Products
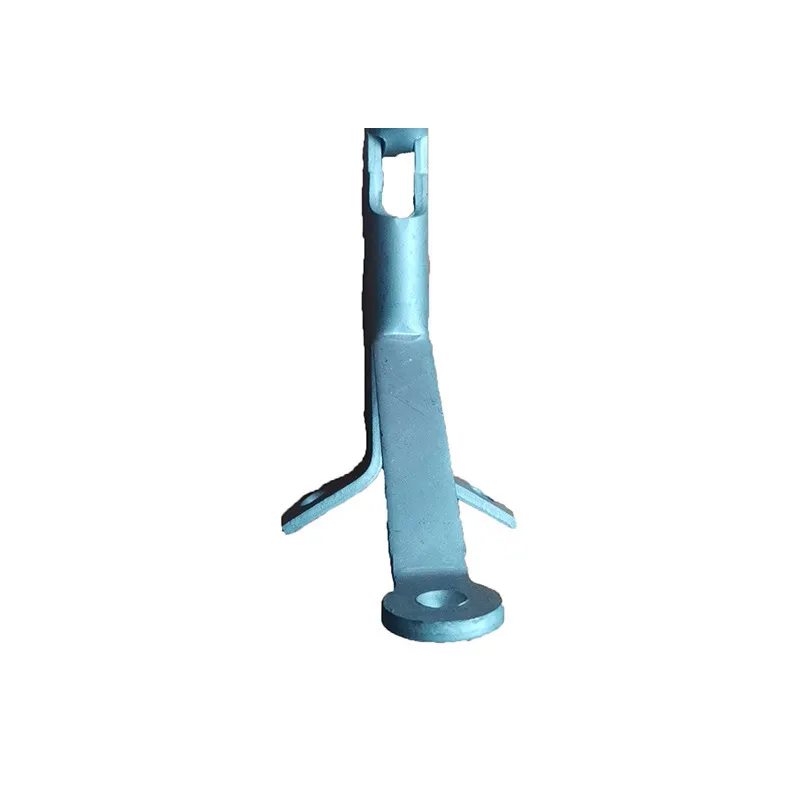
Straight Steel Insulator Legs
Product Description Straight Steel Brackets for Insulators Straight steel brackets for insulators are