Products
Planks
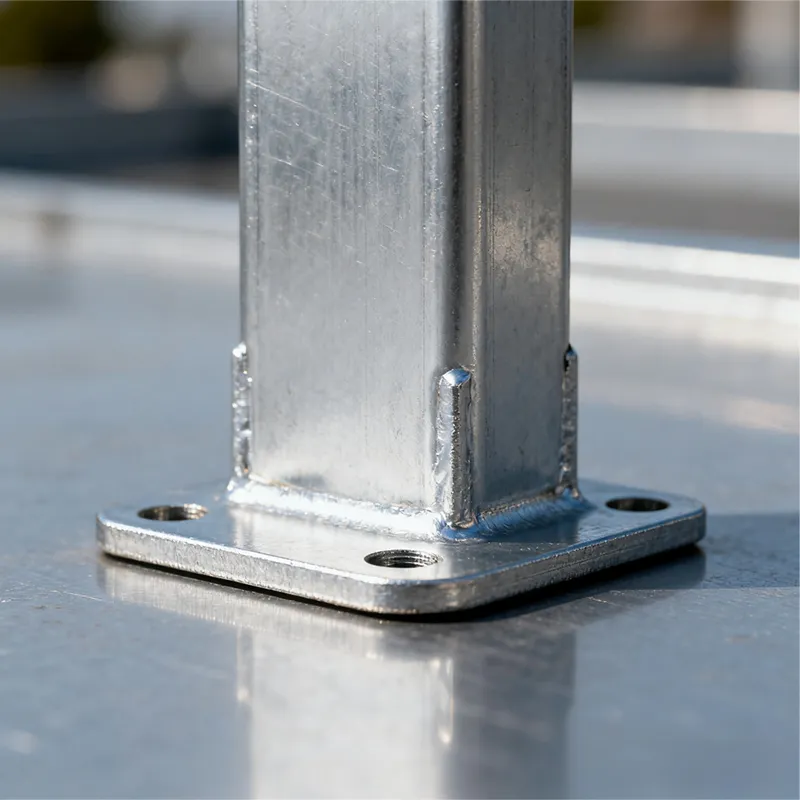
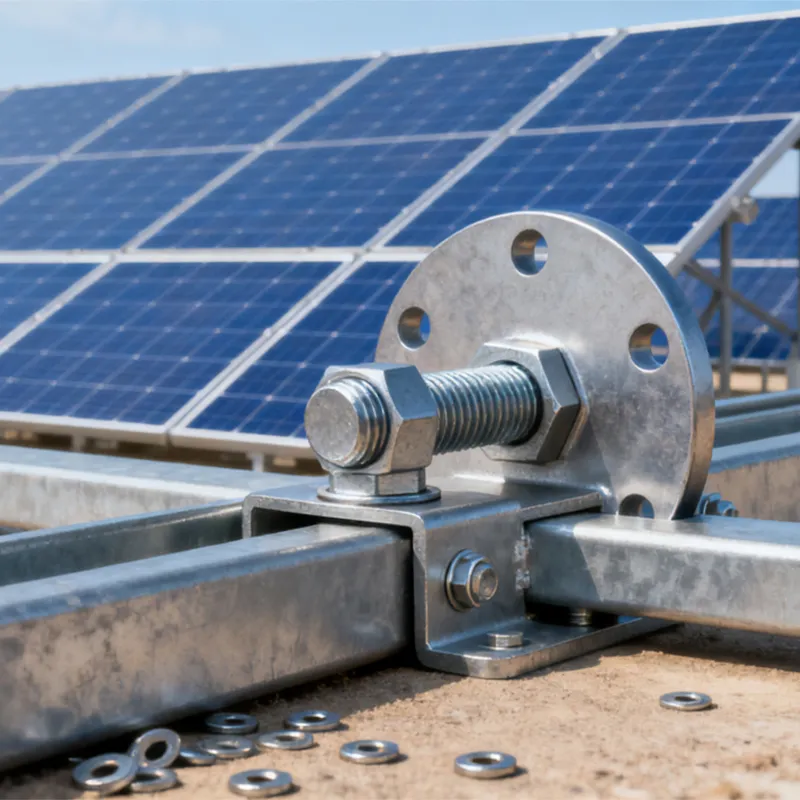
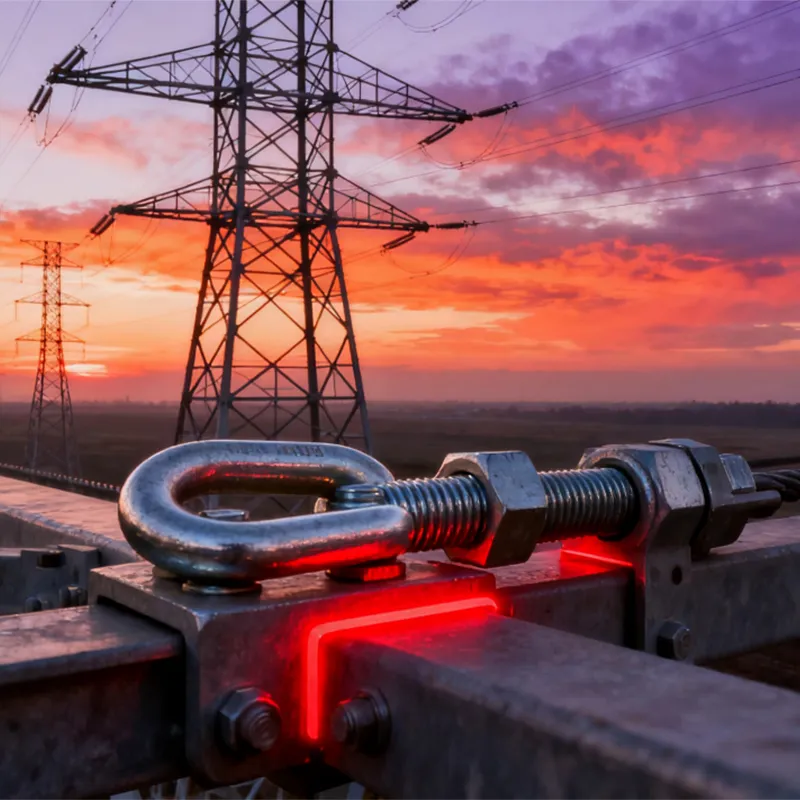
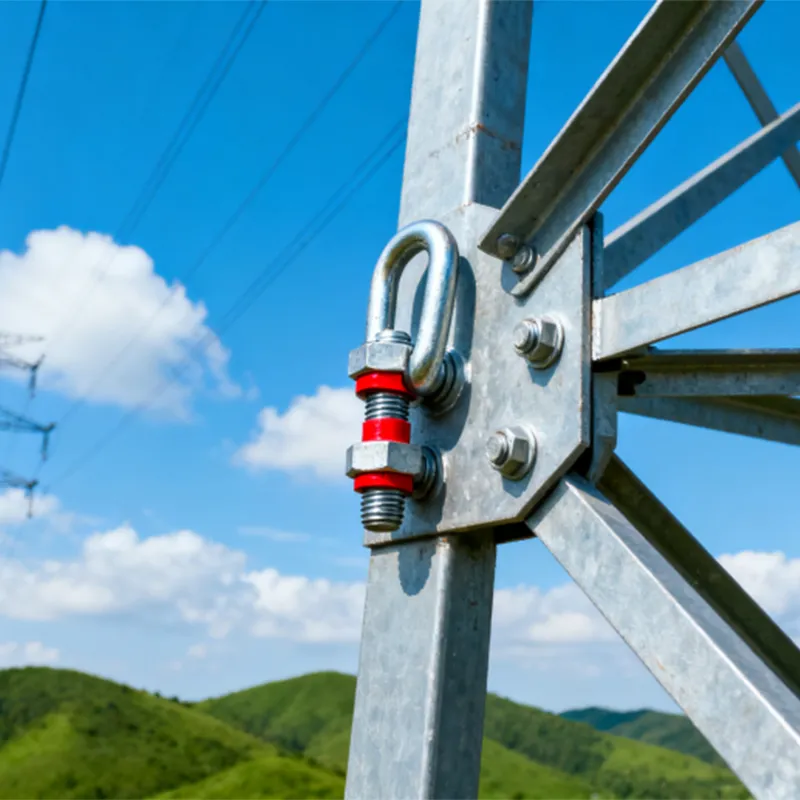
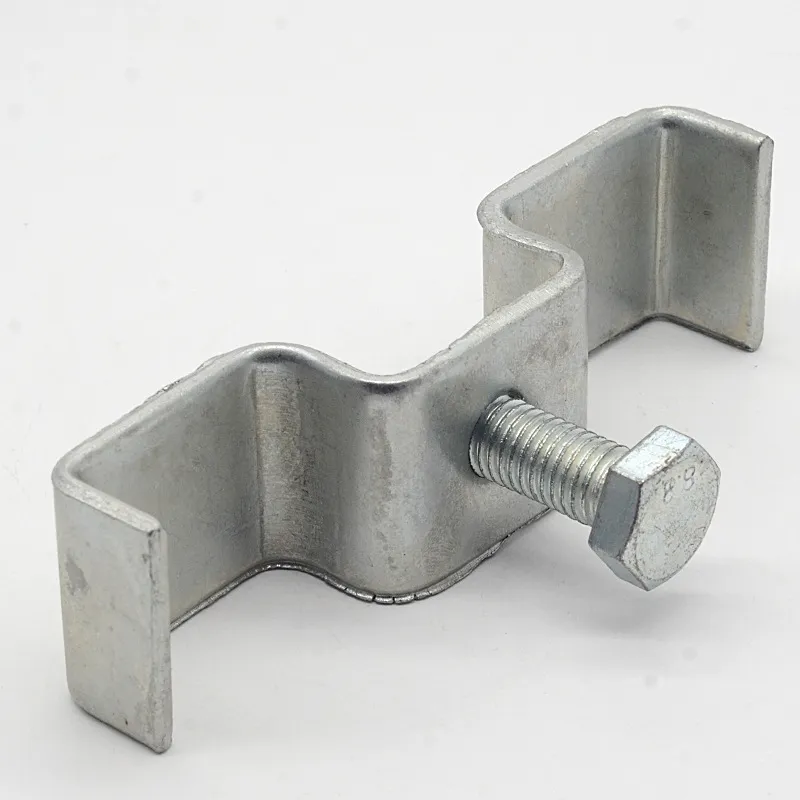
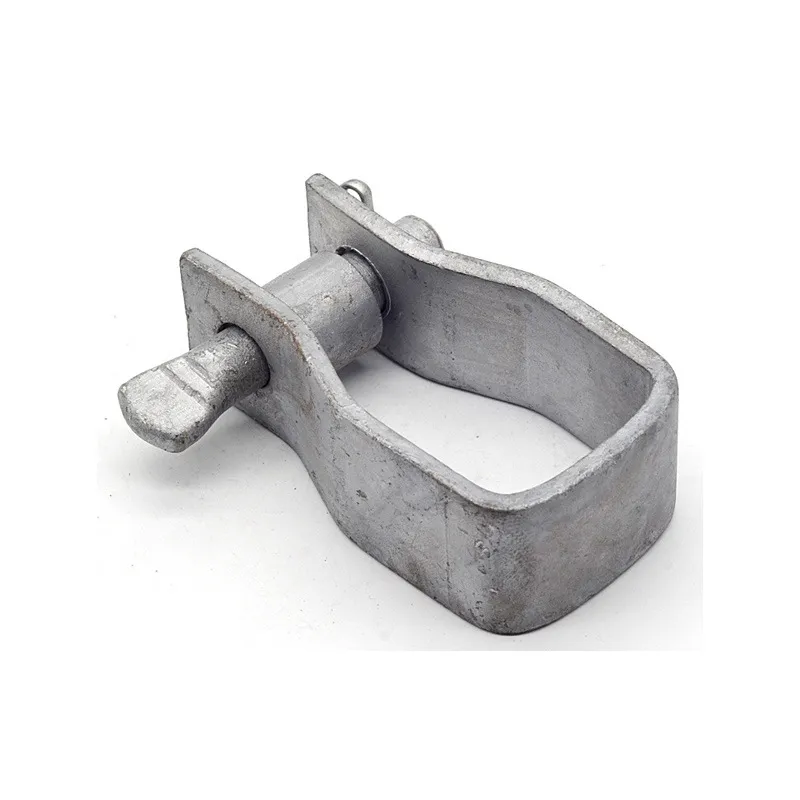
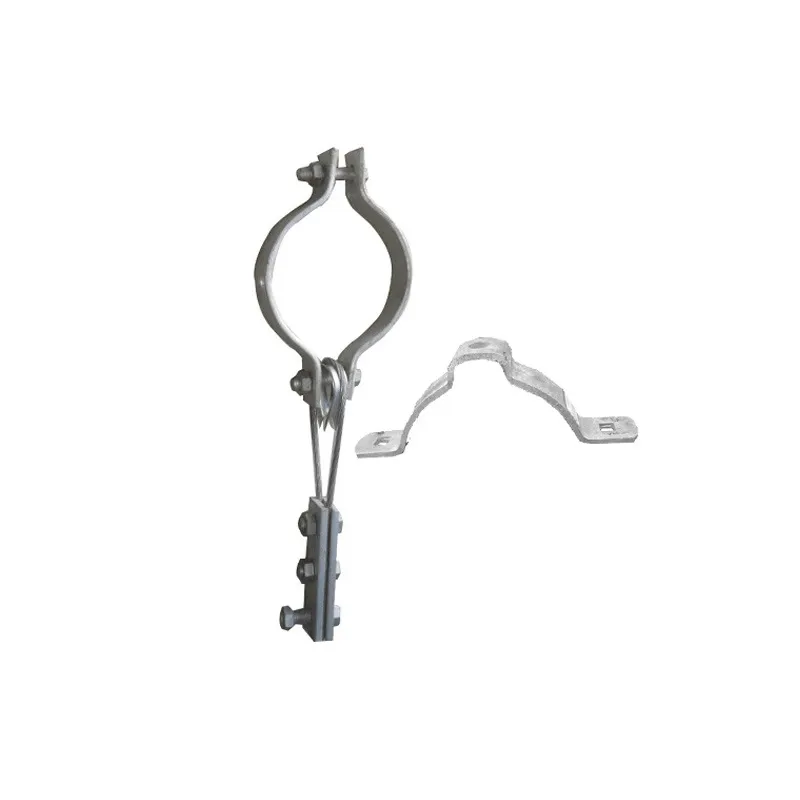
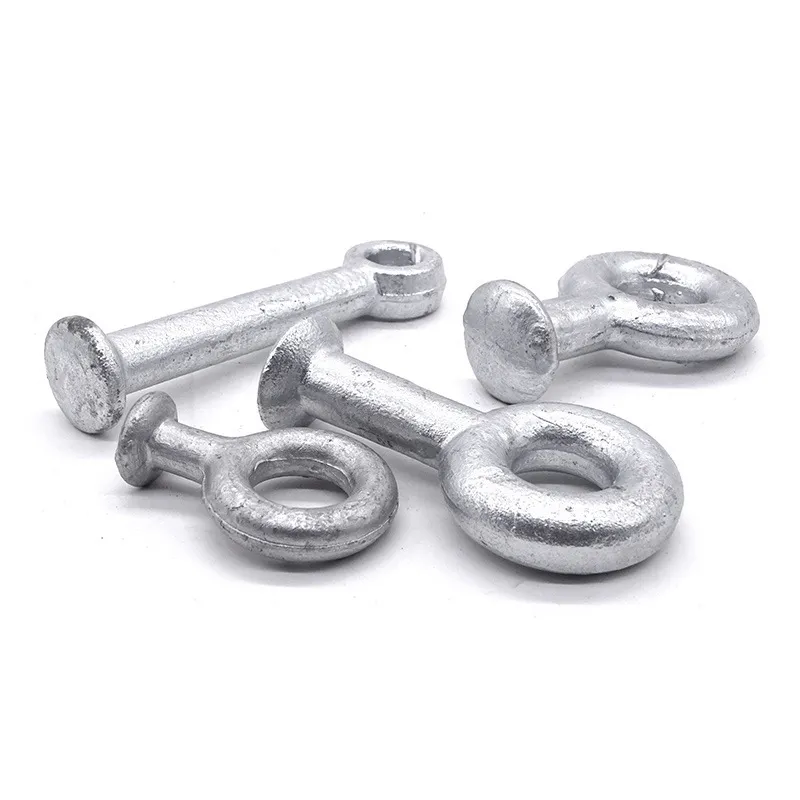
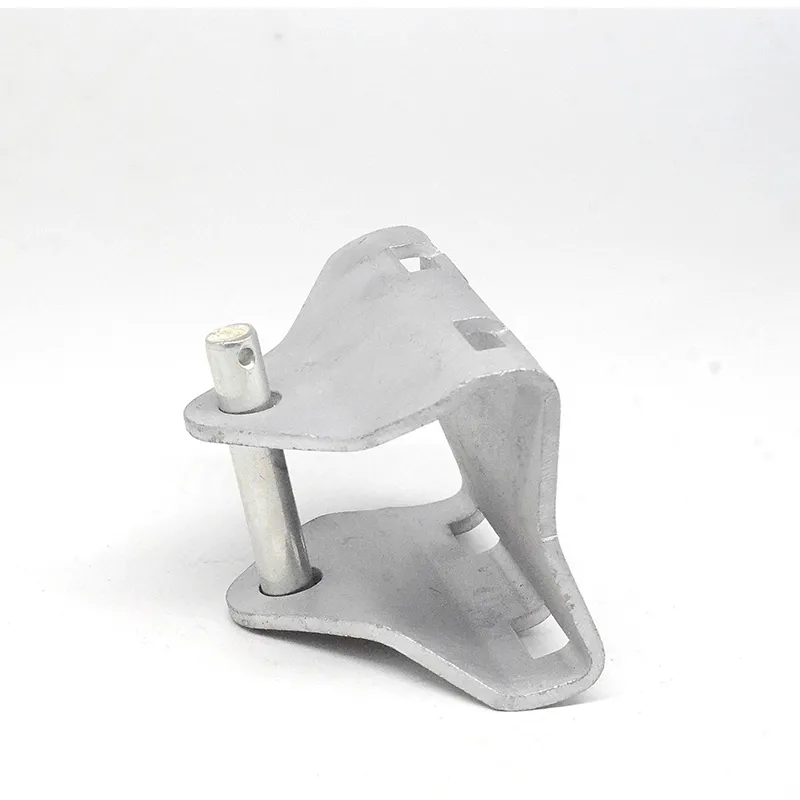
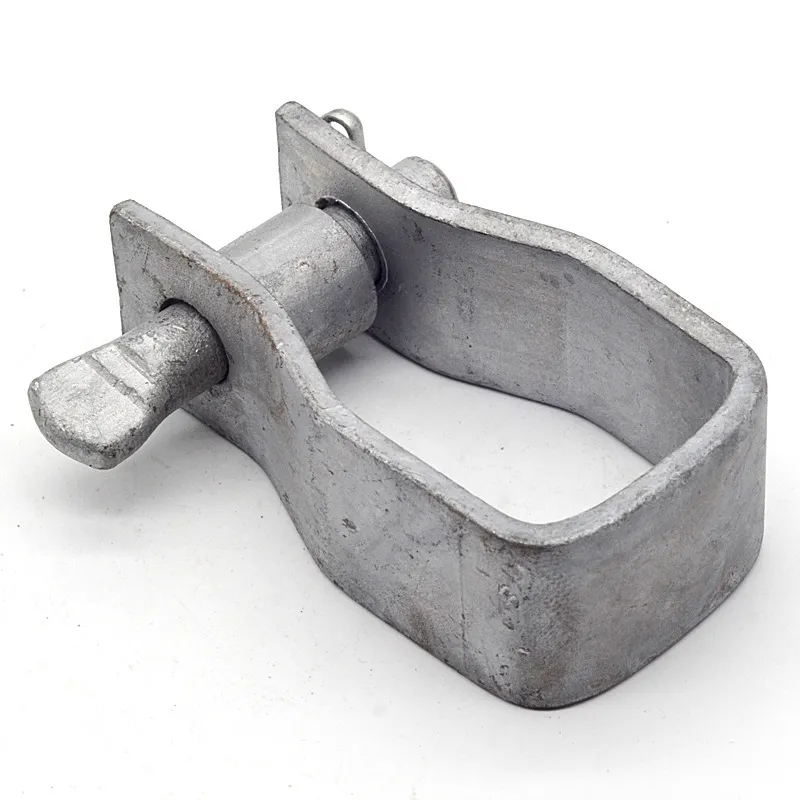
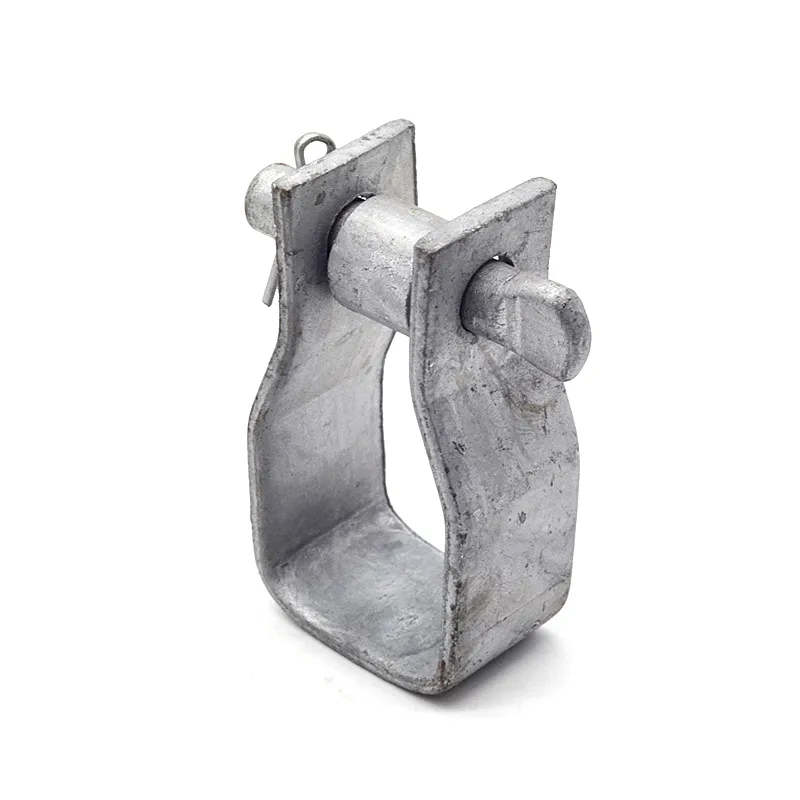
