Products
Square U-shaped pins
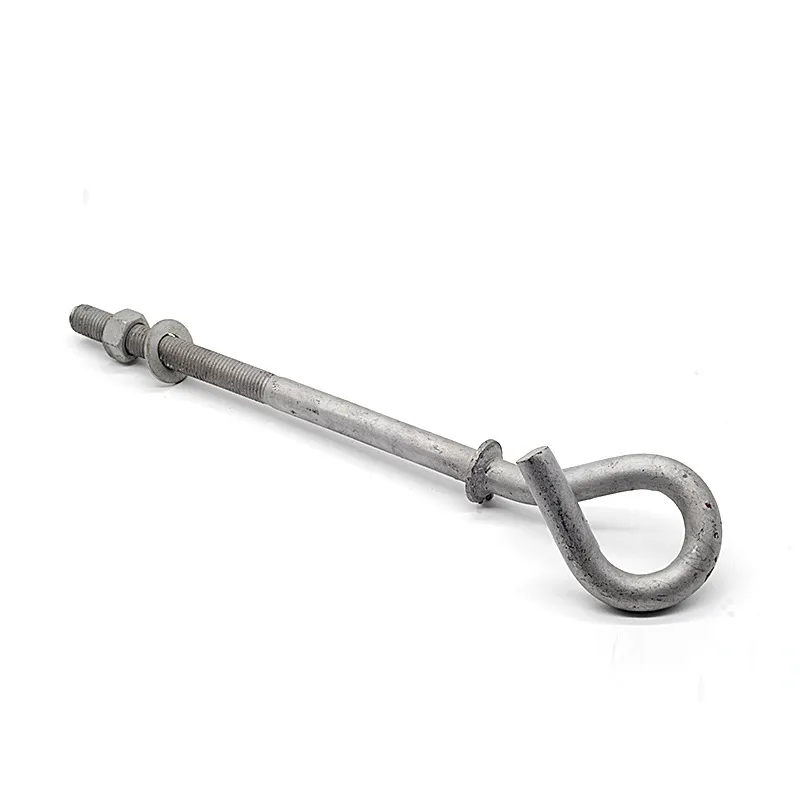
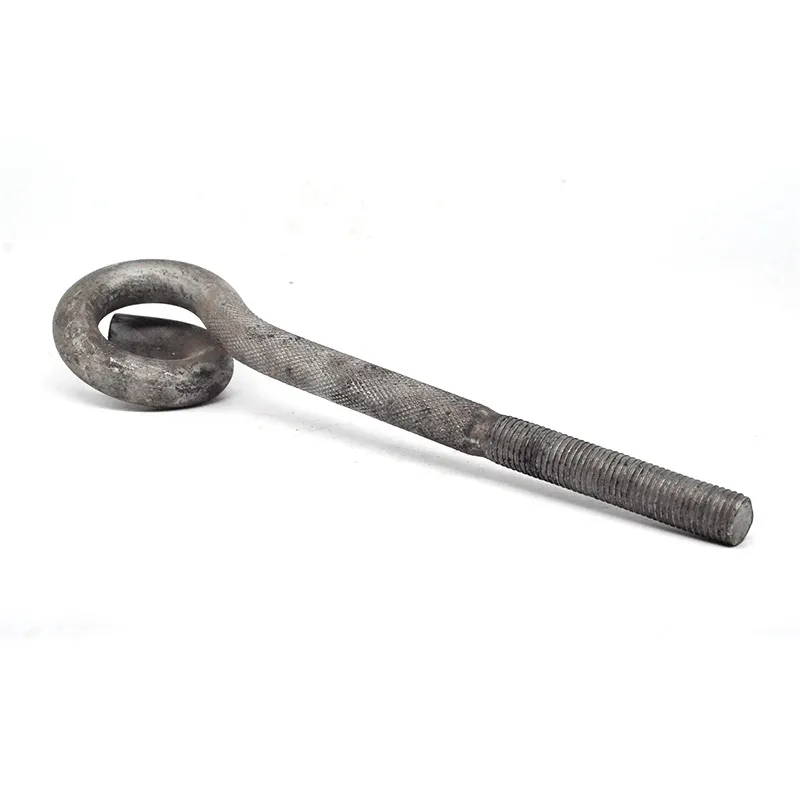
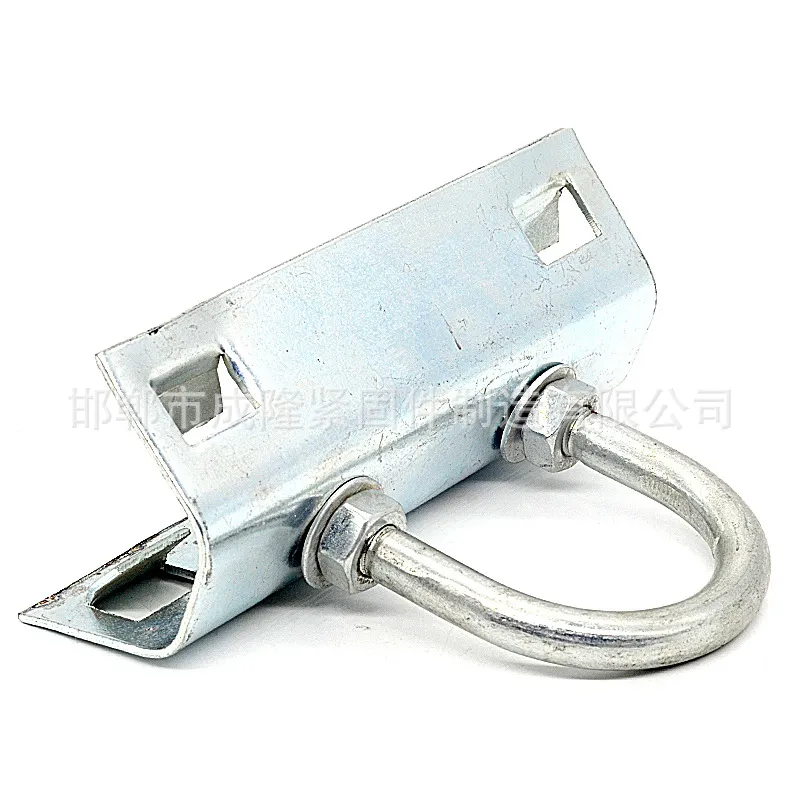
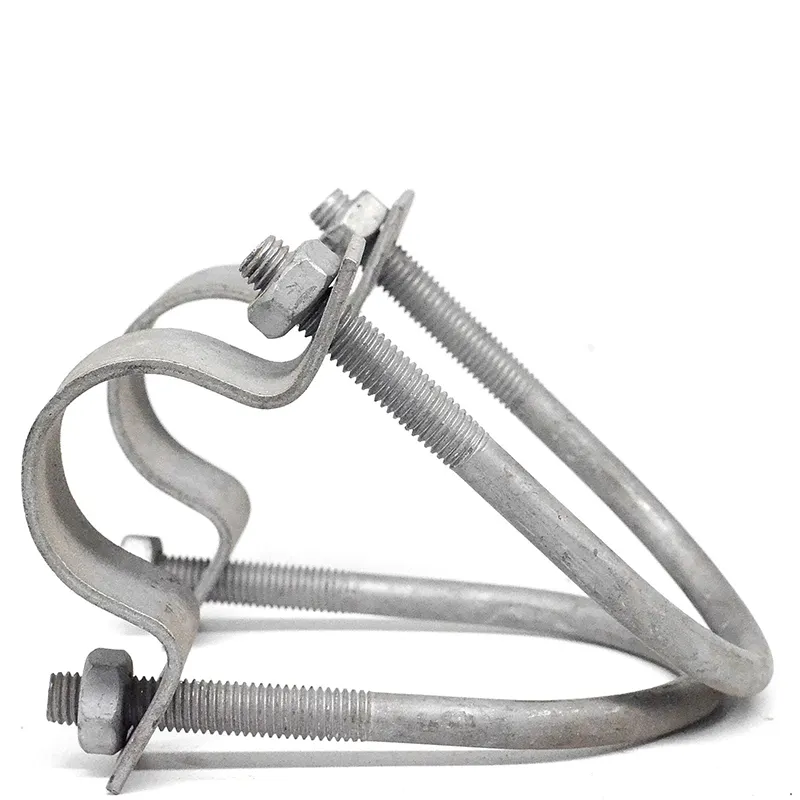