a crucial component of insulators, primarily used to fasten and support insulators in high-voltage overhead power transmission lines. Below is a detailed description: Structural Features S...
Description
marker
Product Description
Straight Steel Brackets for Insulators
Straight steel brackets for insulators are a crucial component of insulators, primarily used to fasten and support insulators in high-voltage overhead power transmission lines. Below is a detailed description:
Structural Features
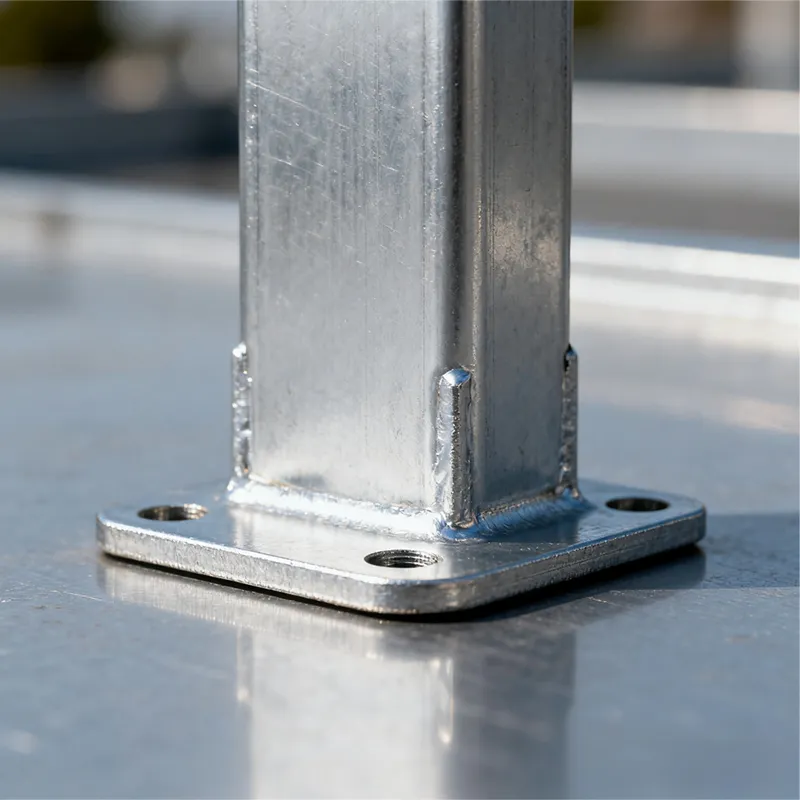