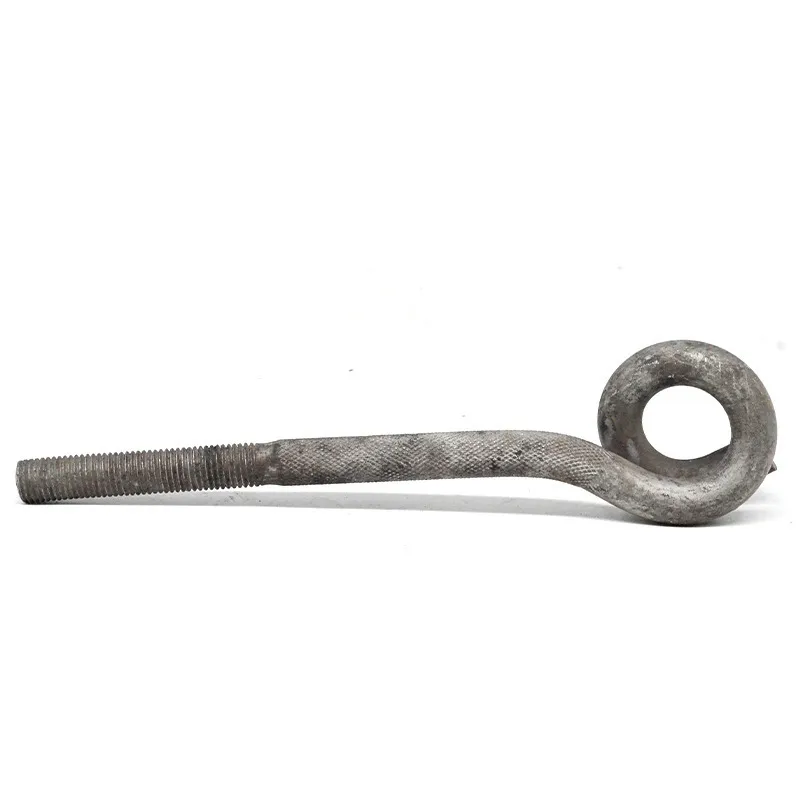
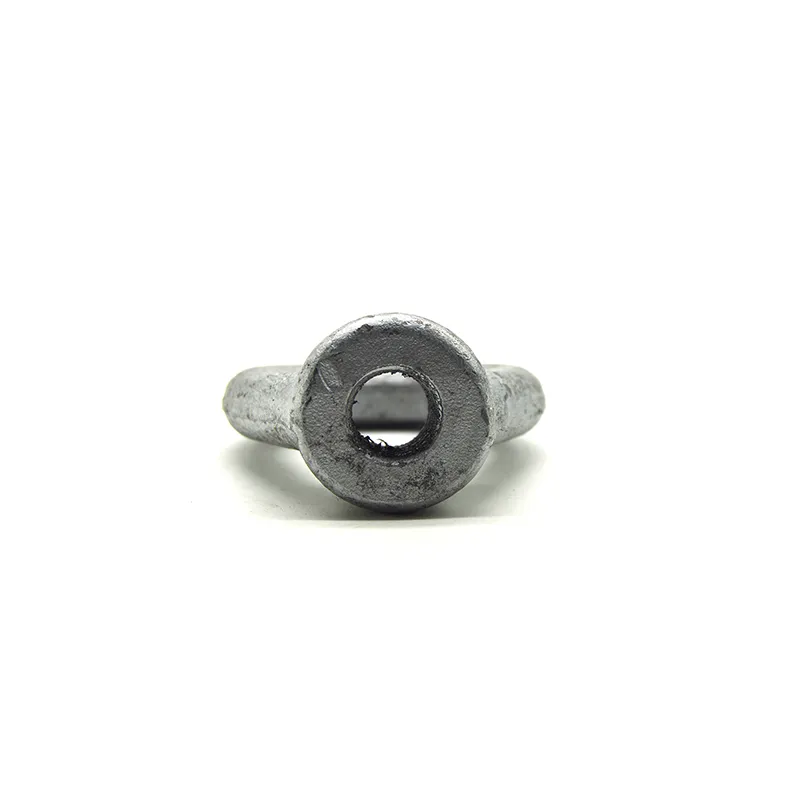
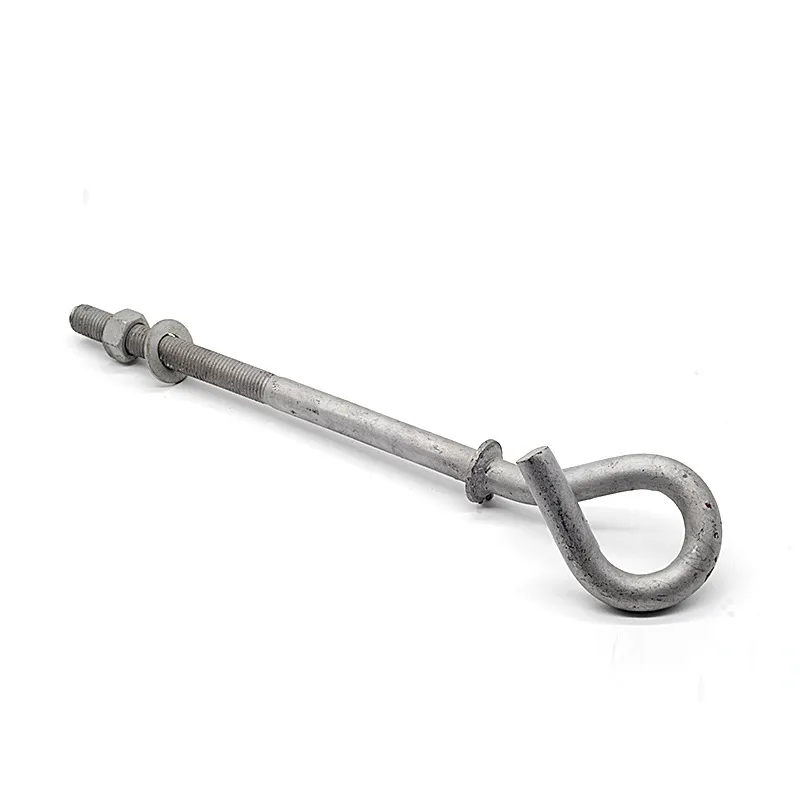
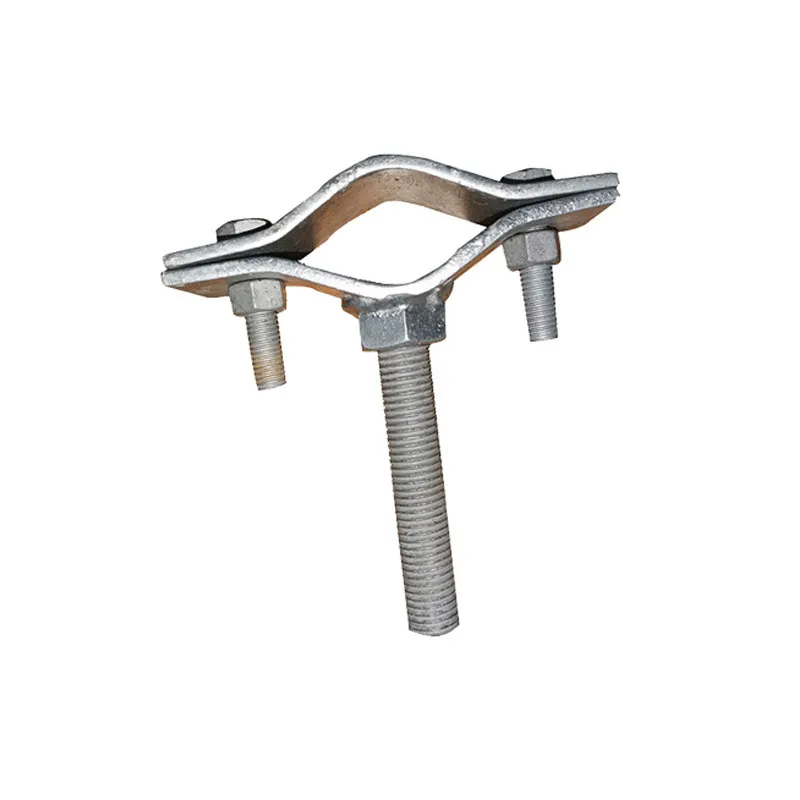
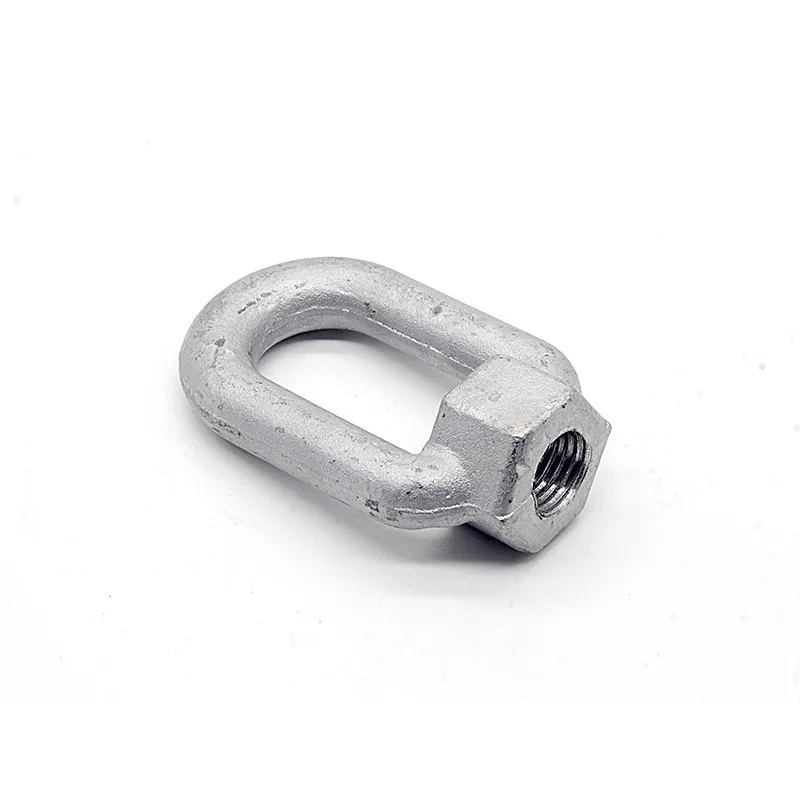
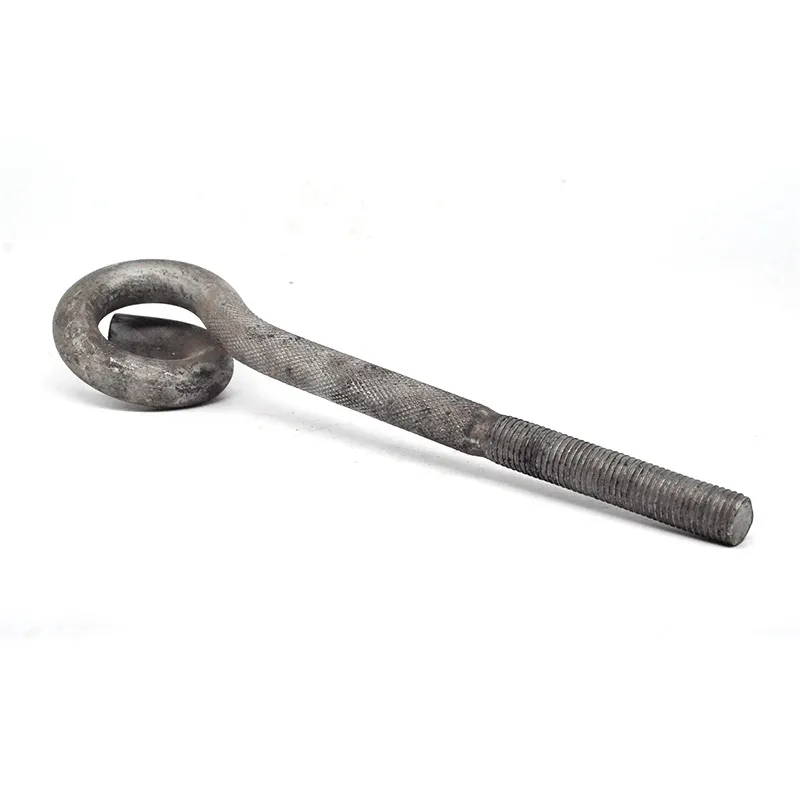
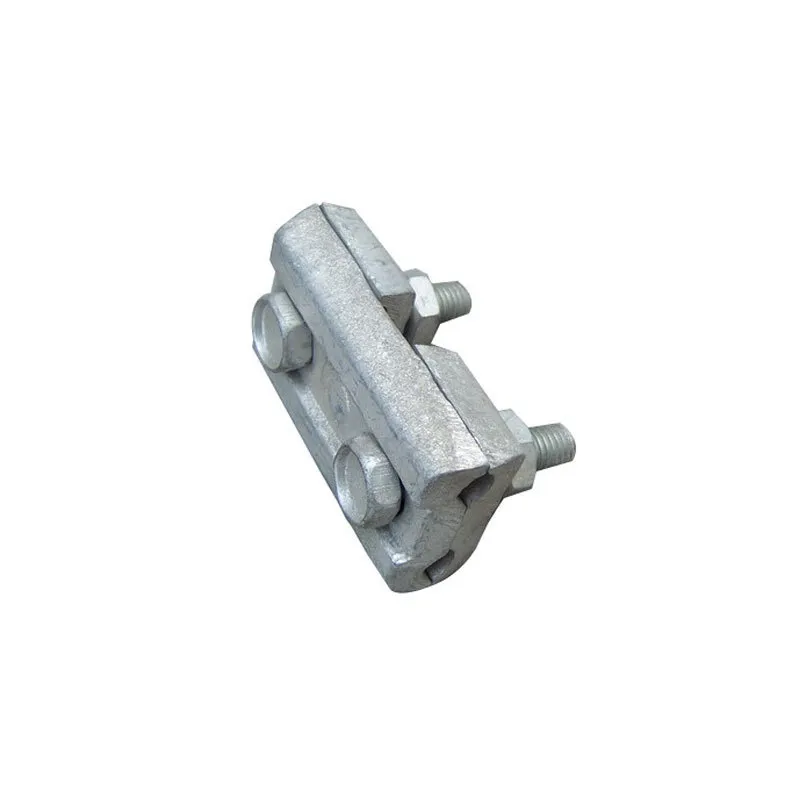
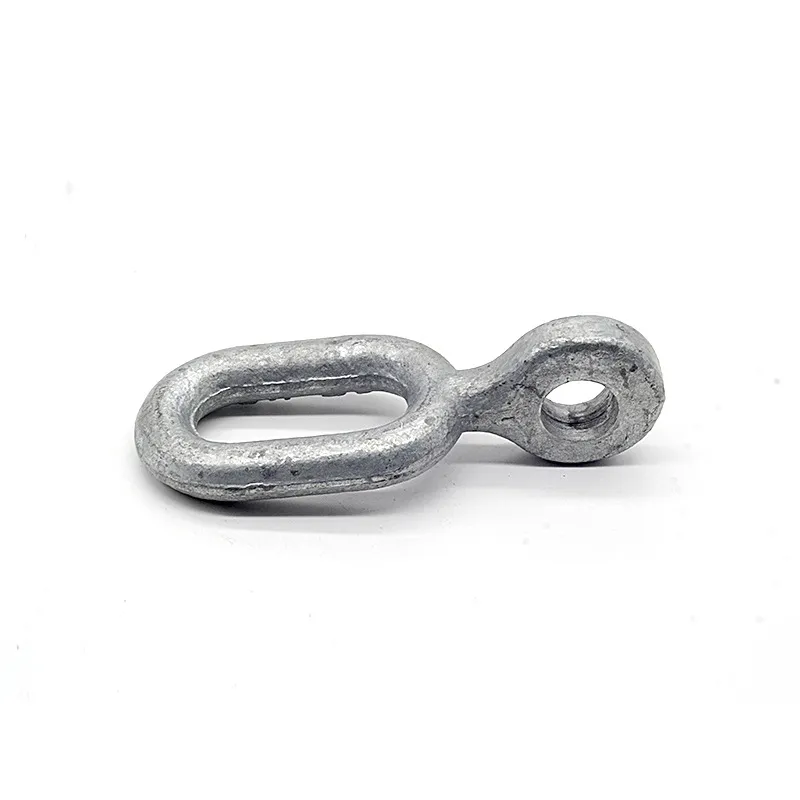
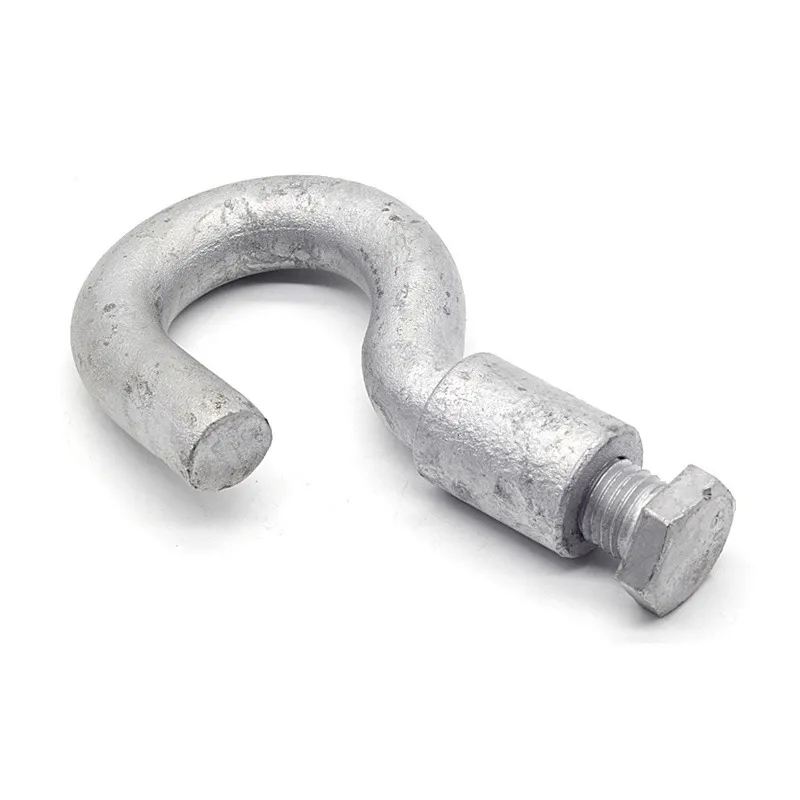
Product Description: Hanging plates are metal components used for connection, transition, or suspension. They mainly serve