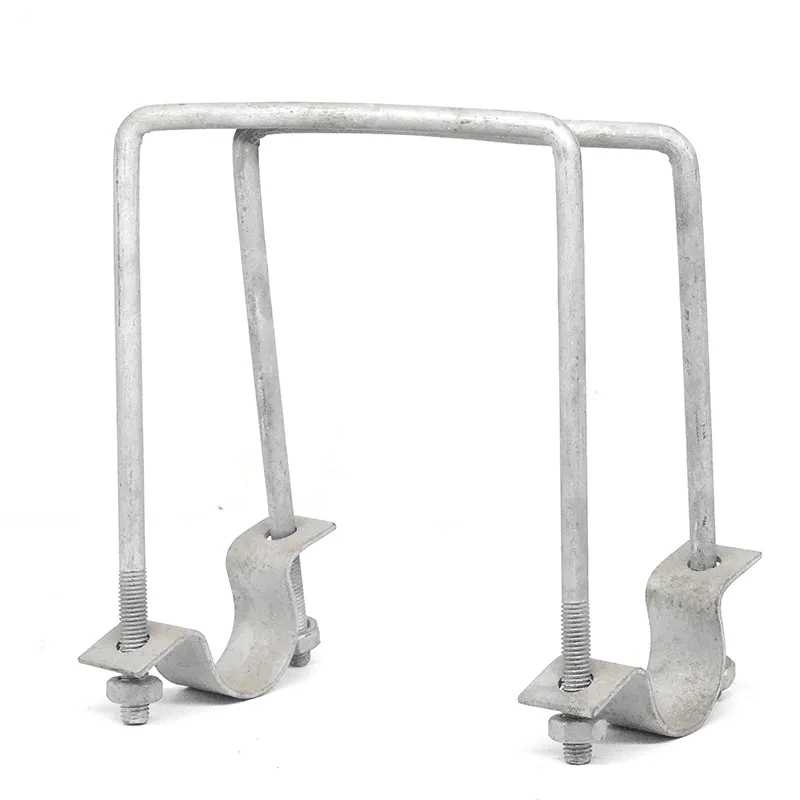
Product Description: Square U-bolts are a type of U-bolt named for their square cross-section, and are widely used fasteners. Below is a detailed description: Design Features Square U-bolts have a U-shaped profile with threaded ends. Unlike standard U-bolts, their cross-section is square. ...
