Products
Insulator steel feet
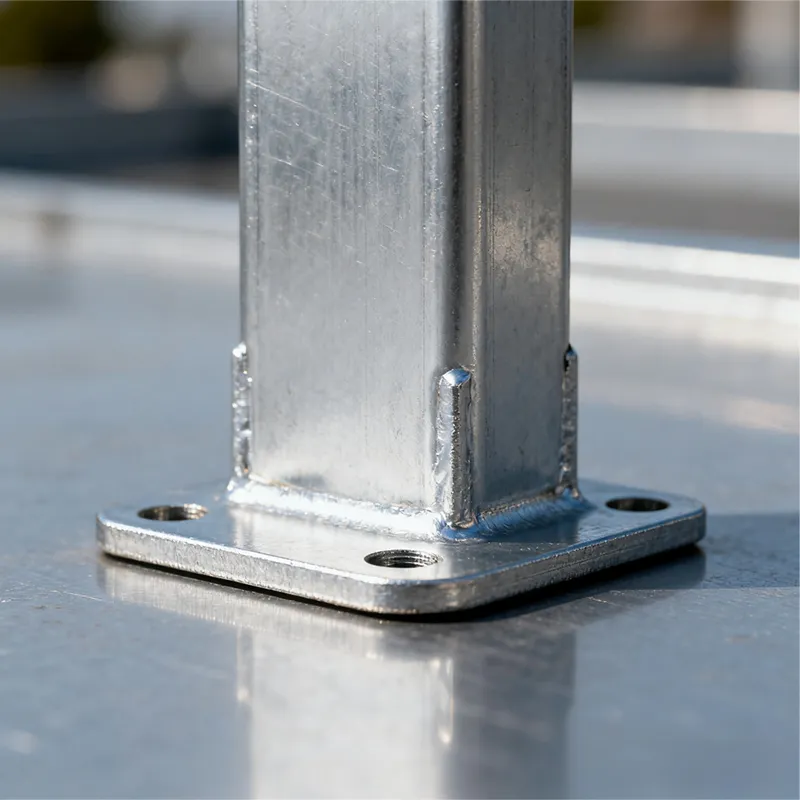
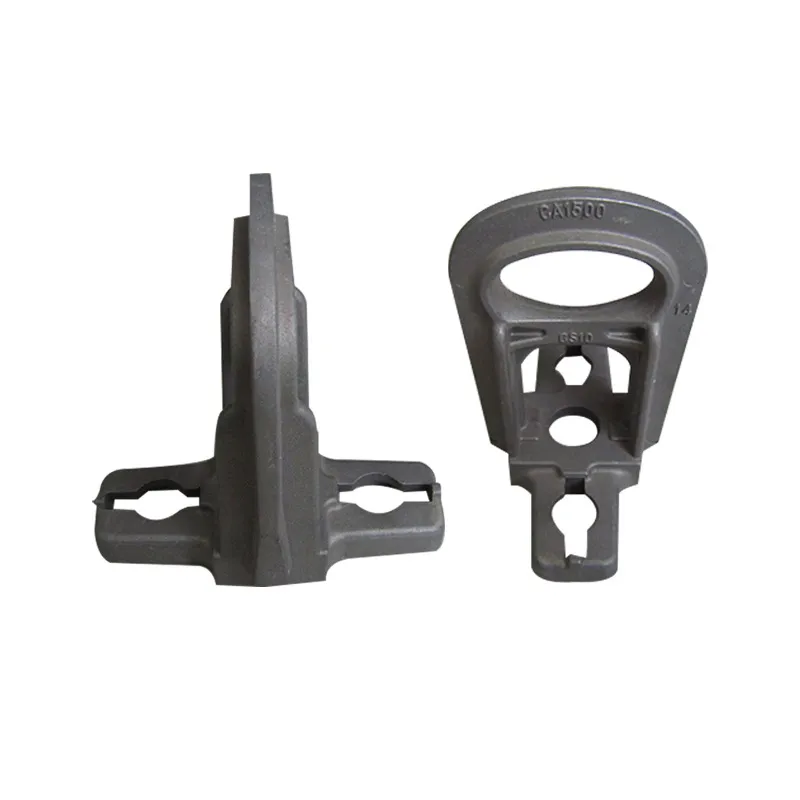
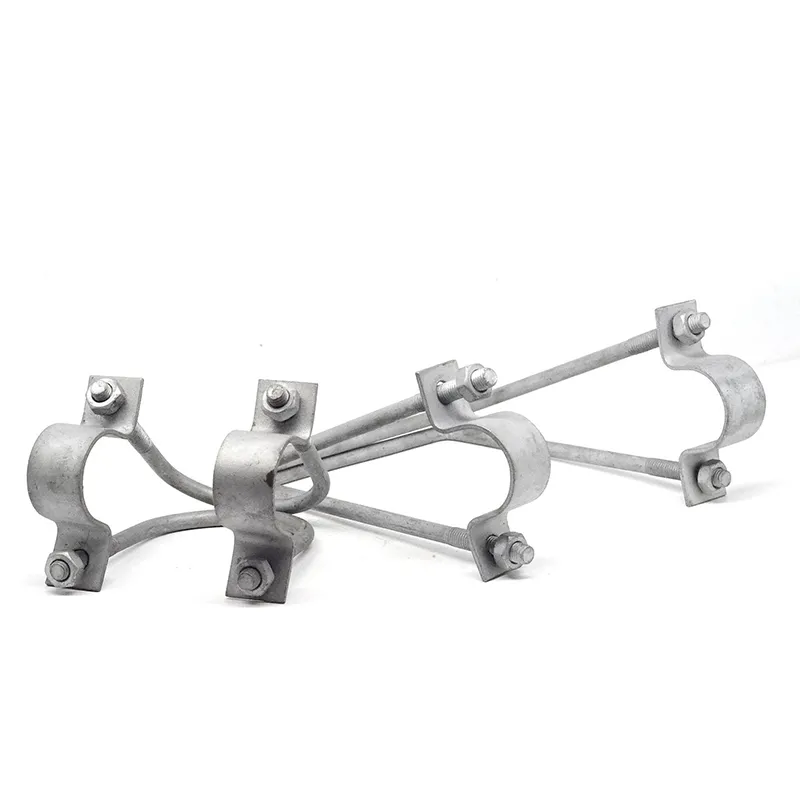
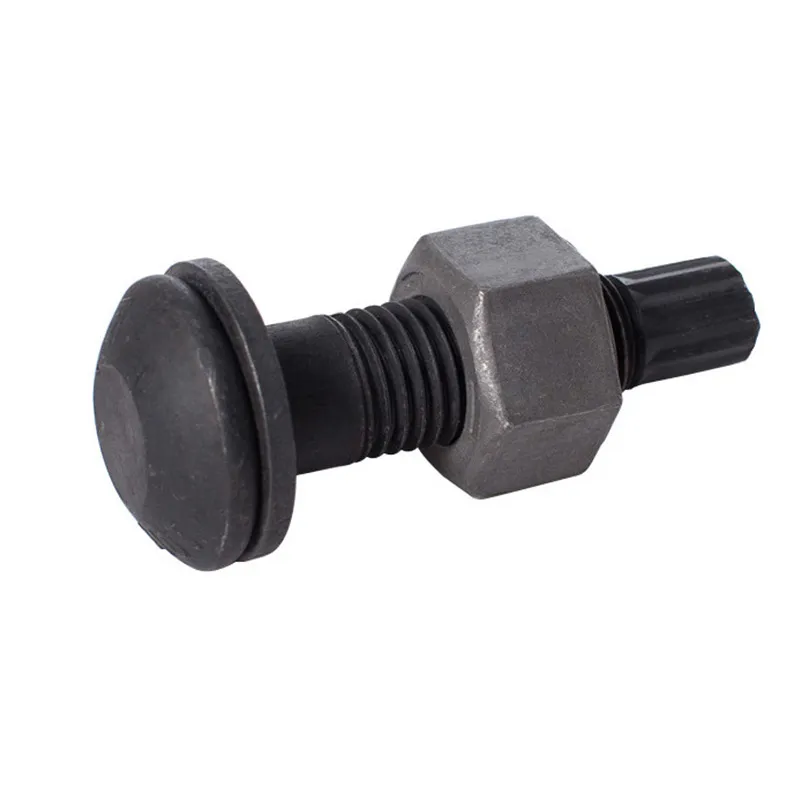
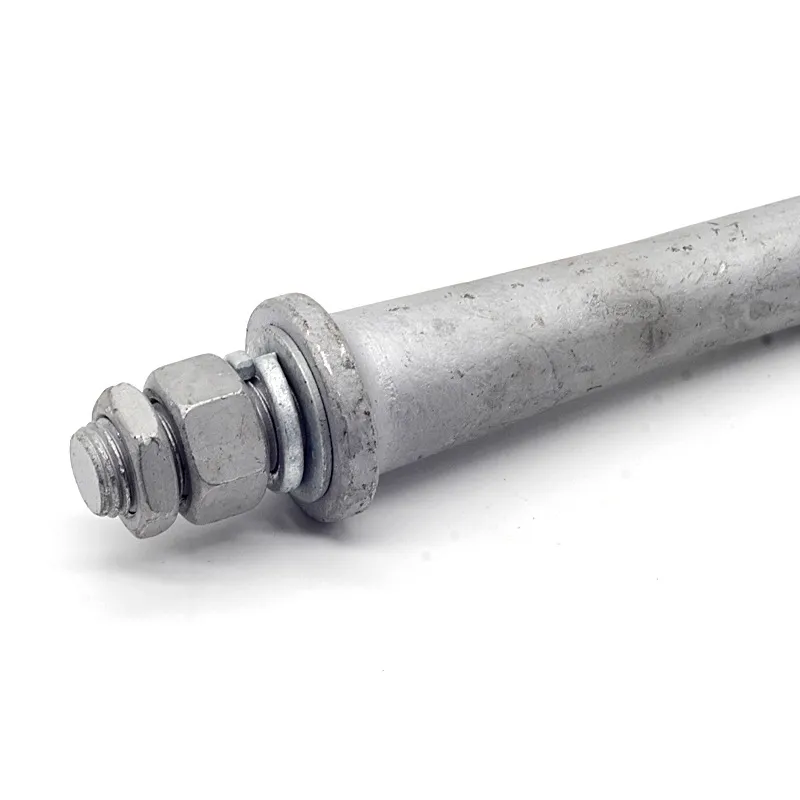
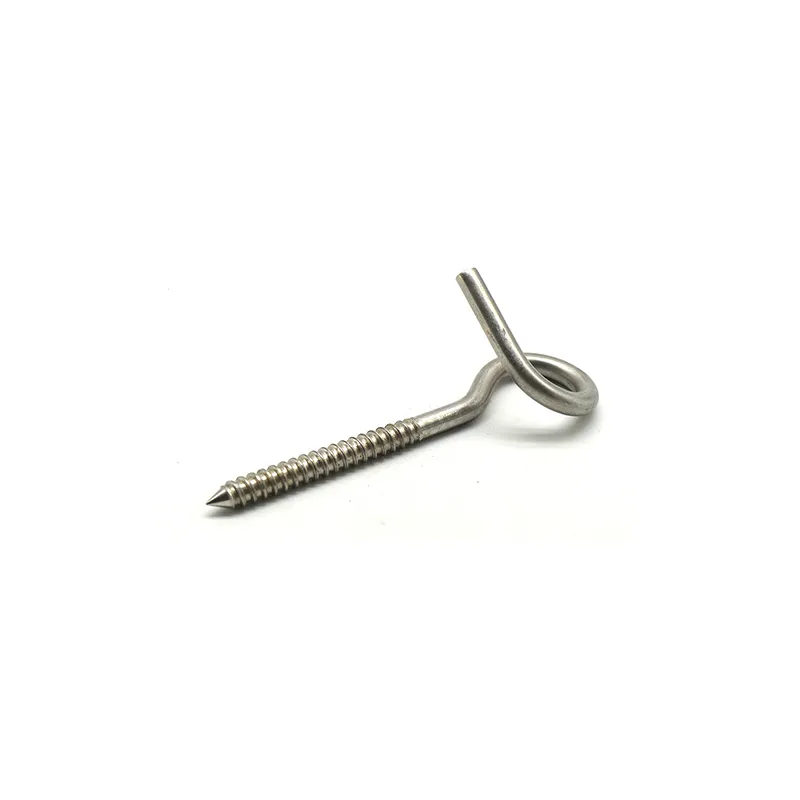
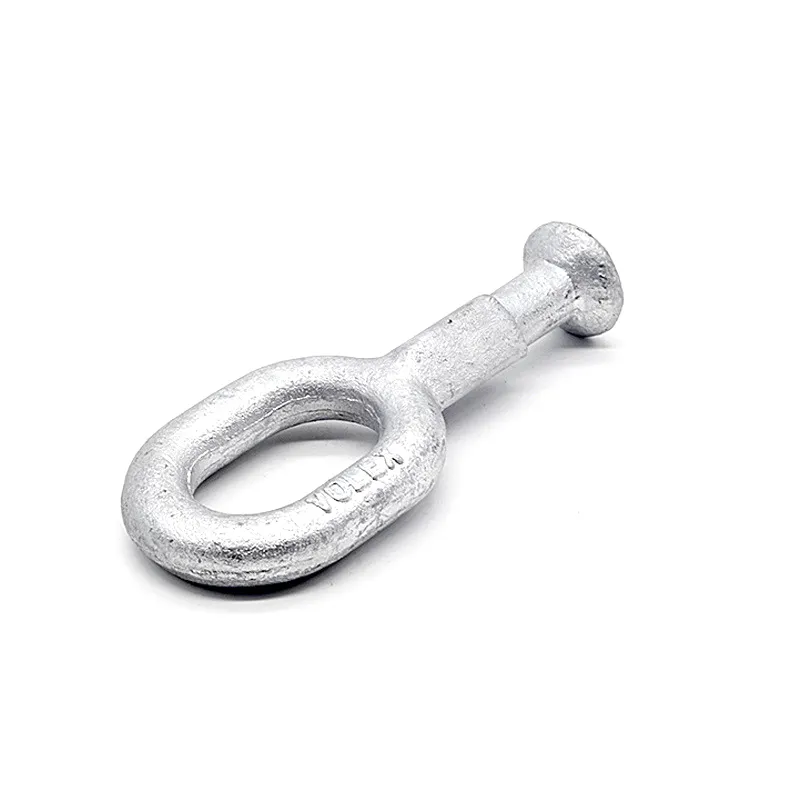
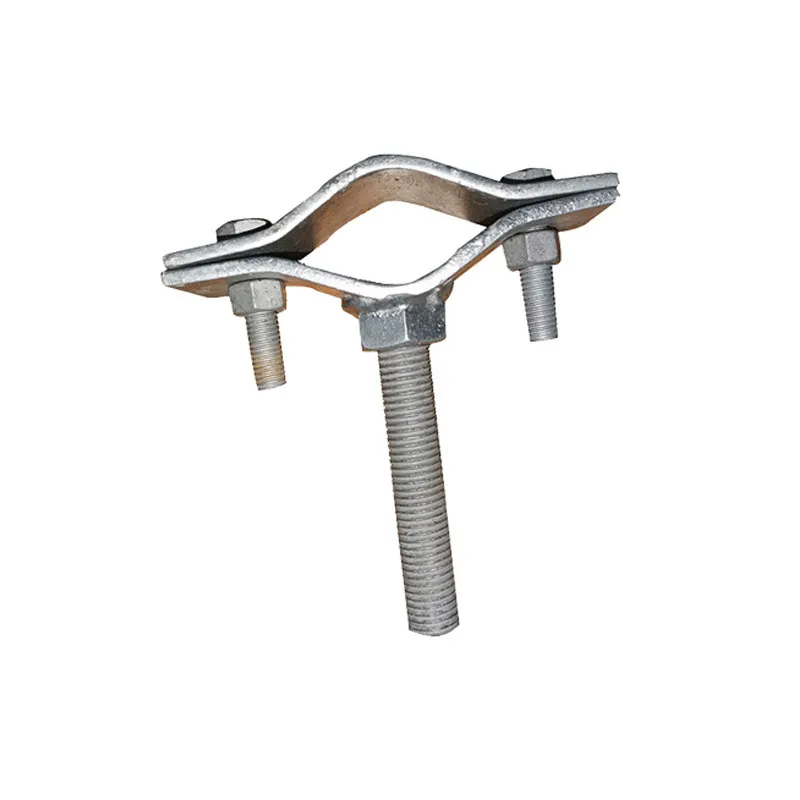
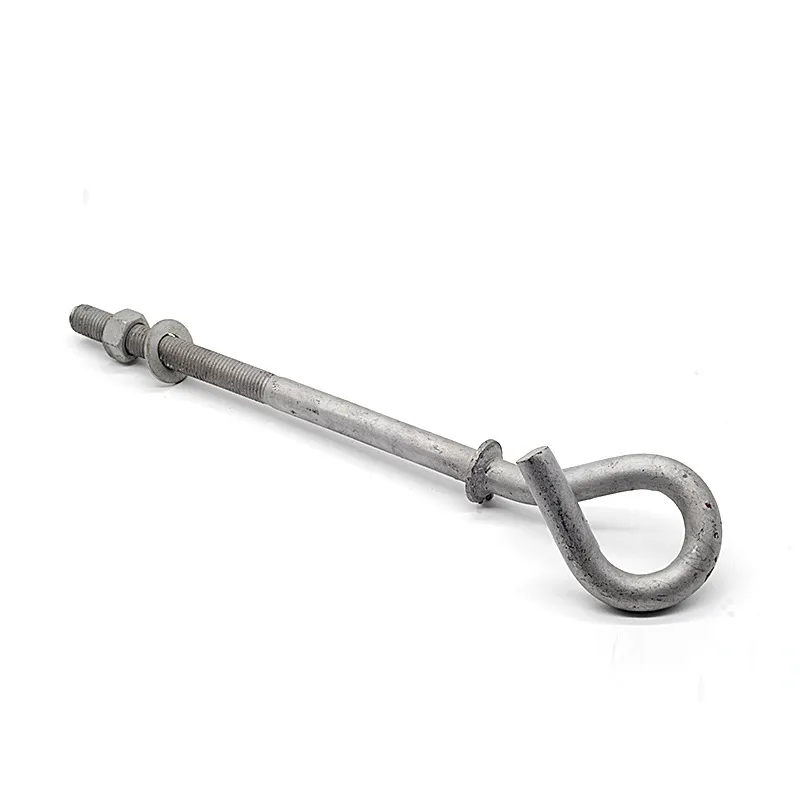
