Products
Galvanized steel ground rods
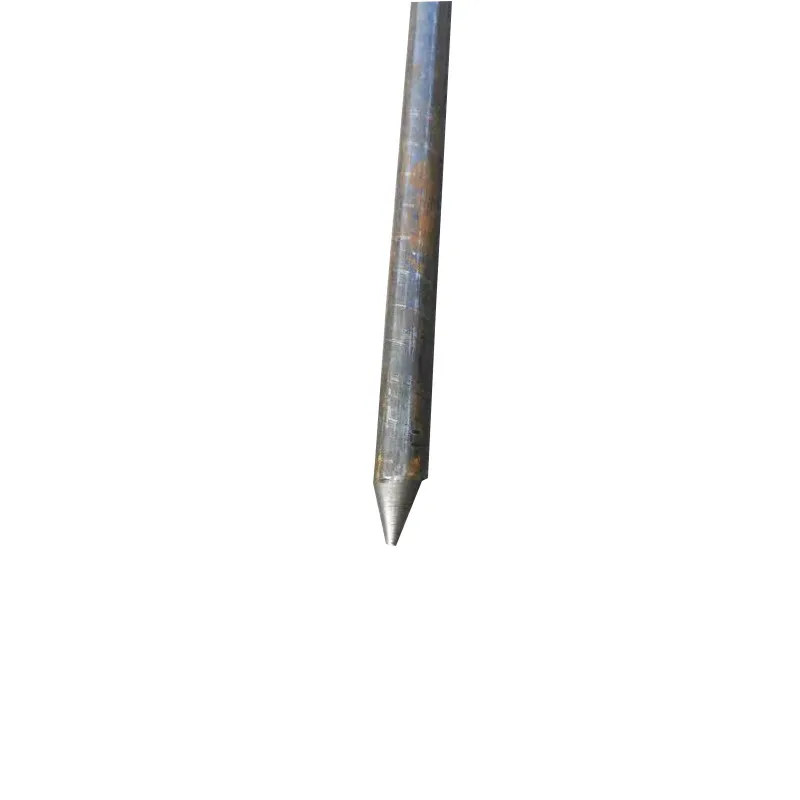
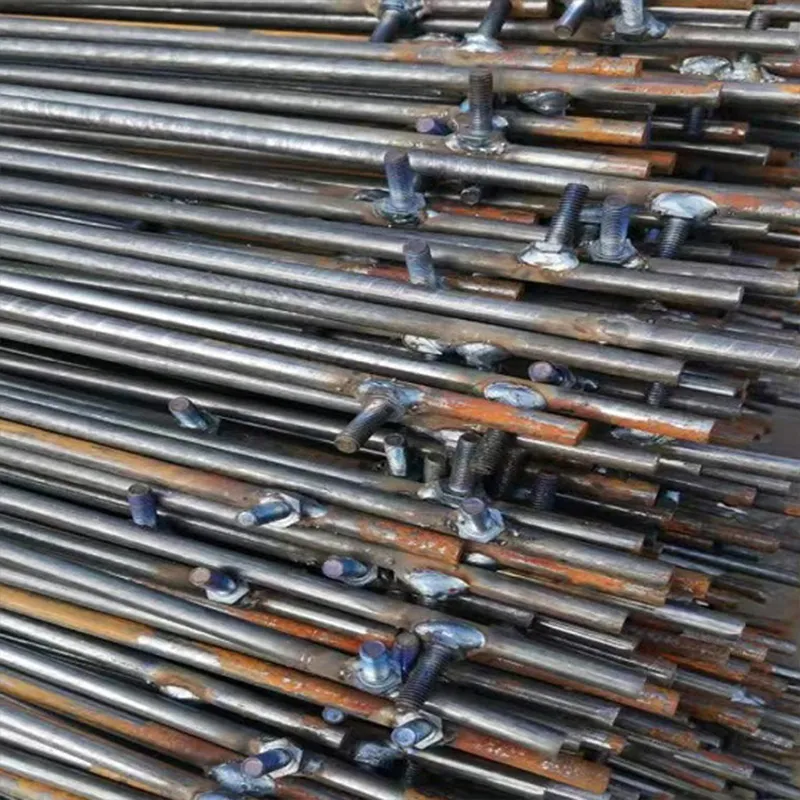
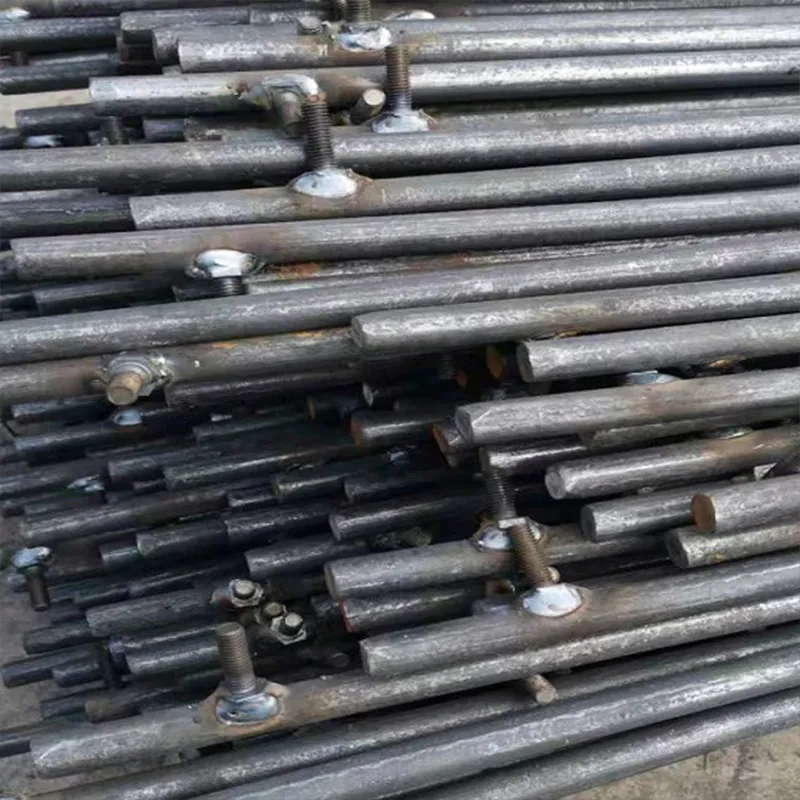
Product description: Galvanized steel ground rods serve as grounding materials for lightning protection systems. Their composite structure combines a “steel reinforcing core for strength” and a “galvanized coating for corrosion resistance,” ensuring effective conduc...
Description
marker
Product description:
Galvanized steel ground rods serve as grounding materials for lightning protection systems. Their composite structure combines a "steel reinforcing core for strength" and a "galvanized coating for corrosion resistance," ensuring effective conductivity and dissipation of lightning and ground fault currents. They are widely used in grounding projects in the construction, energy, and telecommunications industries.
Basic structure and design features:
The structure of galvanized steel ground rods is designed for "high strength" and "durable corrosion resistance," achieving a balance between mechanical properties and electrical conductivity.