Description
marker
Product Description:
Square U-bolts are a type of U-bolt named for their square cross-section, and are widely used fasteners. Below is a detailed description:
Design Features
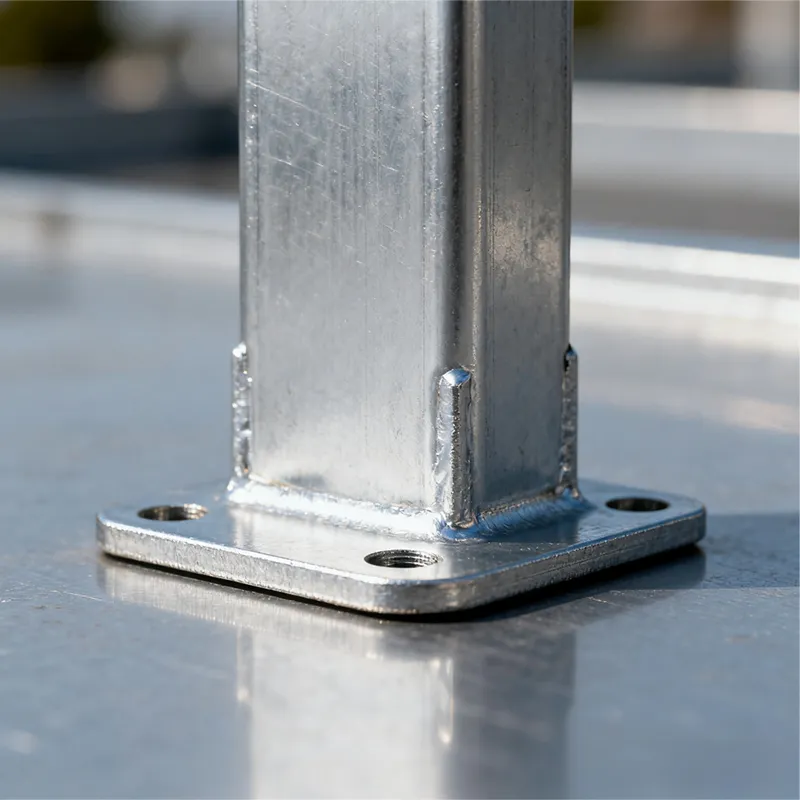
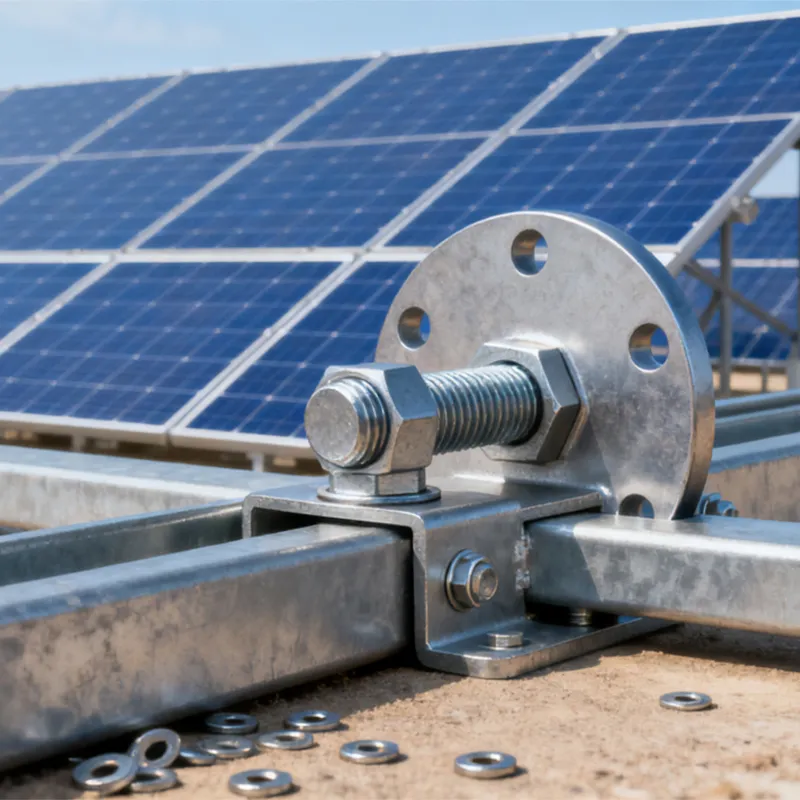
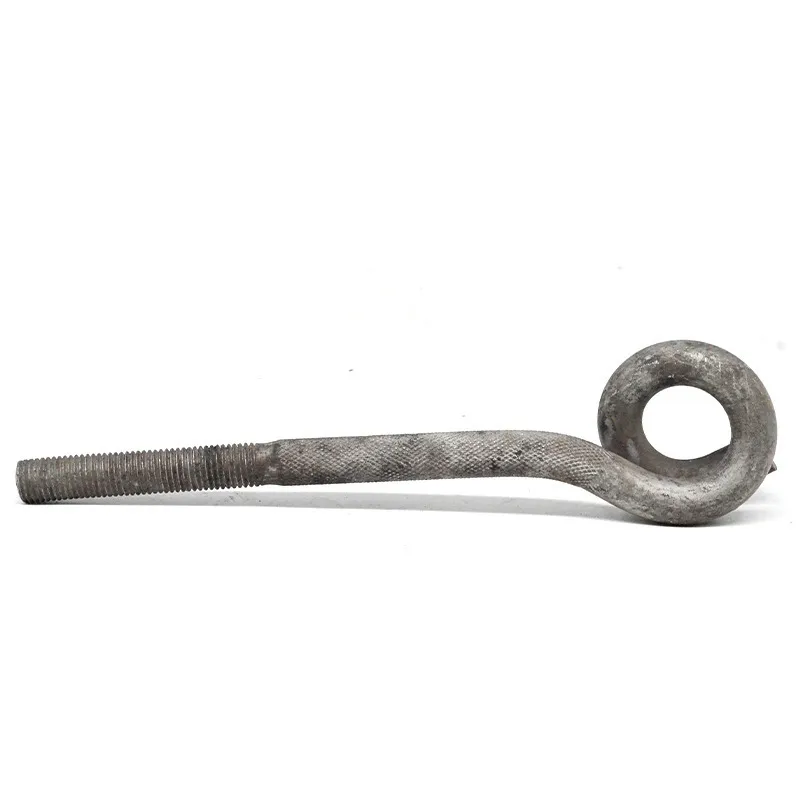
Square U-bolts have a U-shaped profile with threaded ends. Unlike standard U-bolts, their cross-section is square. This square structure provides a larger contact area with the fastened object, enabling more effective load distribution and reducing local stress concentration. It enhances the stability and reliability of the connection. In addition, the four right angles of the square shape serve as alignment guides during installation, facilitating precise positioning, simplifying the mounting process, and improving construction efficiency.