Product Description: Insulator steel feet are an important component of insulators. Below is a detailed description: Structure: Insulator steel feet typically consist of three parts: an upper conical head, a central cylindrical rod, and a lower spherical base. The upper conical head is ful...
Description
marker
Product Description:
Insulator steel feet are an important component of insulators. Below is a detailed description:
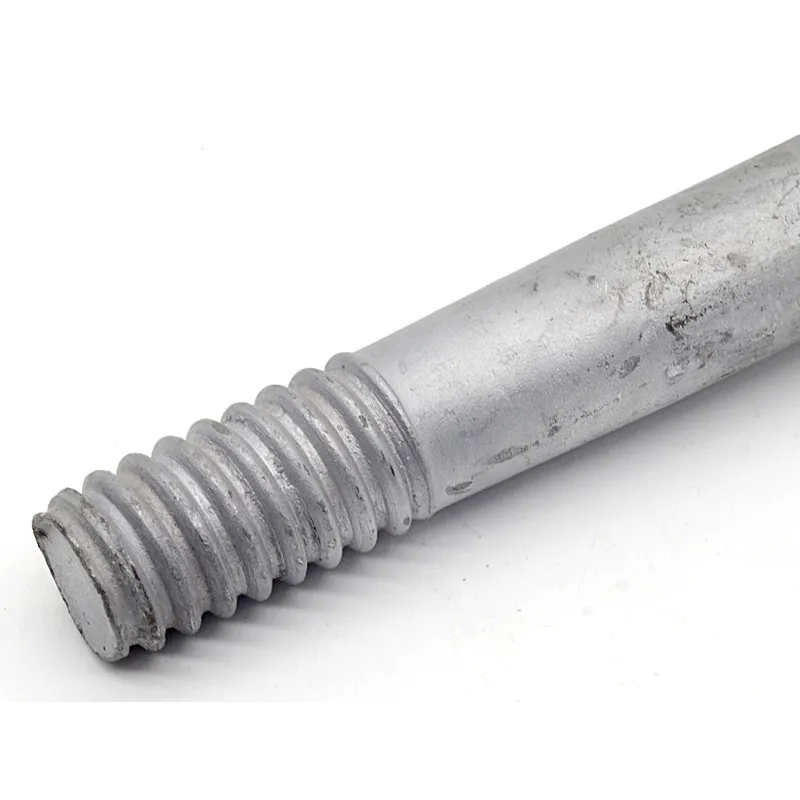
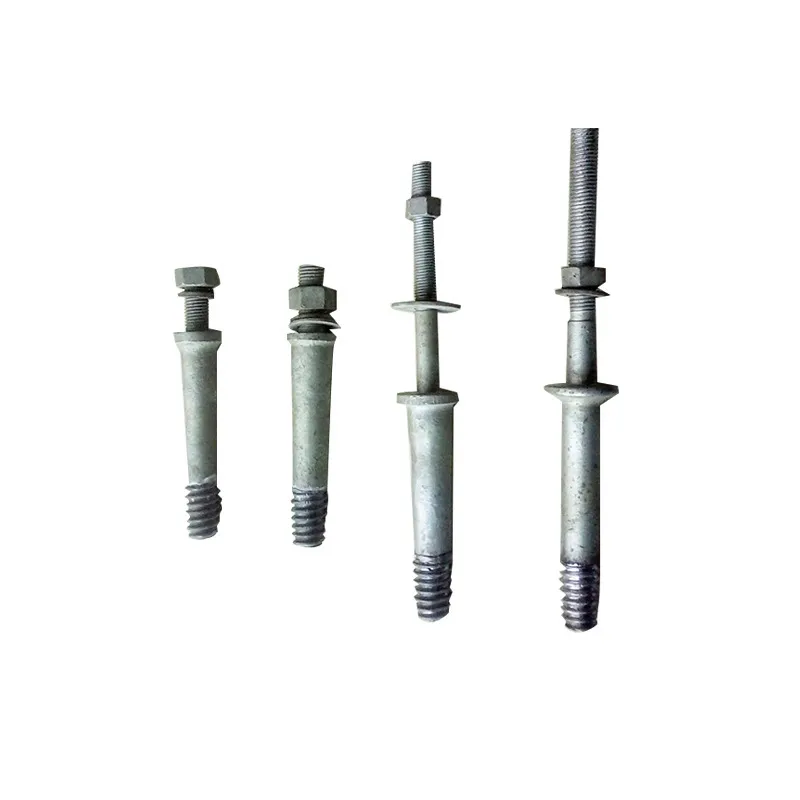
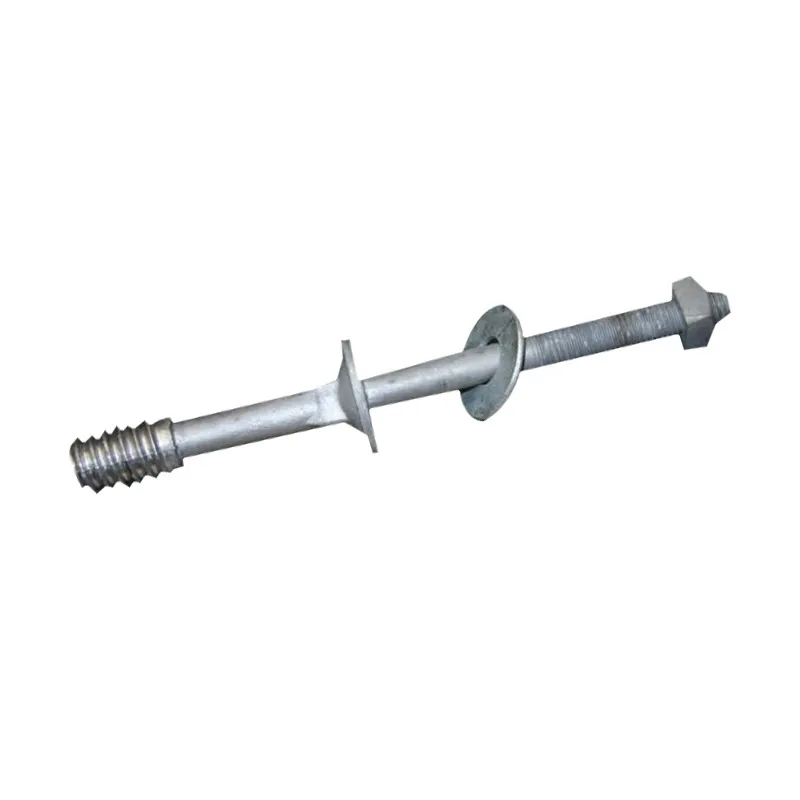
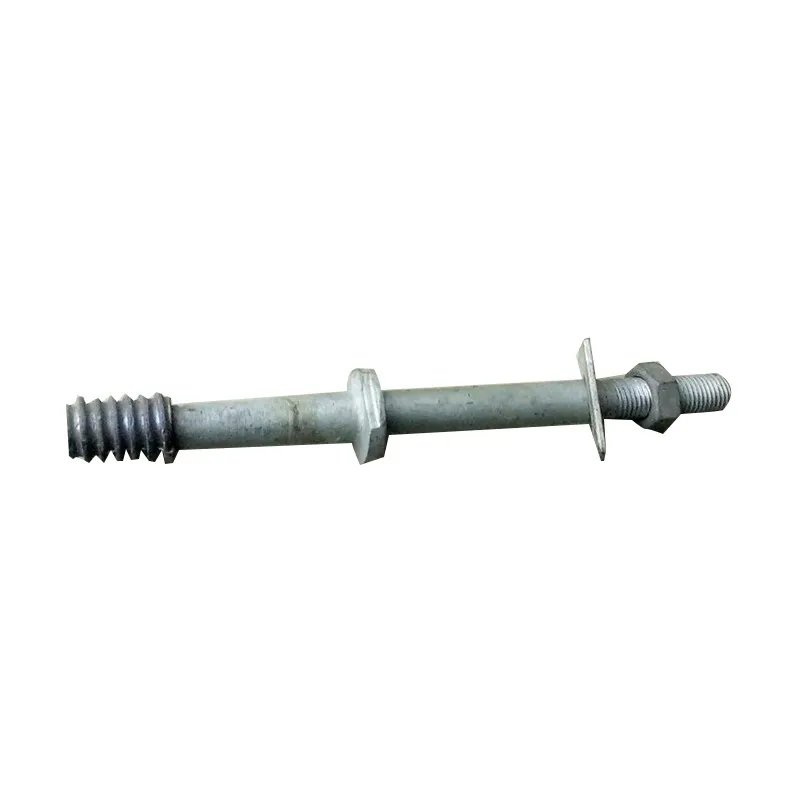
Structure:
Insulator steel feet typically consist of three parts: an upper conical head, a central cylindrical rod, and a lower spherical base. The upper conical head is fully embedded in cement adhesive to securely fix the porcelain or glass insulator body; the central cylindrical rod forms the main body of the steel foot, primarily bearing tensile forces; the lower spherical base facilitates connection to tower or equipment supports.
Materials:
Primarily made of carbon structural steels such as Q235, 45#, 40Mn, 70Mn, 20Mn2, and 20MnV. These steels offer excellent mechanical strength and wear resistance, meeting the operational requirements of insulators under various environmental conditions.
Surface Treatment:
To prevent rust and corrosion, which could reduce mechanical strength and service life, hot-dip galvanizing or stainless steel materials are commonly used for corrosion protection.
Technical Specifications:
Available in various specifications, typically classified by rated electromechanical tensile strength. Common grades range from 70 kN to 550 kN to meet the requirements of DC, AC, high-voltage, and ultra-high-voltage transmission projects.
Function:
Insulator steel feet primarily connect and support insulators, securing them to tower or equipment brackets. Together with insulator caps and insulating components, they withstand conductor weight, wind loads, and potential electrodynamic short-circuit forces, ensuring the stable operation of the power system.
Application Scenarios:
Widely used in power transmission projects, including DC, AC, high-voltage, ultra-high-voltage, and overhead line connections, making them an indispensable component of power systems.

















