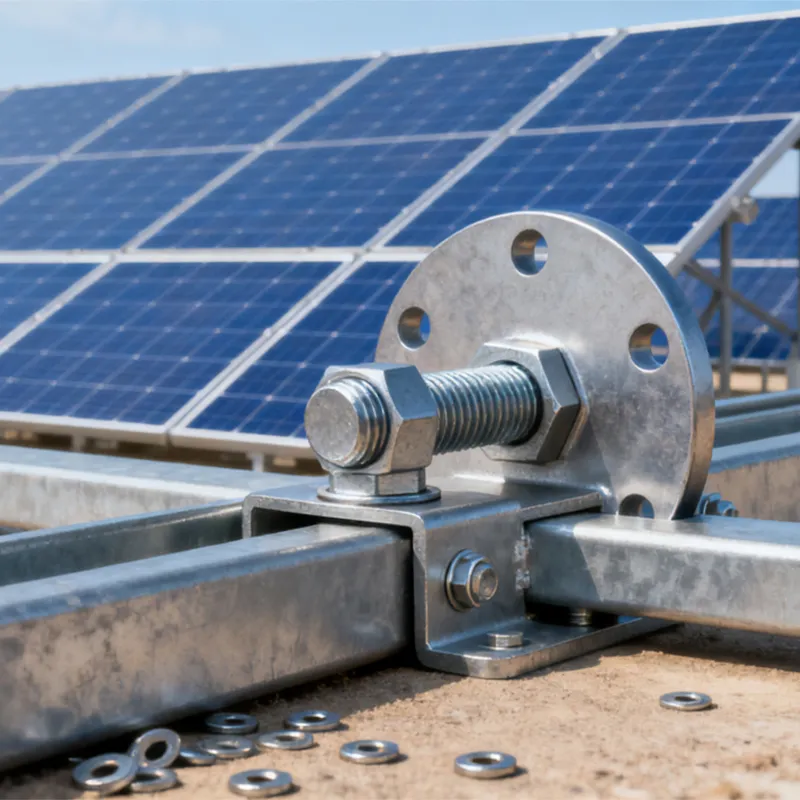
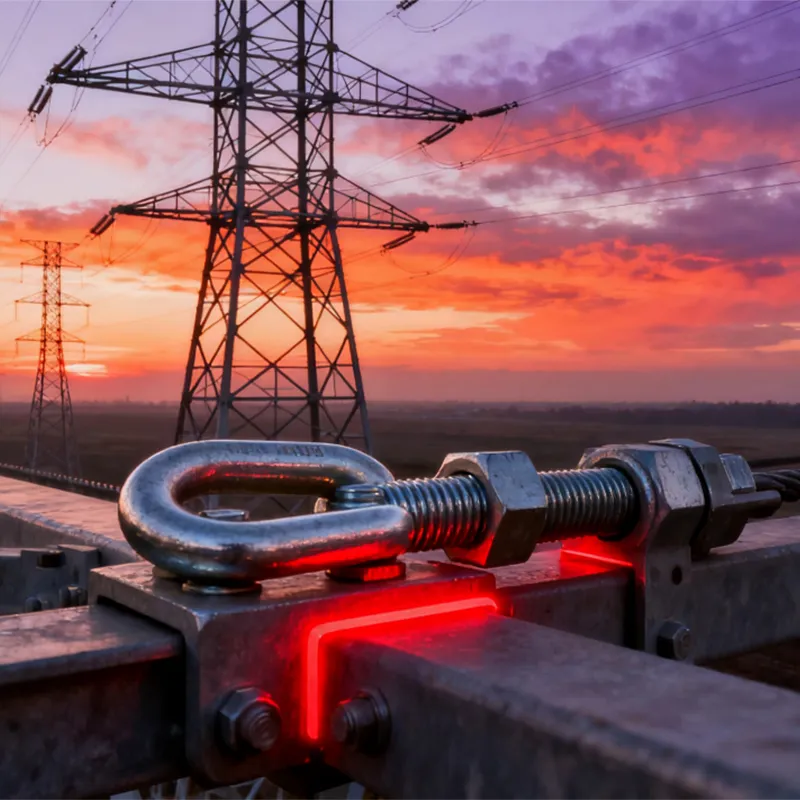
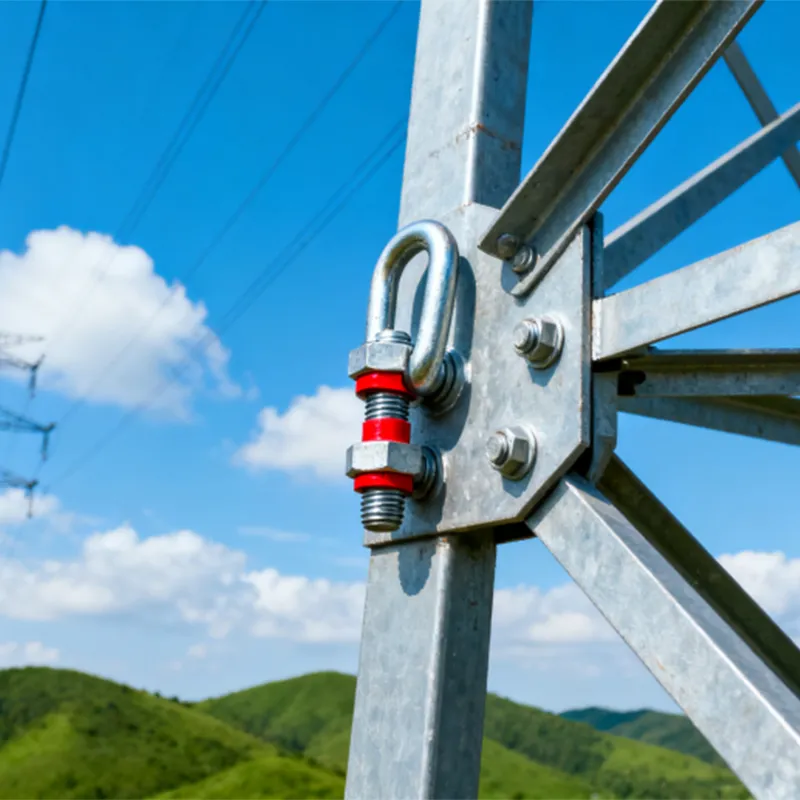
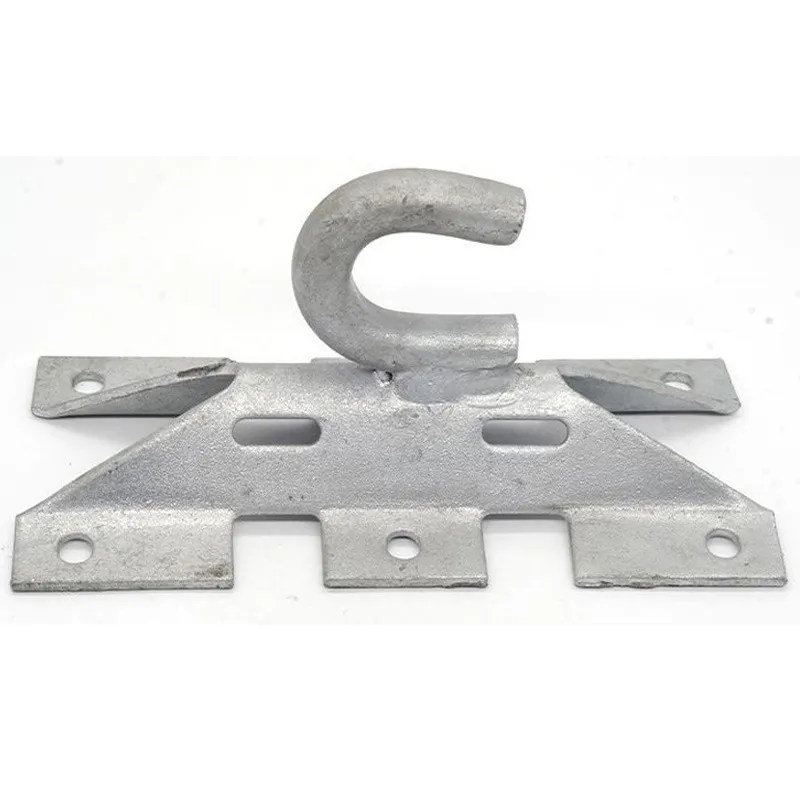
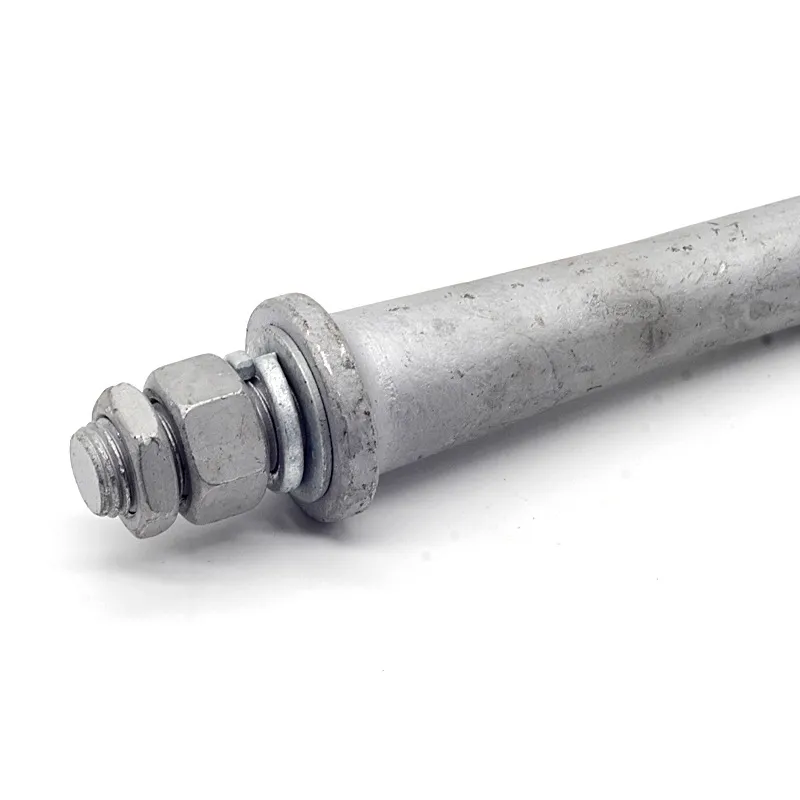