Materials and Surface Treatment
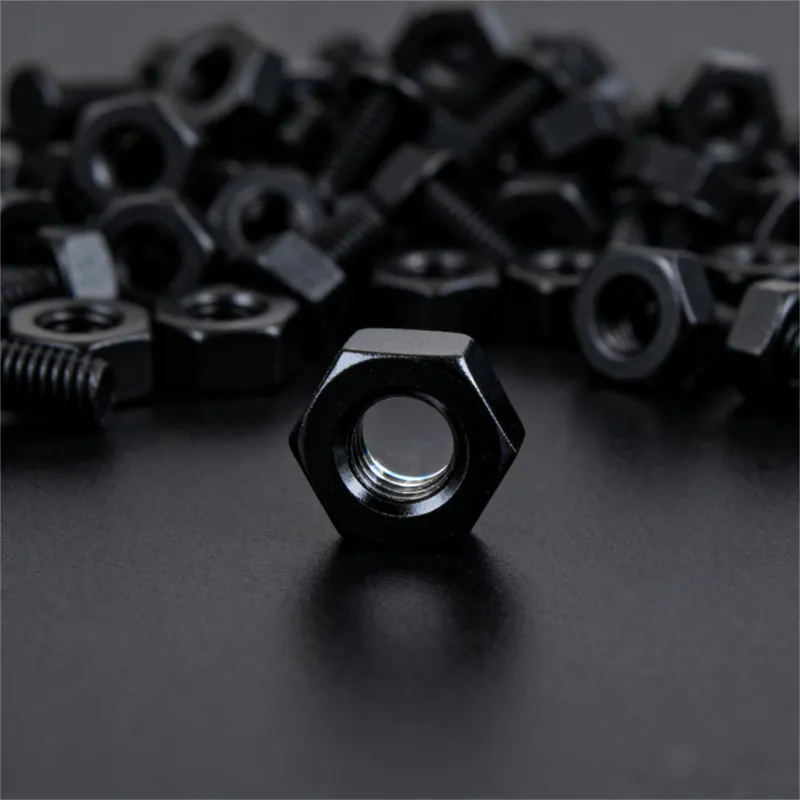
Square U-bolts are usually made of carbon steel, alloy steel, or stainless steel. Carbon steel variants offer high strength at a relatively low cost, making them widely applicable. However, stainless steel square U-bolts provide excellent corrosion resistance, maintaining stable mechanical properties in humid or highly corrosive environments. They are often used in marine engineering, chemical equipment, and similar industries. To further improve corrosion resistance and service life, common surface treatments include galvanization, blackening, or Dacromet coating.