to transfer loads between structures such as towers, supports, and fittings. Widely applied in energy, telecommunications, and construction, they are important interme...
Description
marker
Product Description:
Hanging plates are metal components used for connection, transition, or suspension. They mainly serve to transfer loads between structures such as towers, supports, and fittings. Widely applied in energy, telecommunications, and construction, they are important intermediate elements in connection systems.
Main Structure and Design Features:
The structure of hanging plates is oriented toward "stable force transmission" and "adaptive connection". This requires precise alignment with the upper and lower components in the force flow to ensure effective load transfer.
Main Structure:
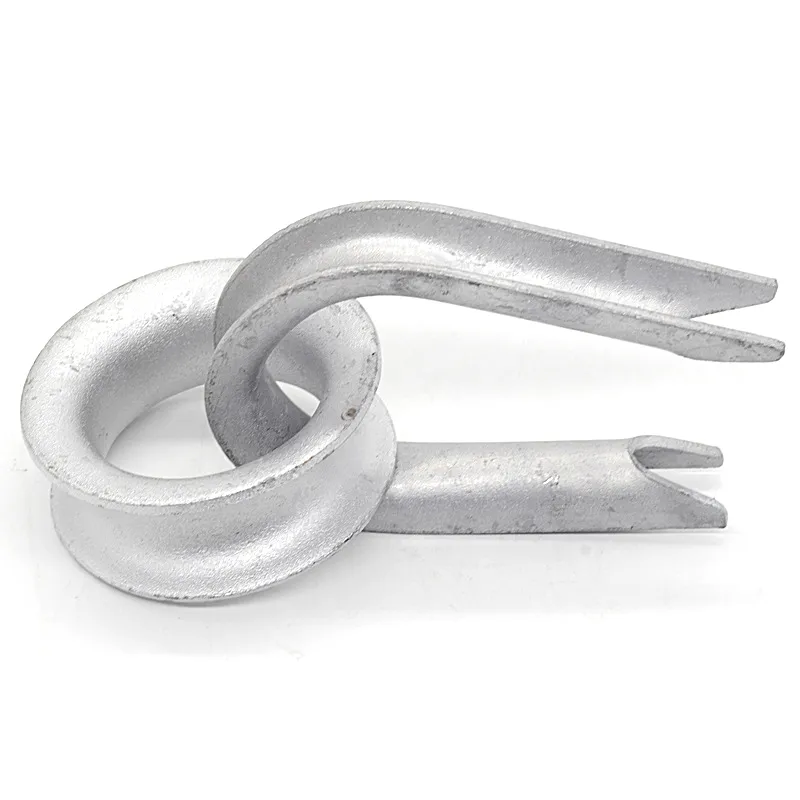
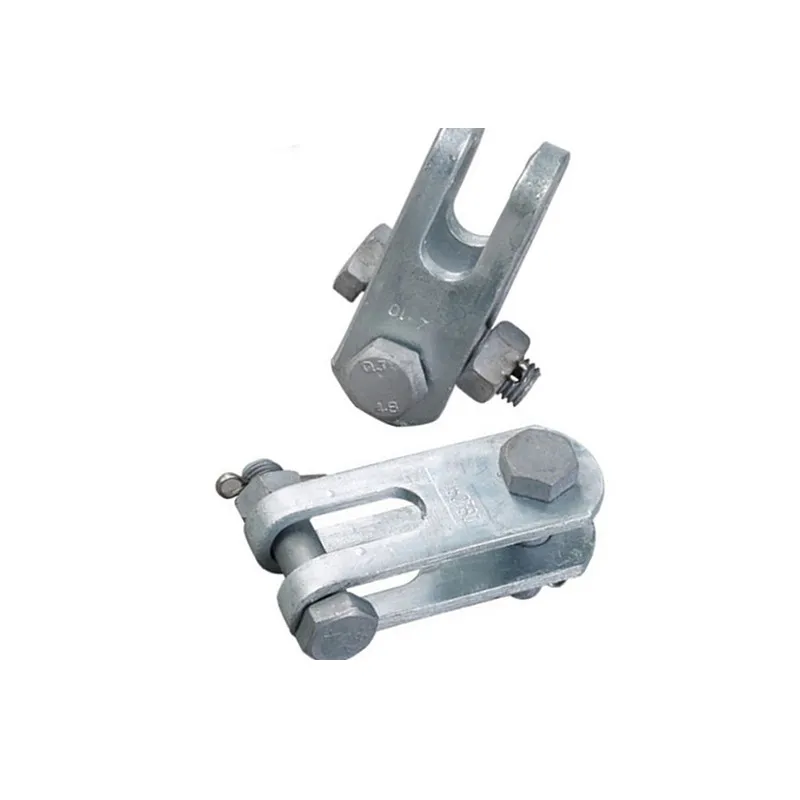
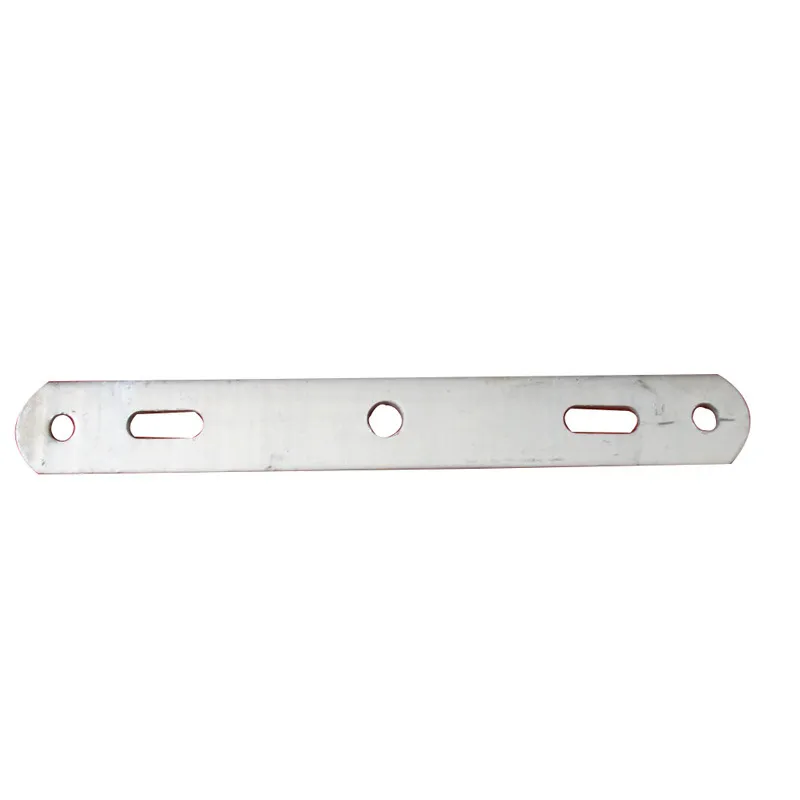