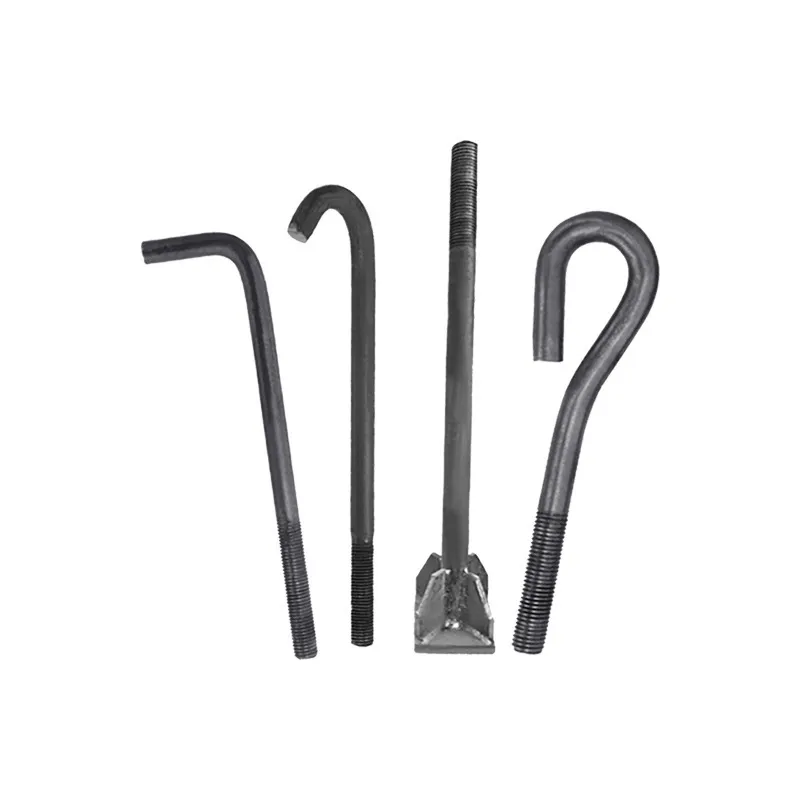
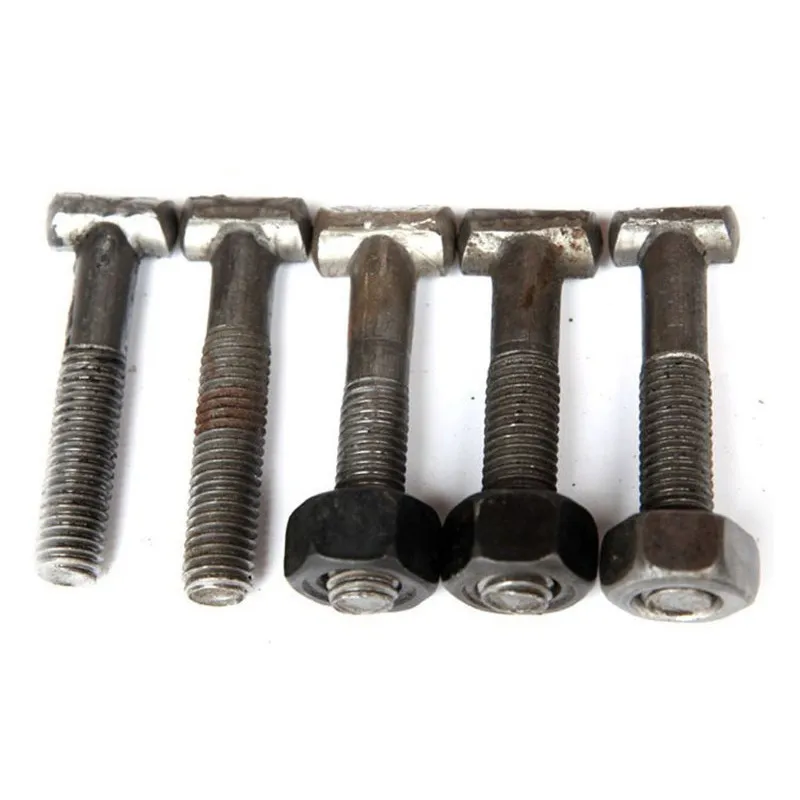
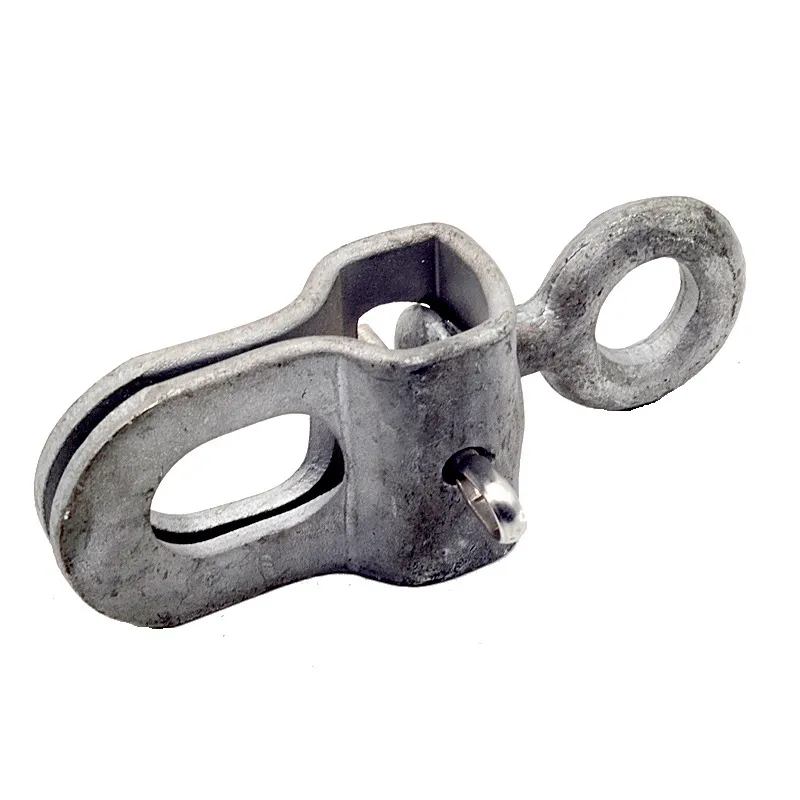
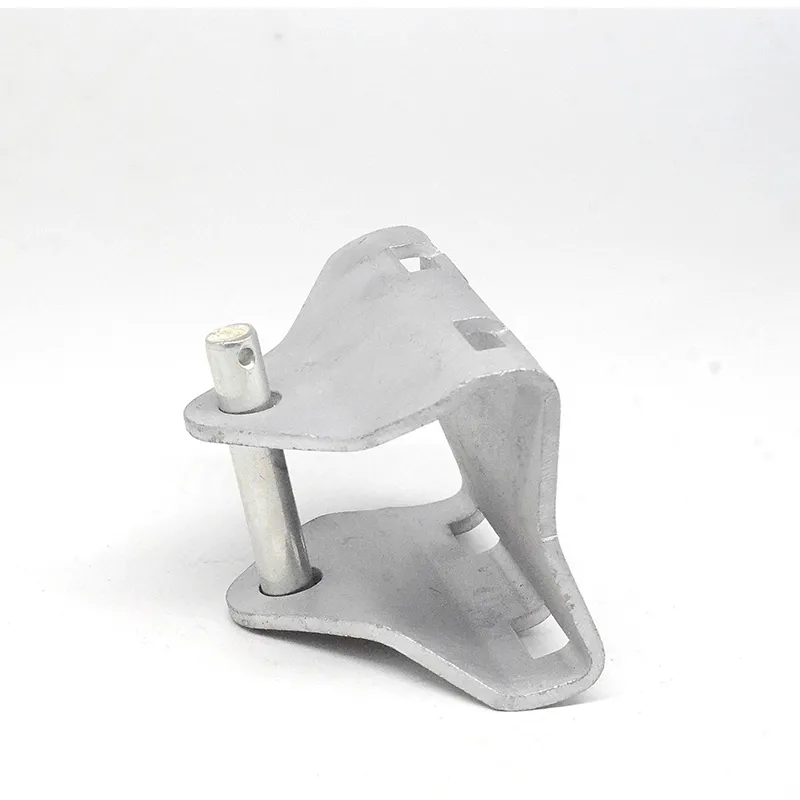
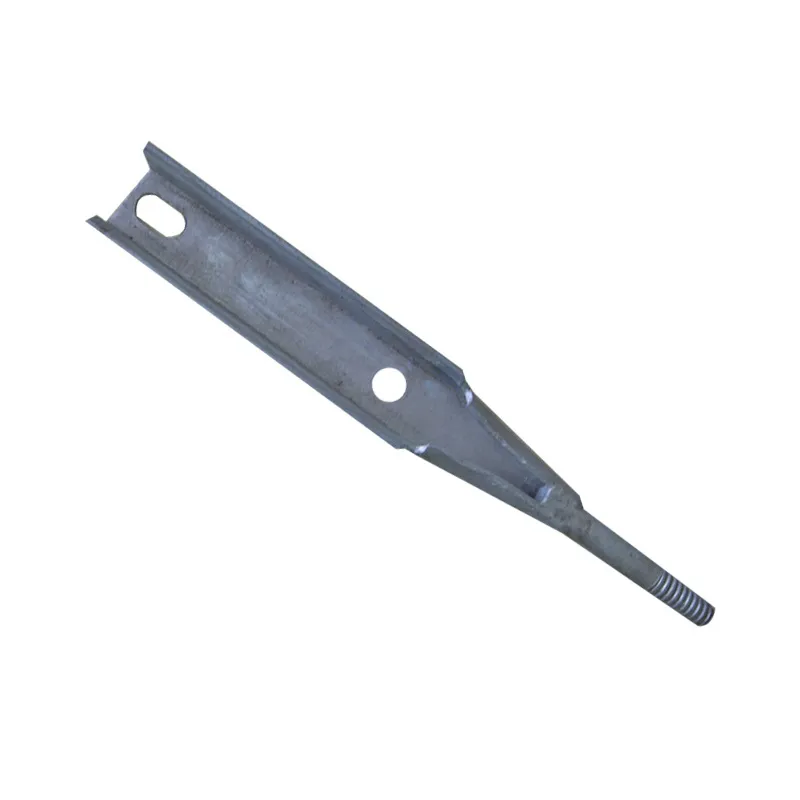
Basic Construction: Using a composite "core material + coating" construction, the core consists of a low-carbon steel core (e.g., Q235 steel) coated with a dense layer of zinc. Some models feature a ribbed or rolled texture on the surface of the steel core to improve adhesion between the zinc coating and the steel core, preventing coating peeling.
Key Design Features:
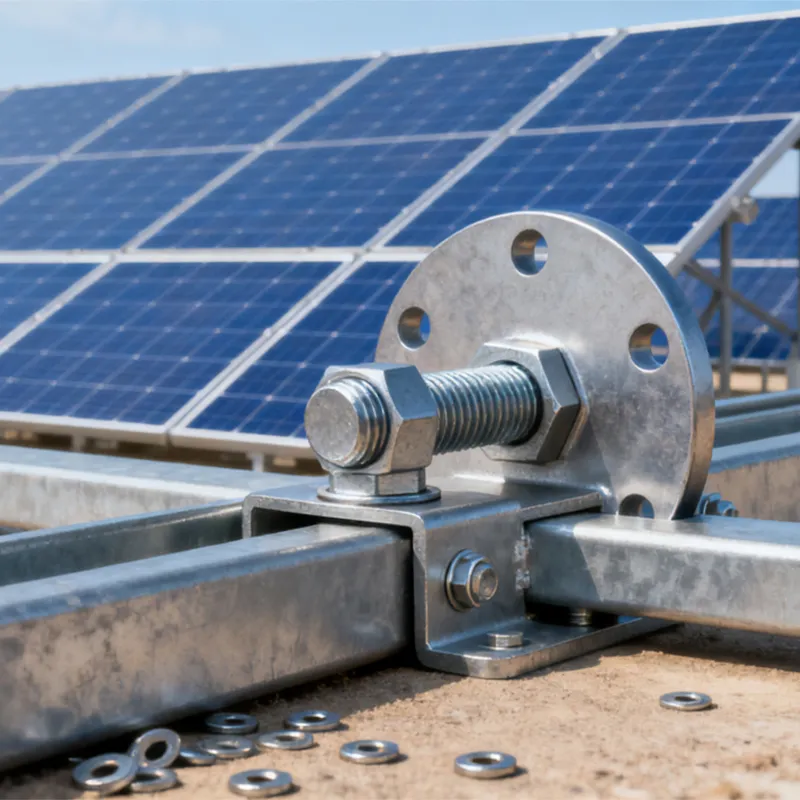
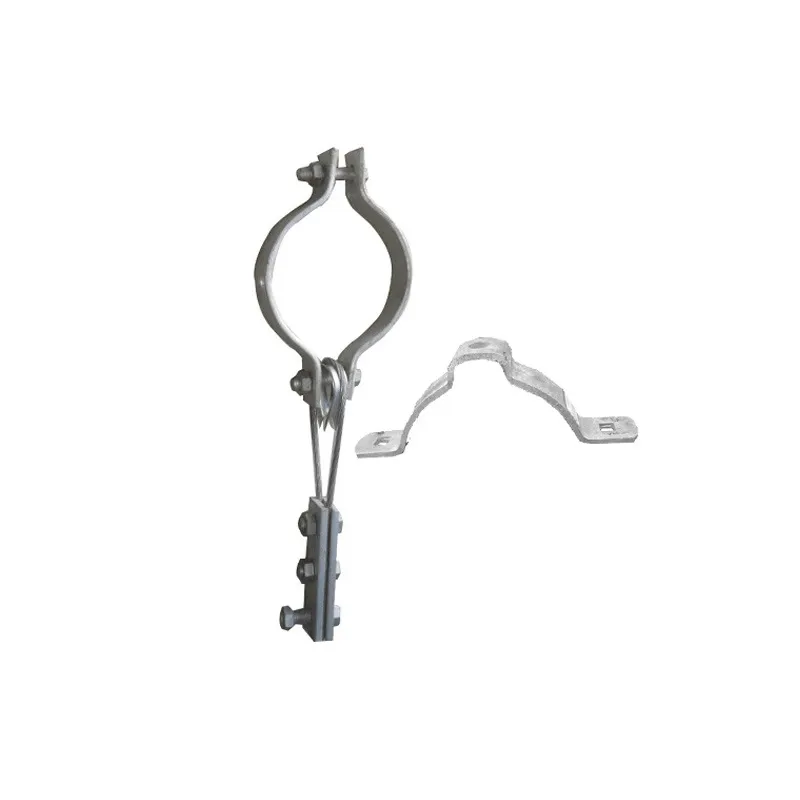