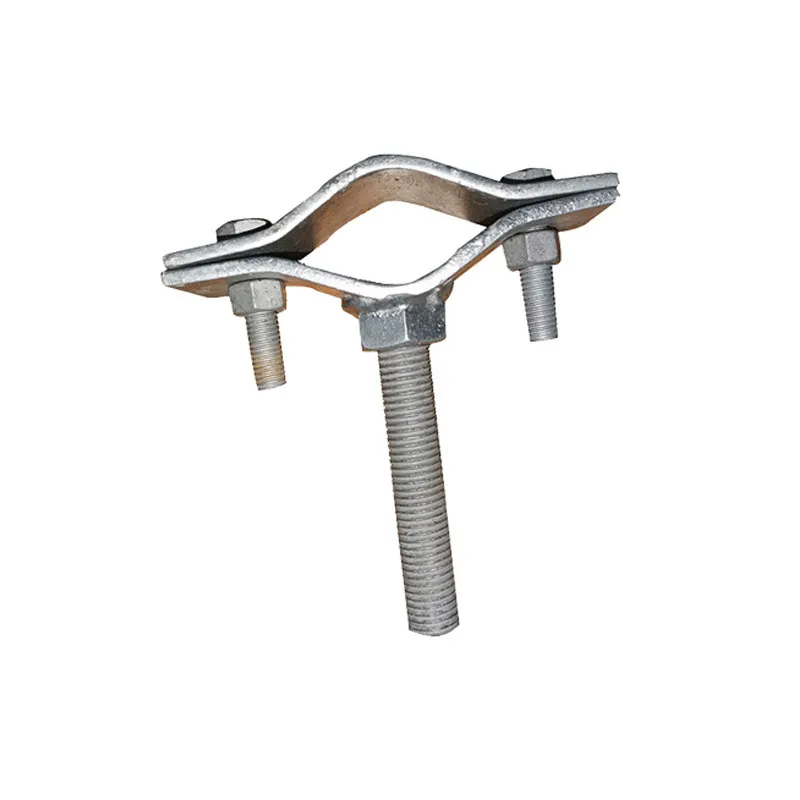
Technical Specifications and Sizes
Square U-bolts come in various technical specifications. Common thread diameters include M6, M8, and M10, while lengths vary based on practical requirements—from tens of millimeters to several meters. In addition, dimensions such as the width, height, and bend radius of the U-shaped section can be customized to meet specific installation and fastening needs.
