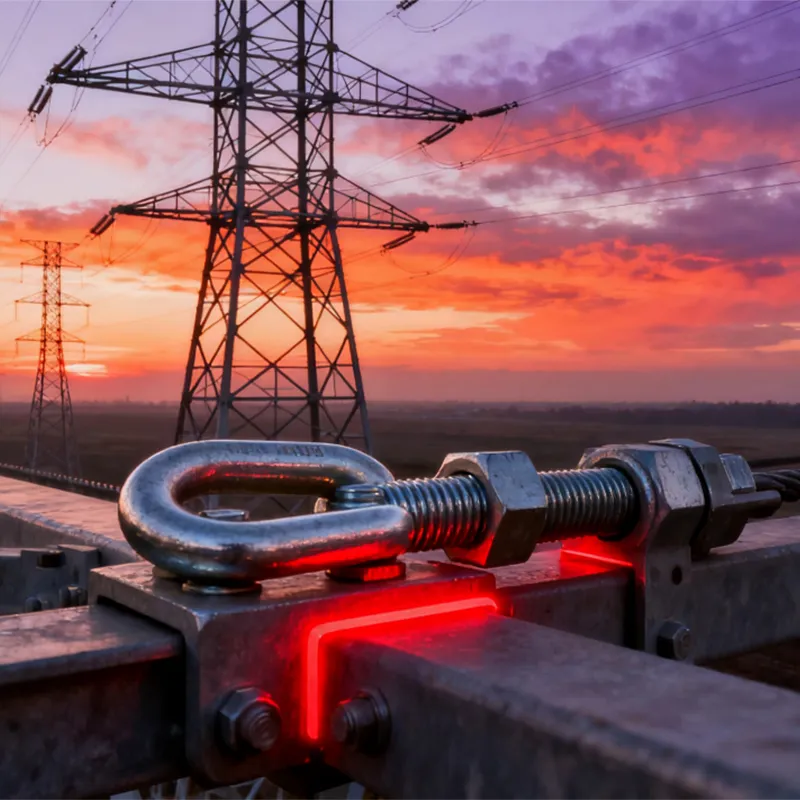
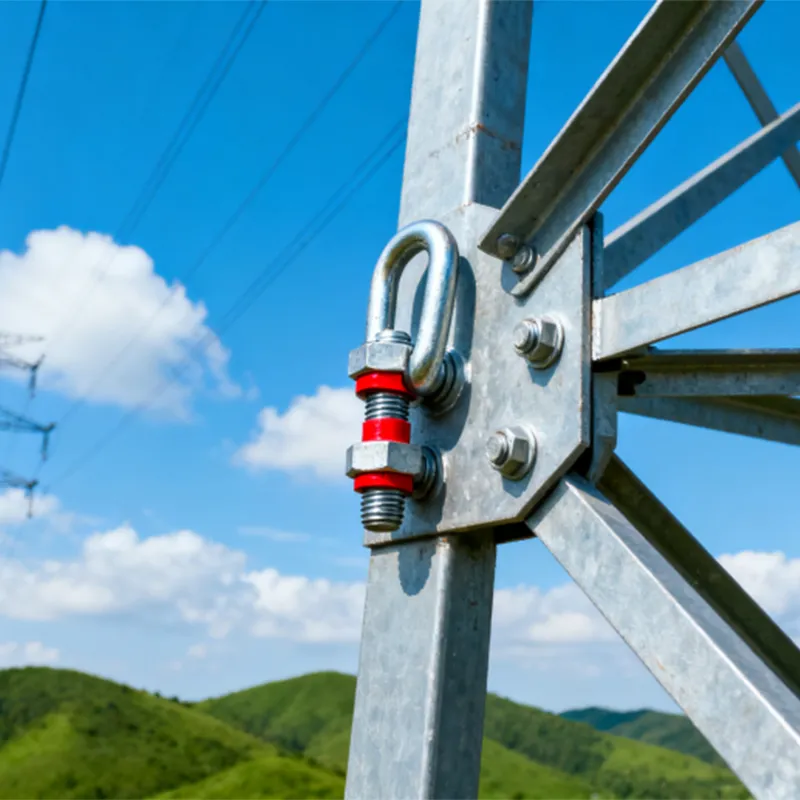
The functionality of an arched rod depends on its distinctive shape and mechanical properties. When subjected to tensile forces, the arched section undergoes elastic deformation, converting external tension into internal stresses. Thanks to the curved structure of the arch, these stresses are distributed along its curvature, enabling the rod to withstand significant tensile loads without damage or deformation. At the same time, the connection points at both ends transmit tensile forces to the associated structural components, thereby ensuring force transmission and structural stability.
