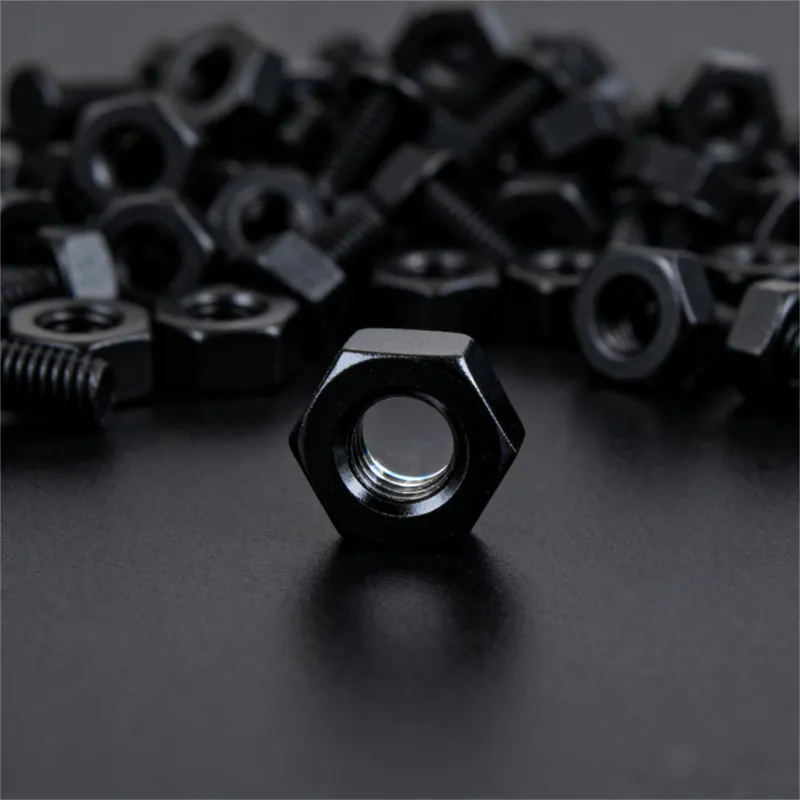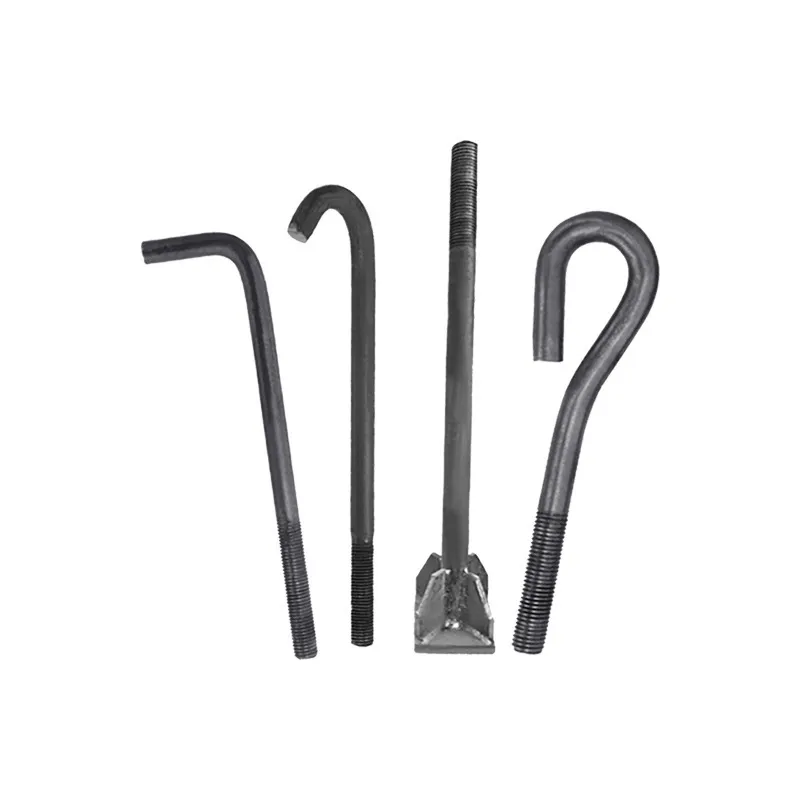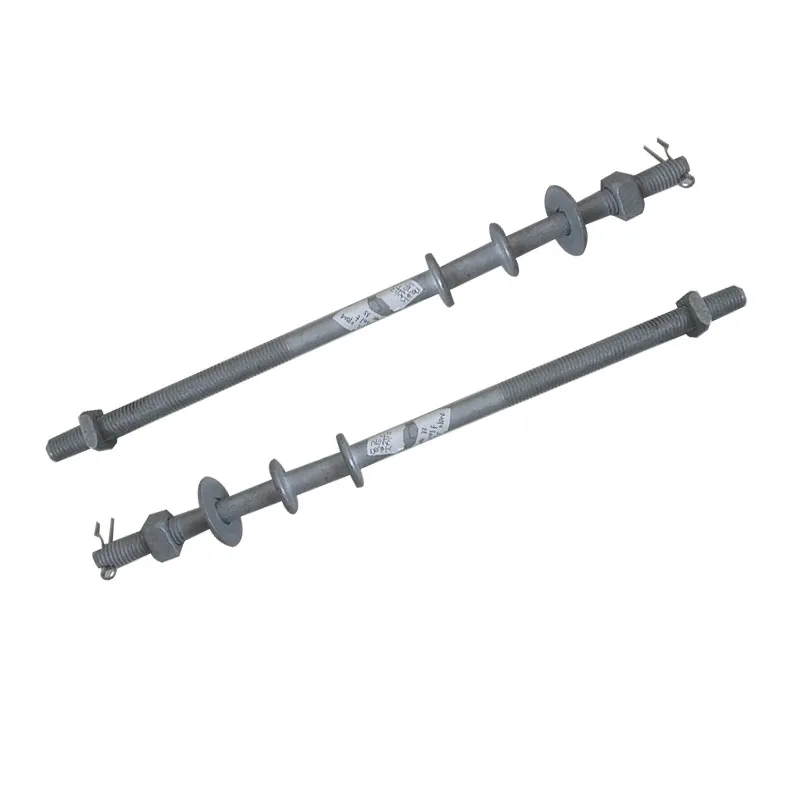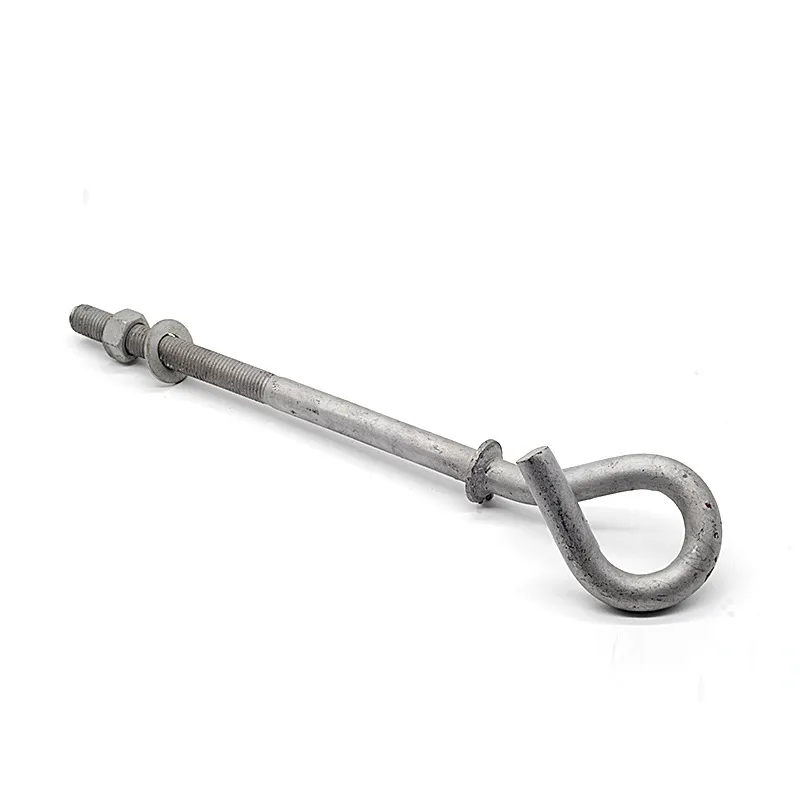
Products
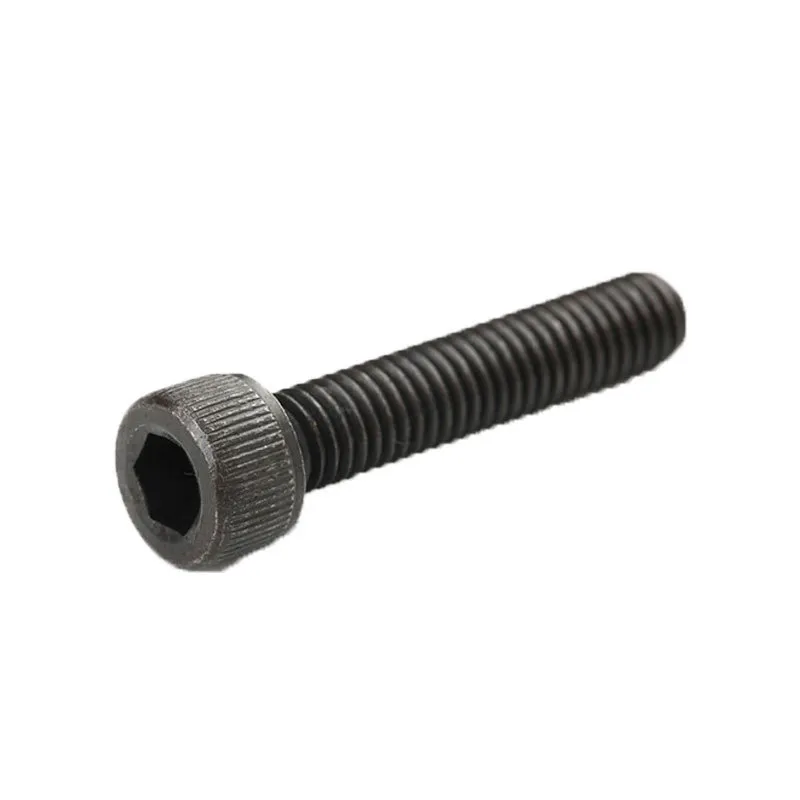
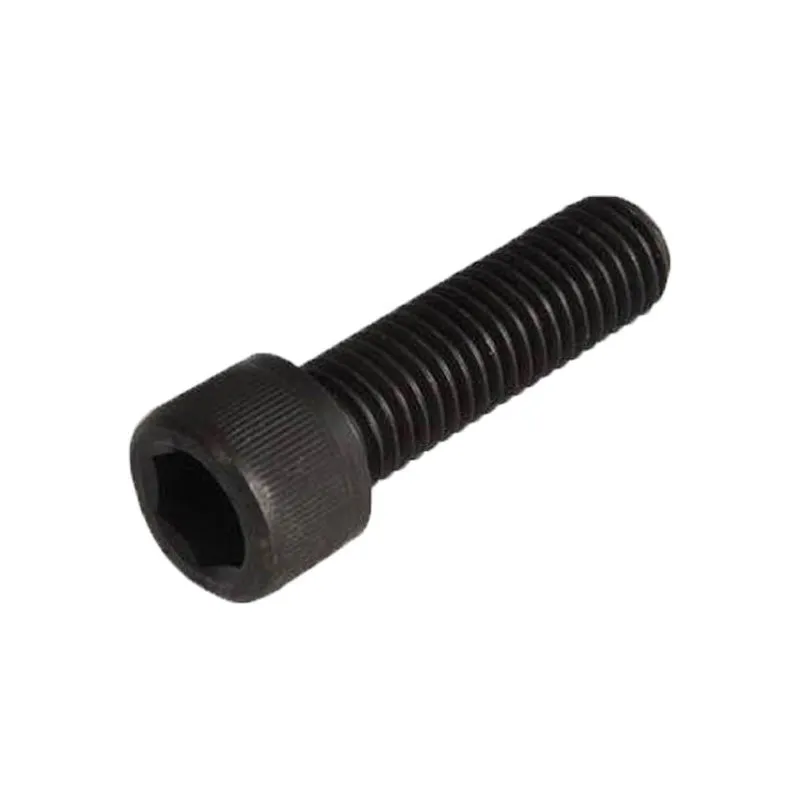
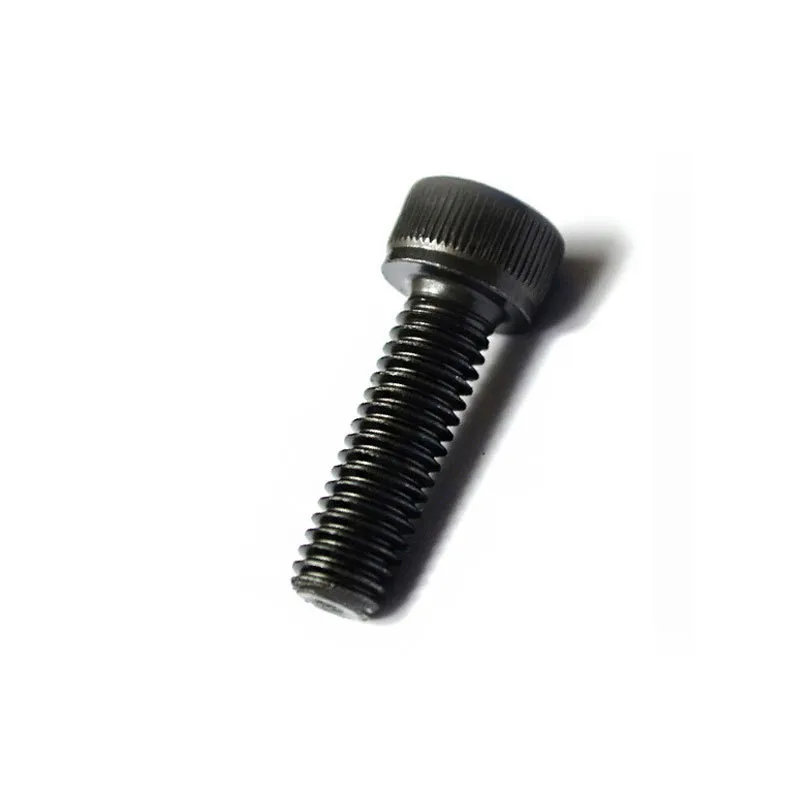
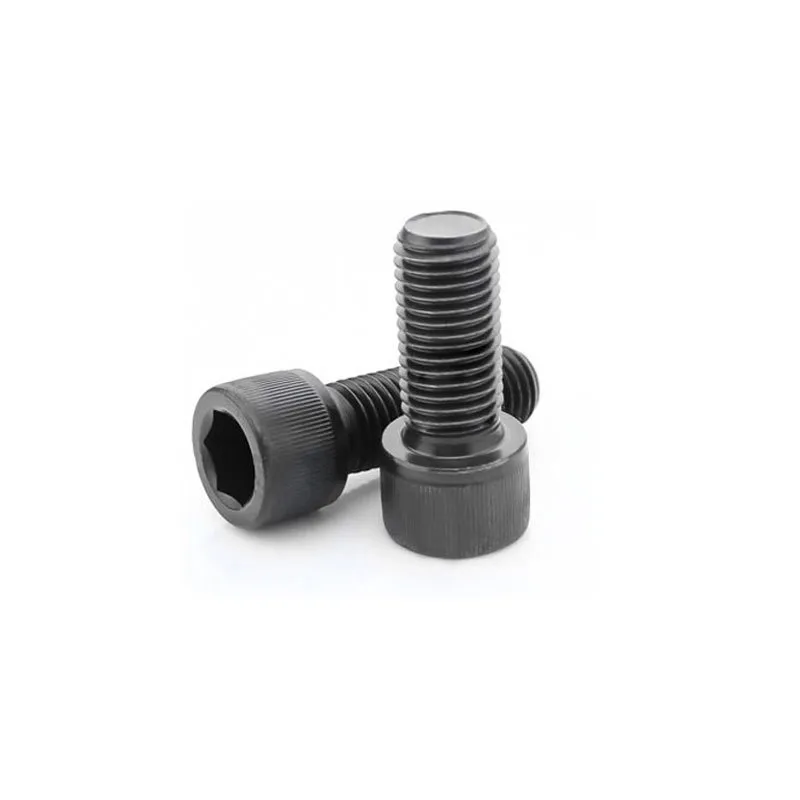
Hexagon socket head cap screws
Product description: Socket head cap screws are fasteners with a cylindrical head and an internal hexagon at the top. Their main advantages include a flat profile and minimal space requirements after installation, while the internal hexagonal design allows them to withstand high tightening...
Description
marker
Product description:
