Products
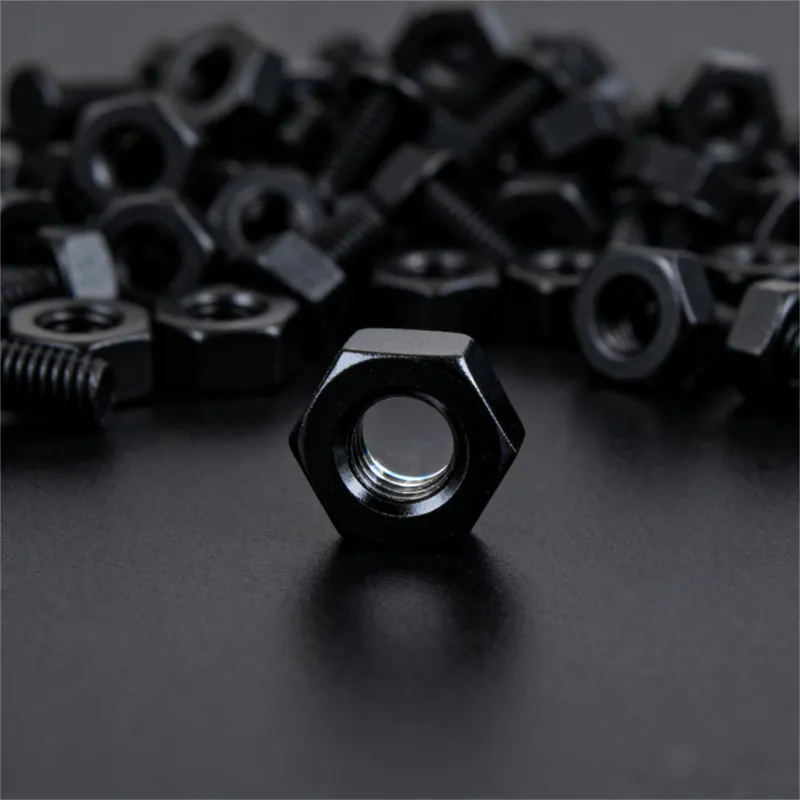
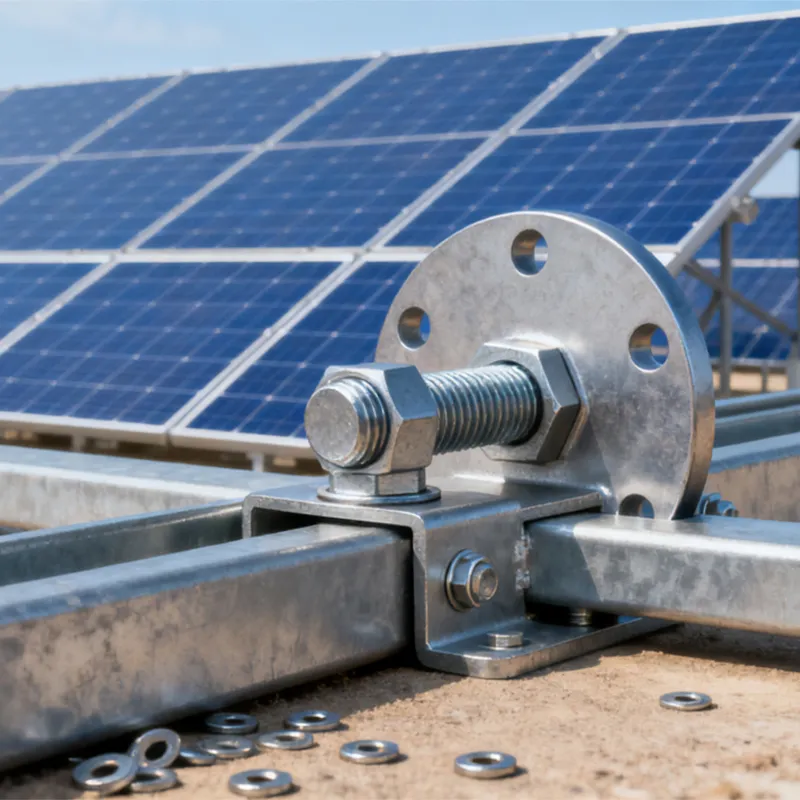
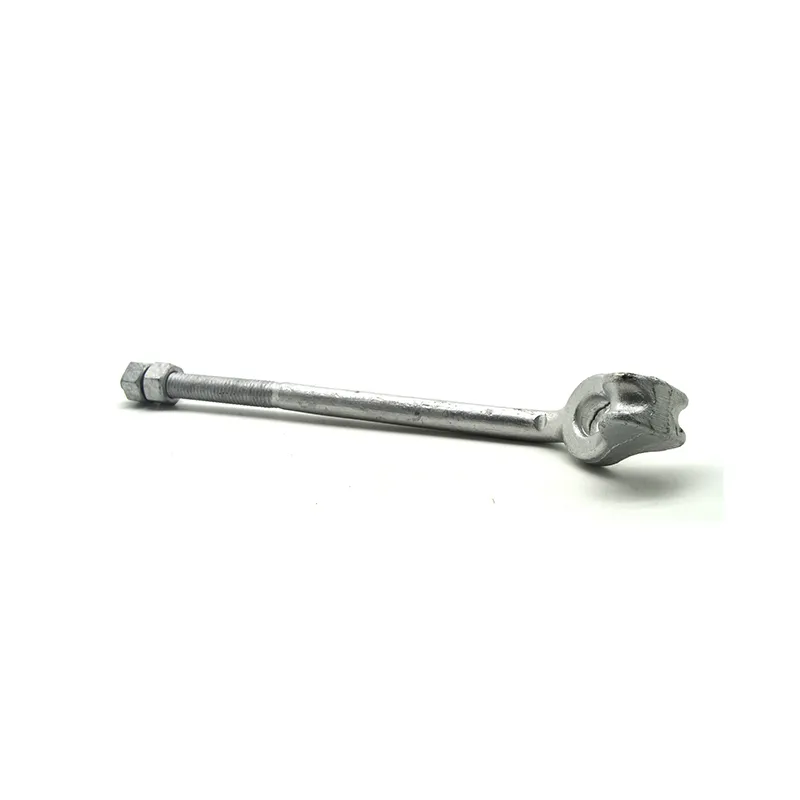
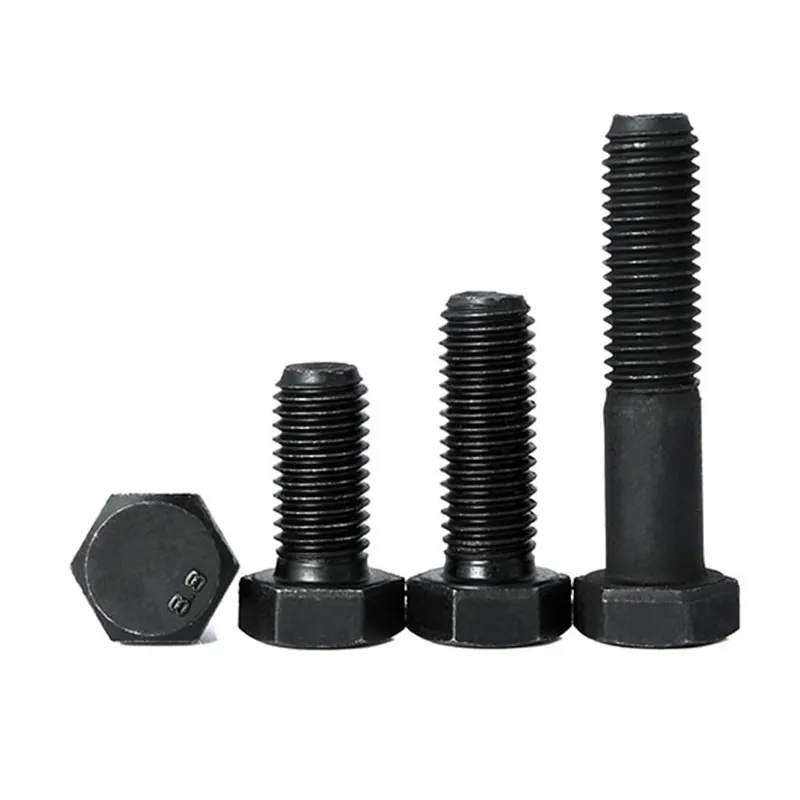
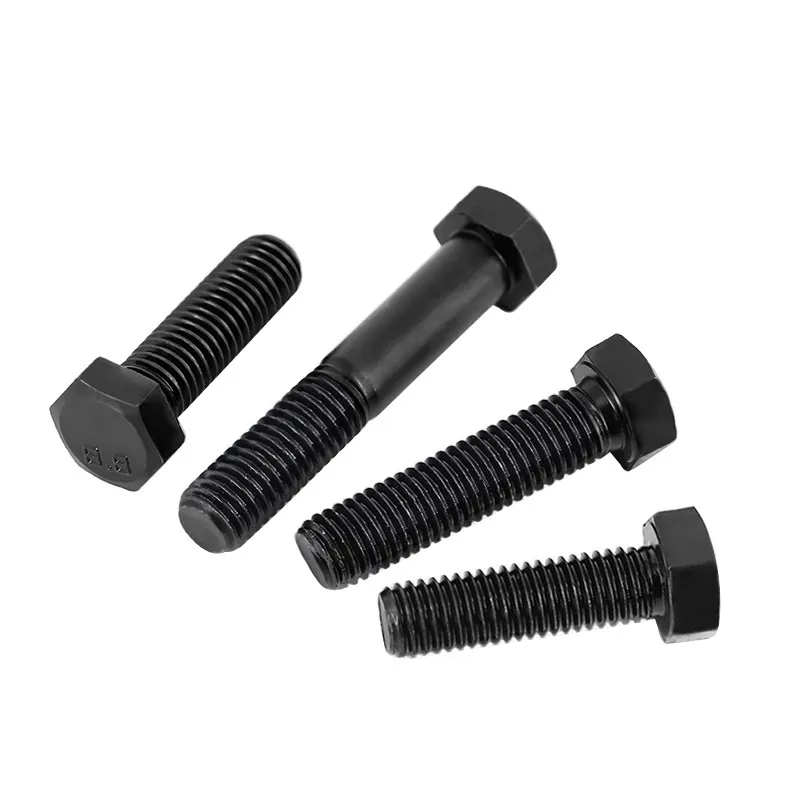
High-strength bolts with external hexagonal heads
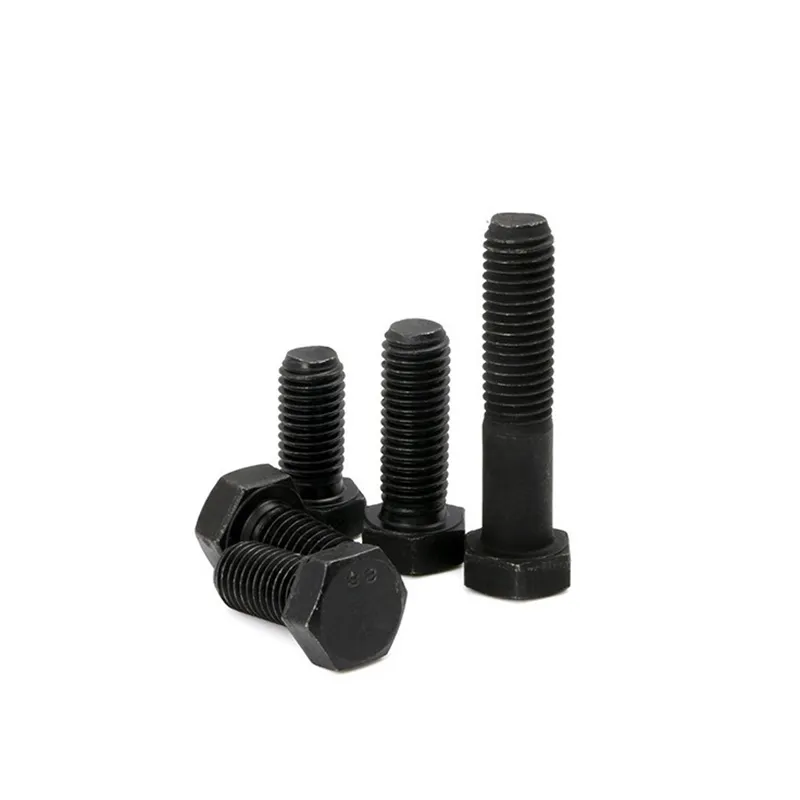
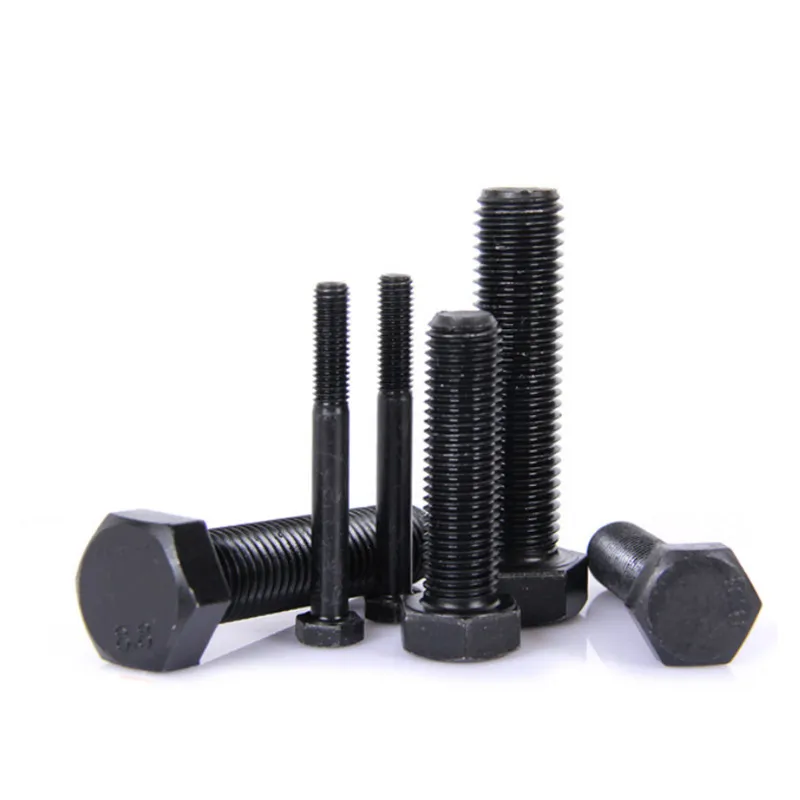
Product Description: High-strength hexagonal head bolts are the most widely used high-strength fasteners in industry. Named for their hexagonal heads, their main advantages lie in compatibility with universal wrenches, uniform force distribution, and stable transmission of heavy loads. The...
Description
marker
Product Description:
High-strength hexagonal head bolts are the most widely used high-strength fasteners in industry. Named for their hexagonal heads, their main advantages lie in compatibility with universal wrenches, uniform force distribution, and stable transmission of heavy loads. They are suitable for situations requiring both connection strength and ease of assembly/disassembly.