Basic versions usually come in the form of a "flat plate" or "channel" made of metal, with 1-2 connecting holes cut into the surface (for bolts or pins). More complex structures (such as connecting plates) have multiple connecting holes, facilitating the simultaneous fastening of several components.
Key Structural Details:
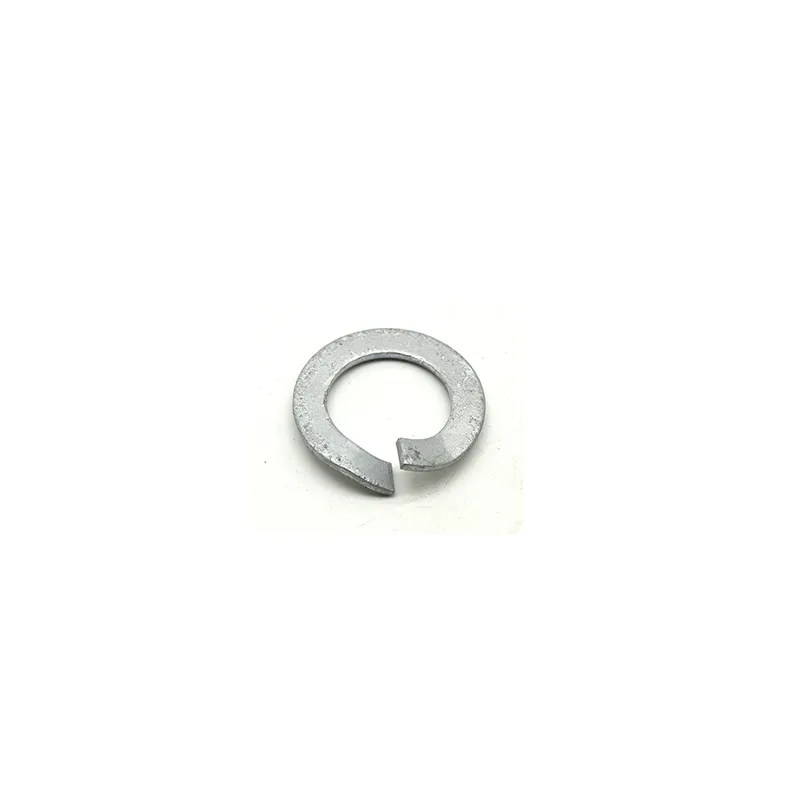
Connecting holes are mainly "circular" or "elliptical". Circular holes facilitate fixed connections (without adjustment capability), while elliptical holes allow slight position adjustment during installation (considering component dimensions).
Panel edges feature "chamfers" to prevent sharp edges from damaging personnel, cables, or slings, as well as to reduce stress concentration.
Some hanging plates (e.g., ball-headed plates) are equipped with a "ball structure" that enables rotation at different angles. This compensates for changes in line sag or tower inclination, preventing damage caused by rigid connections under load.
Would you like me to polish this text for **more concise technical expression** or translate it into another language (e.g., Chinese) for easier internal communication?
Common Structural Types:
Single-hole hanging plate: Features one connecting hole for simple two-point linear connections (e.g., between a tower and a U-bolt).
Two-hole hanging plate: Equipped with two connecting holes (usually symmetrically arranged) for transmitting transverse or longitudinal loads (e.g., between insulators and clamps).
Connecting plate (multi-hole hanging plate): Has three or more connecting holes for joining multiple conductors, optical cables, or fittings (e.g., connecting spacer rods for separable conductors).
Would you like me to create a **simplified structural type comparison table** for this section, making it easier to quickly distinguish the characteristics and application scenarios of each type?











