Applications
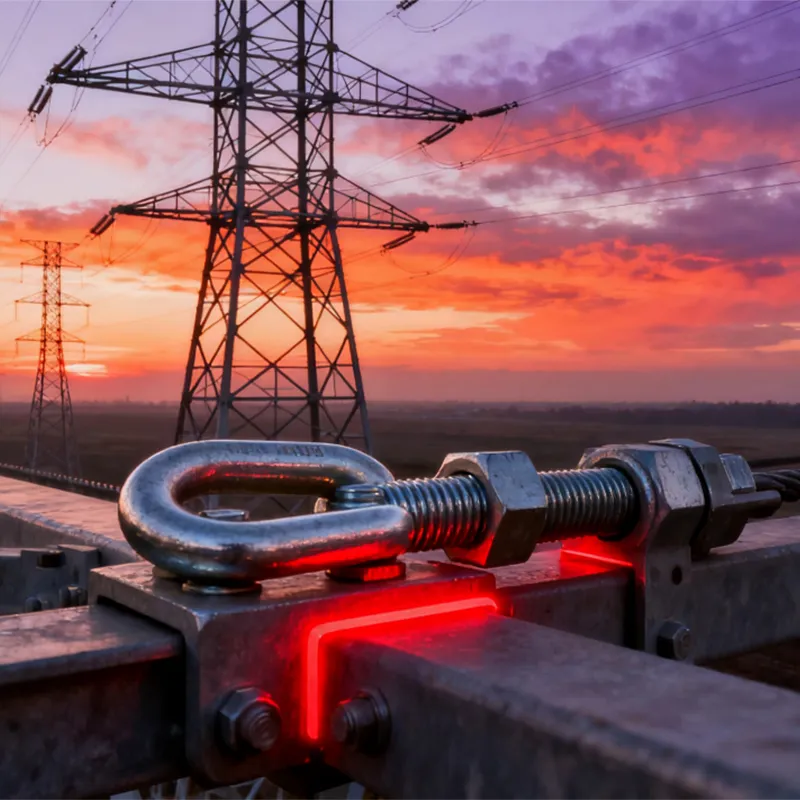
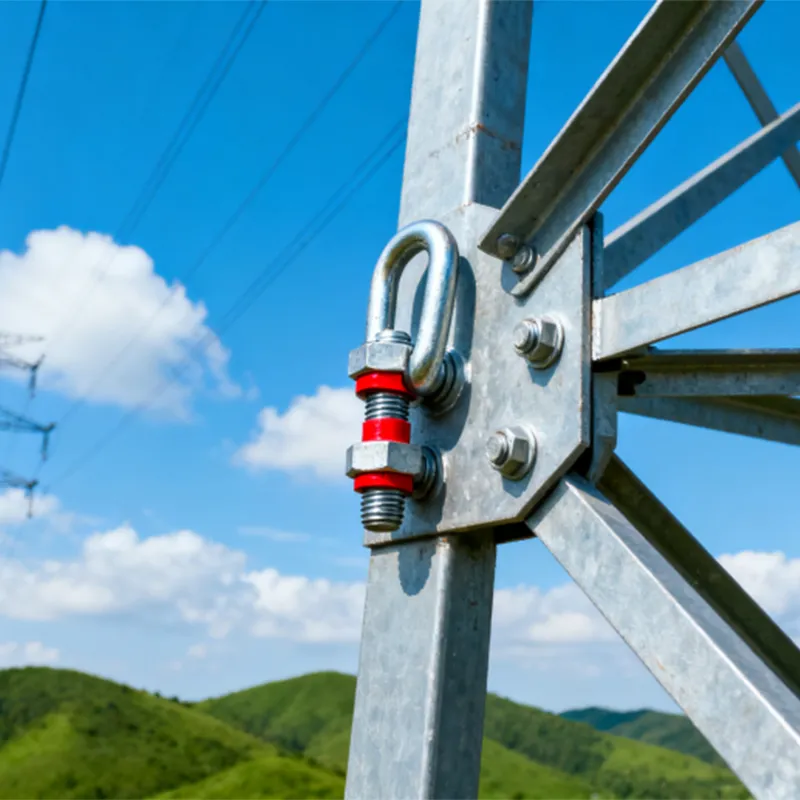
Square U-bolts are mainly used for fastening square or rectangular objects. Their applications include: fastening steel structures and scaffolding in construction settings; securing square pipes and profiles in mechanical components; stabilizing automotive chassis and frames in the automotive industry (e.g., connecting leaf springs); and fastening structural elements in bridge, tunnel, and railway construction projects.
















