Main Structure and Design Features:
The structure of hexagonal head bolts is focused on "effective force application" and "stable load-bearing capacity", ensuring high versatility and compatibility with various installation tools.
Main Structure
It consists of a hexagonal head and a threaded rod, which comes in two types: fully threaded and partially threaded.
- Fully threaded rod: Suitable for fastening thinner parts, where the full length of the thread can fully engage with the nut.
- Partially threaded rod: The diameter of the unthreaded part exceeds the major diameter of the thread, which enhances shear resistance. It is ideal for thicker components or applications subject to shear loads.
Key Design Features
- The width and thickness of the opposite sides of the hexagonal head comply with standard specifications, allowing the use of various tools including open-end wrenches, socket wrenches, and socket head wrenches for universal torque application.
- The head and shank are usually forged as a single unit, eliminating welded connections that create weak points. This ensures uniform stress distribution and prevents breakages.
- Some high-precision models feature chamfered thread ends for quick nut engagement, improving installation efficiency.
Materials and Strength Classes:
Material composition and strength classes determine the "high strength" of the product, enabling it to meet various load requirements.
Main Materials
The main materials are alloy steel 40Cr and steel 20MnTiB. Through quenching and tempering heat treatment, they provide a balance of high strength and toughness, and serve as the primary raw materials for bolts of strength classes 8.8 and 10.9.
For ultra-high strength class 12.9 bolts, steel 35CrMoA or 42CrMo is mainly used, which can achieve a tensile strength of over 1200 MPa for applications under extreme load conditions.
In environments requiring corrosion resistance, surfaces made of 304/316 stainless steel or alloy steel treated with Dacromet or hot-dip galvanizing are used, suitable for humid or chemical environments.
Strength Classes
In industry, strength classes 8.8 and 10.9 are commonly used, while class 12.9 is applied in special cases. The definitions of the classes comply with the national standard GB/T 3098.1.
First digit: Indicates the minimum nominal tensile strength (unit: MPa). For example, "8" in class 8.8 means tensile strength ≥ 800 MPa.
Second digit: Indicates the ratio of yield strength to tensile strength. For example, "8" in class 8.8 means yield strength ≥ 800 MPa × 0.8 = 640 MPa.















