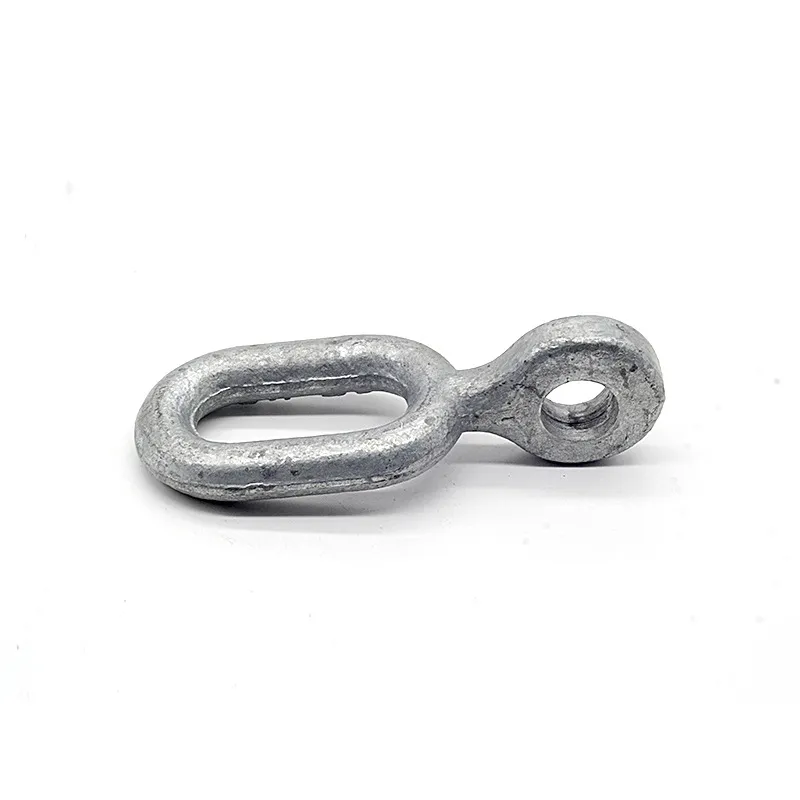
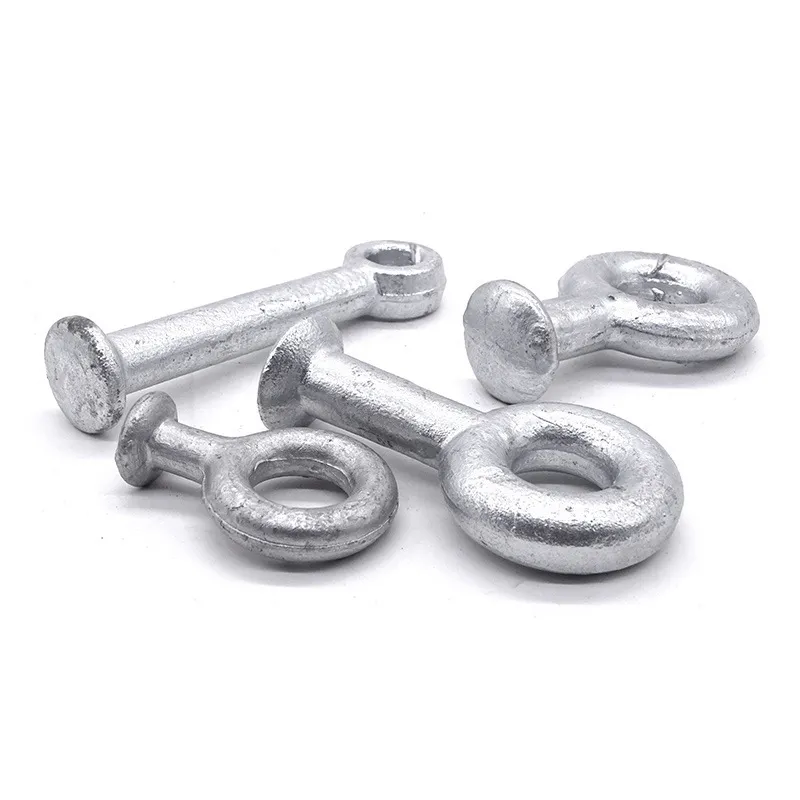
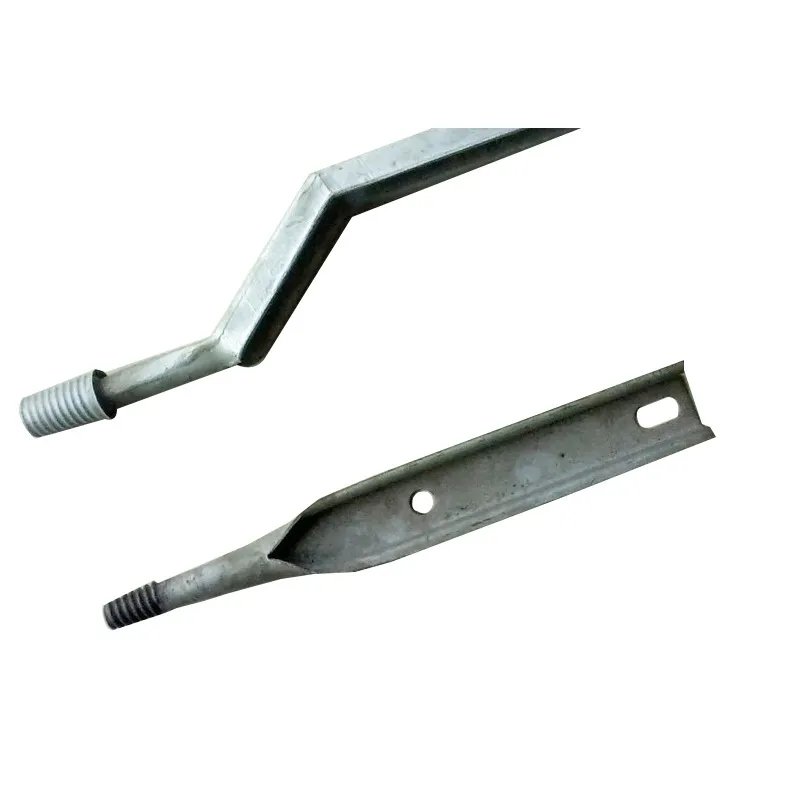
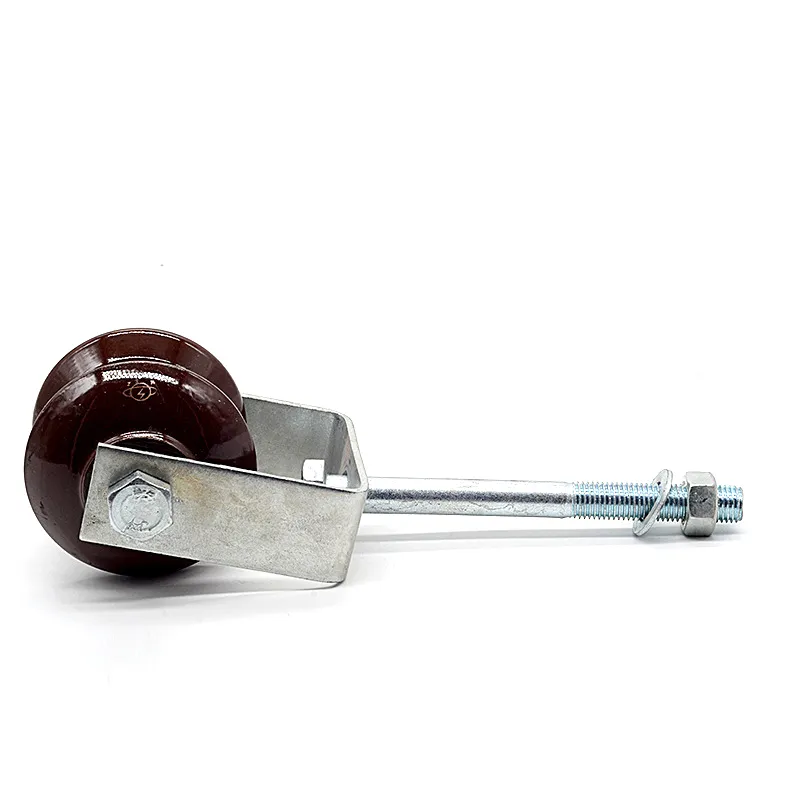
One end is typically tapered to facilitate manual or mechanical driving and drilling for underground installation, reducing soil resistance. The opposite end may have threaded connections or mounting holes for connection to ground electrodes or conductors (e.g., galvanized flat steel) to form a complete grounding network.
The zinc layer thickness is strictly controlled (typically ≥0.6 mm), significantly exceeding that of standard galvanized components. This creates a "sacrificial anode" in the soil, where the zinc layer corrodes preferentially compared to the steel core, extending the life of the ground rod.
Some products feature an additional anti-corrosion coating (e.g., epoxy resin) over the zinc layer, suitable for highly corrosive soil environments such as high salinity, alkalinity, or humidity, further enhancing corrosion resistance.
Advantages of the material and performance characteristics:
The choice of material directly determines the strength, electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance of the grounding rod. Its composite structure offers numerous performance advantages.














