Application Areas:
Architecture: In large-span structures such as stadiums, exhibition halls, and warehouses, arched tie rods are part of tensioned beam systems. These structures consist of arch beams, lower chord arched tie rods, and braces. By applying pre-tension through stretching the arched tie rods, the stress distribution within the structure is effectively regulated, enabling deformation control and covering large spans.
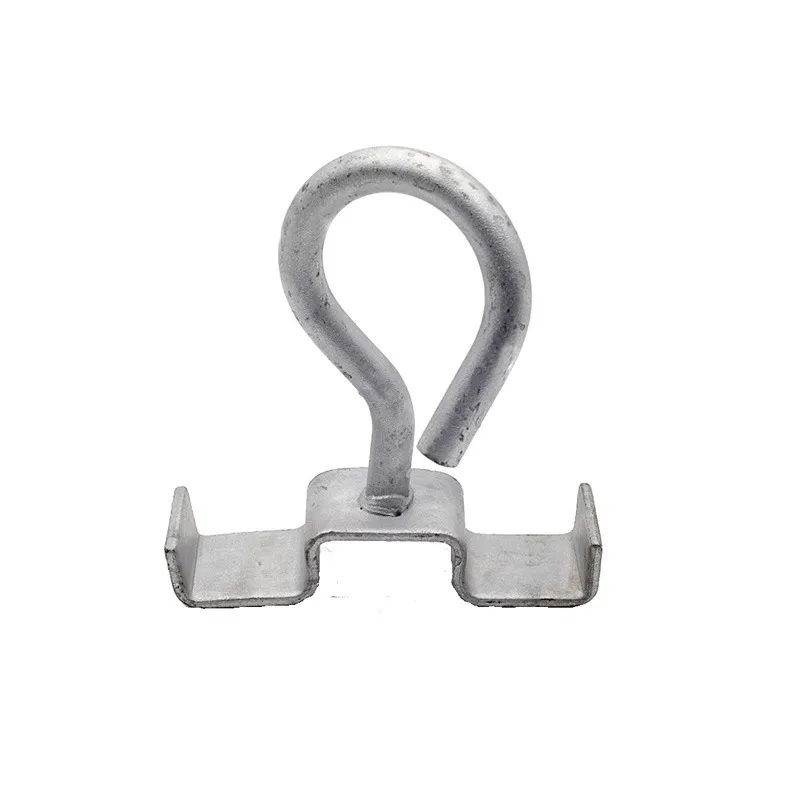
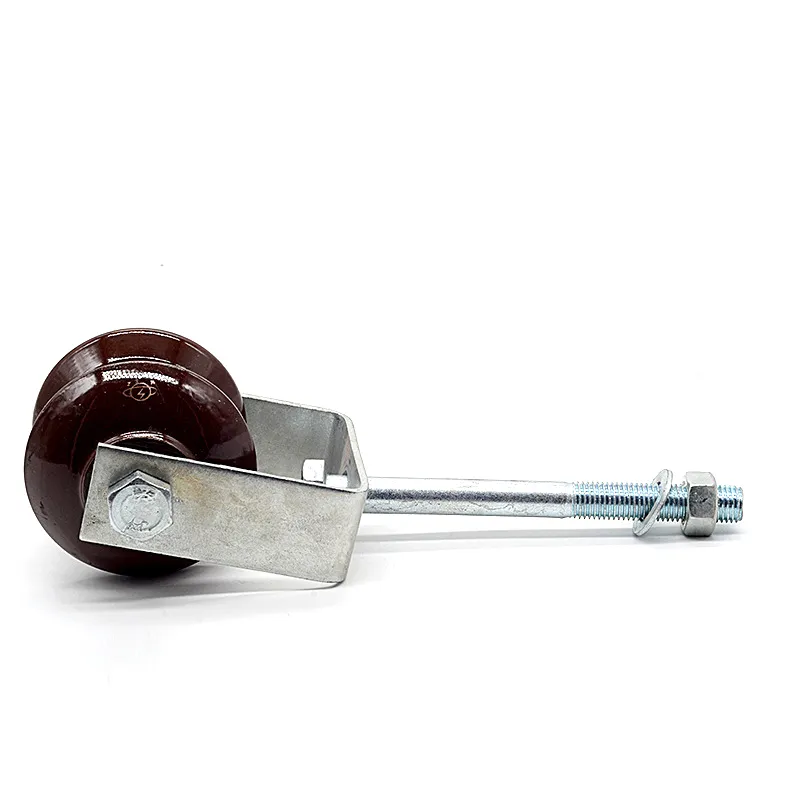
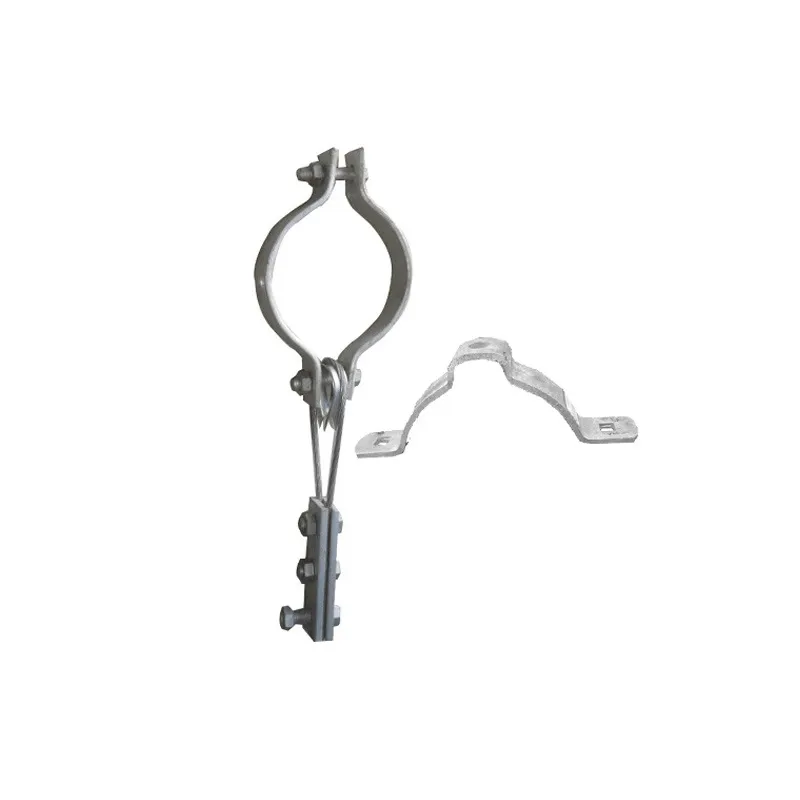
Electrical Engineering: Arched tie rods serve as anti-deflection elements for power transmission line supports, also known as arched stays. Installing a central support column with arched tie rods attached to its top and bottom ends forms an arched structure. This significantly enhances the support’s bending resistance, providing the necessary support and stability—especially in confined spaces or areas with terrain restrictions.
Mechanical Engineering: In certain machinery, arched tie rods facilitate force transmission and motion. Used in lifting equipment and machine tools, they function as connecting and transmitting components, ensuring operational reliability and precision.











