Socket head cap screws are fasteners with a cylindrical head and an internal hexagon at the top. Their main advantages include a flat profile and minimal space requirements after installation, while the internal hexagonal design allows them to withstand high tightening torques. They are suitable for applications requiring compact mounting space and high connection strength.
Basic design and construction features:
The design of hexagon socket head bolts is focused on a "low footprint" and "efficient force transmission," which distinguishes them from traditional hex bolts.
Basic Design: Consists of a cylindrical head and a threaded shank. The top of the head has a machined internal hexagon (compatible with hex keys), and the shank can be fully or partially threaded.
Fully threaded shank: Suitable for thin-walled components where the full thread length ensures complete engagement with the nut.
Partially threaded shank: The unthreaded portion has a diameter greater than the large thread diameter, increasing shear resistance. Ideal for thick components or applications subject to lateral loads.
Key Design Features:
The low head height (typically 1/3–1/2 the diameter) allows the bolt to be installed flush with the surface of the mounted component, taking up minimal additional space. This makes it ideal for tight spaces, such as the interior of equipment or tight connections.
The hex head is precision machined to ensure a precise fit, preventing slippage when torque is applied. This allows for greater torque transfer than flat-head or Phillips-head bolts, reducing the risk of head damage.
Some models feature anti-slip grooves or locating rings on the sides of the head, which increase friction with the fastened component and prevent loosening due to vibration.
Materials and strength classes:
Materials and strength grades range from standard to high-strength to meet a variety of load-bearing requirements.
Primary Materials:
Standard Applications: Q235 carbon steel or 10# steel. Economical and easy to machine, suitable for low-load and dry environments (e.g., furniture, light equipment).
Medium to High-Strength Applications: 45# steel or 40Cr alloy steel. Enhanced properties through quenching and tempering, suitable for mechanical and automotive components (e.g., engine end covers, gearbox joints).
High-Strength/Corrosion-Resistant Applications:
304/316 stainless steel and 12.9 alloy steel are selected for heavy loads or resistance to humid, acidic, or alkaline environments (e.g., precision tools, chemical processing equipment).
Strength Classes:
Common classes include 4.8, 8.8, 10.9, and 12.9, whose values correspond to national standards:
Using class 8.8 as an example:
- The first "8" indicates a minimum nominal tensile strength of 800 MPa.
- The second "8" indicates a yield strength to tensile strength ratio of 0.8, meaning a yield strength ≥ 640 MPa.
Class 12.9 represents an ultra-high-strength category with a tensile strength ≥ 1200 MPa, suitable for extremely harsh applications (e.g., aerospace, heavy engineering).
















