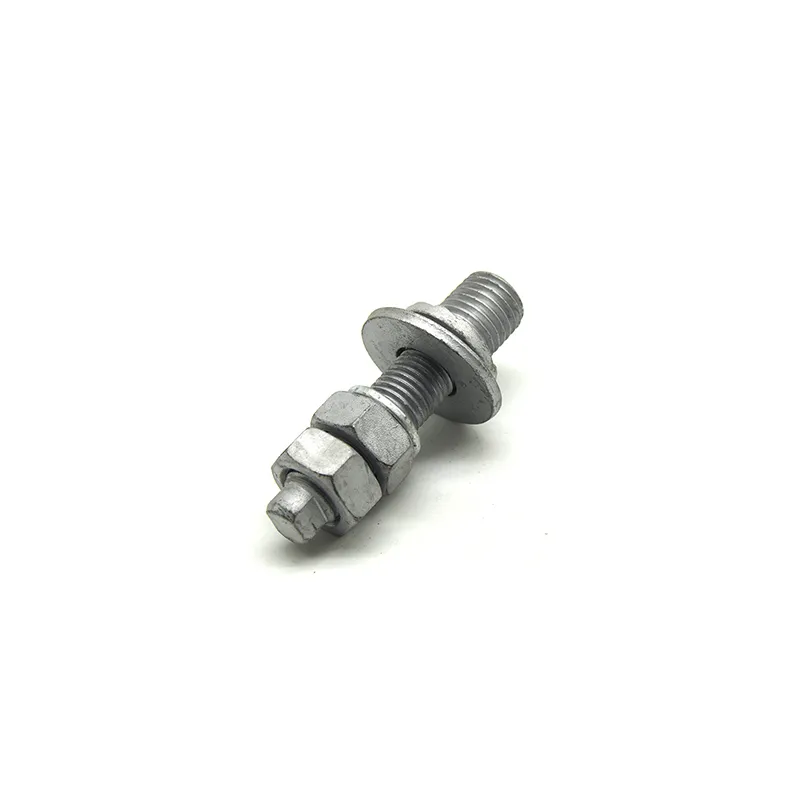
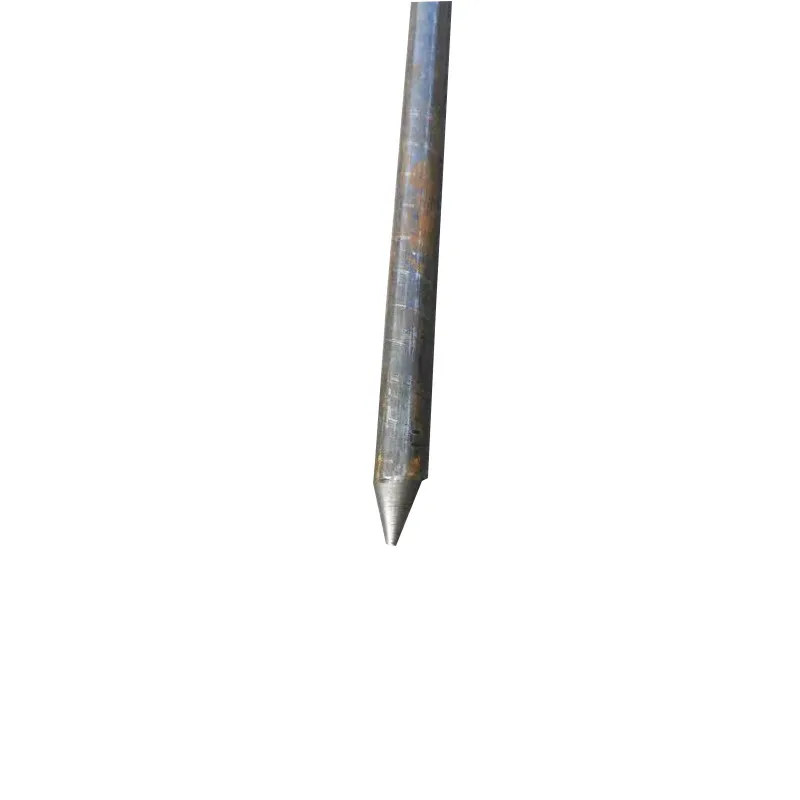
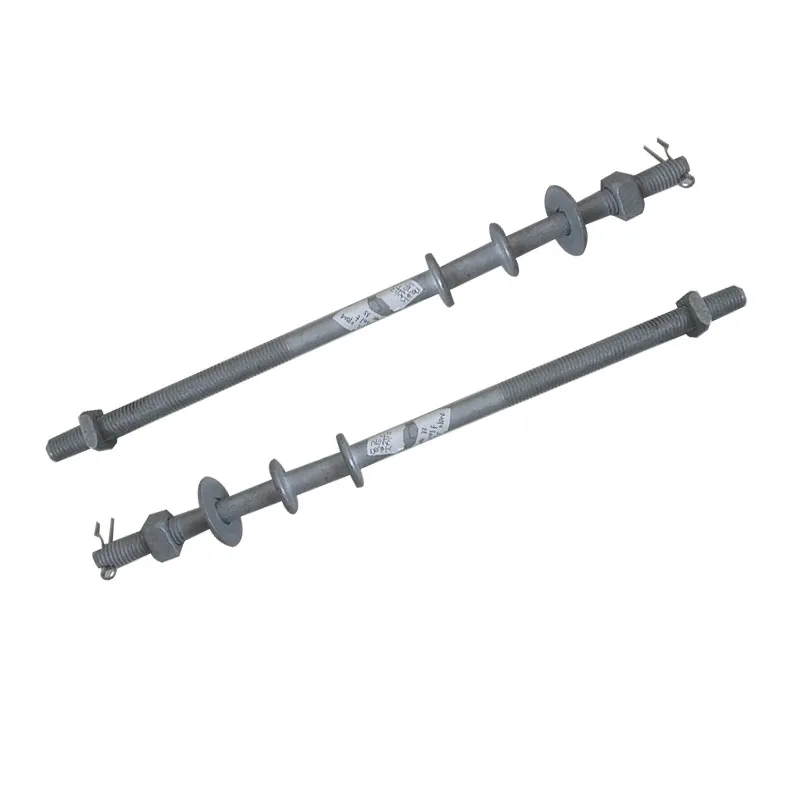
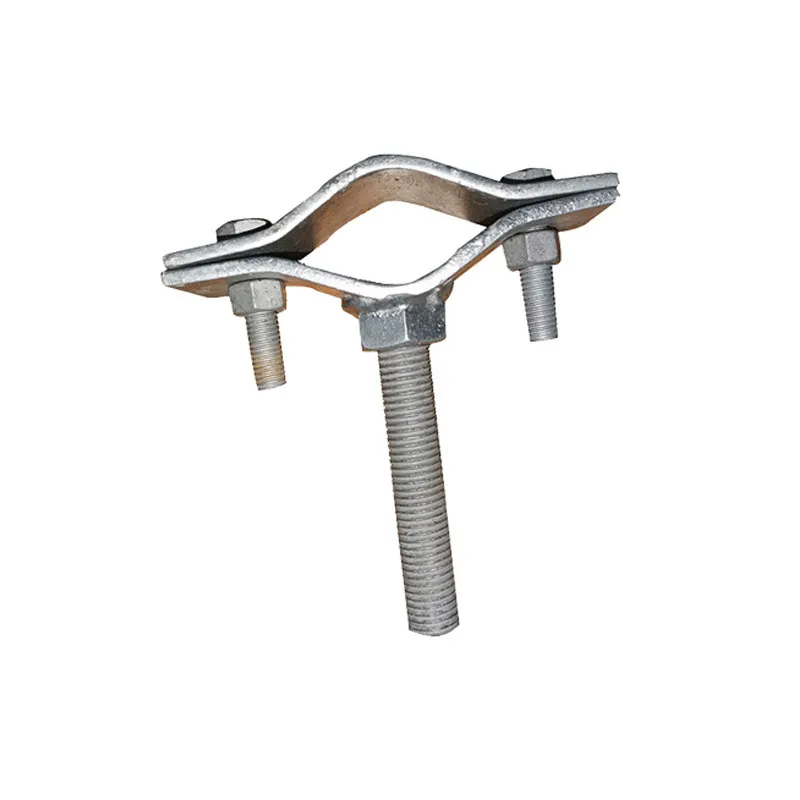
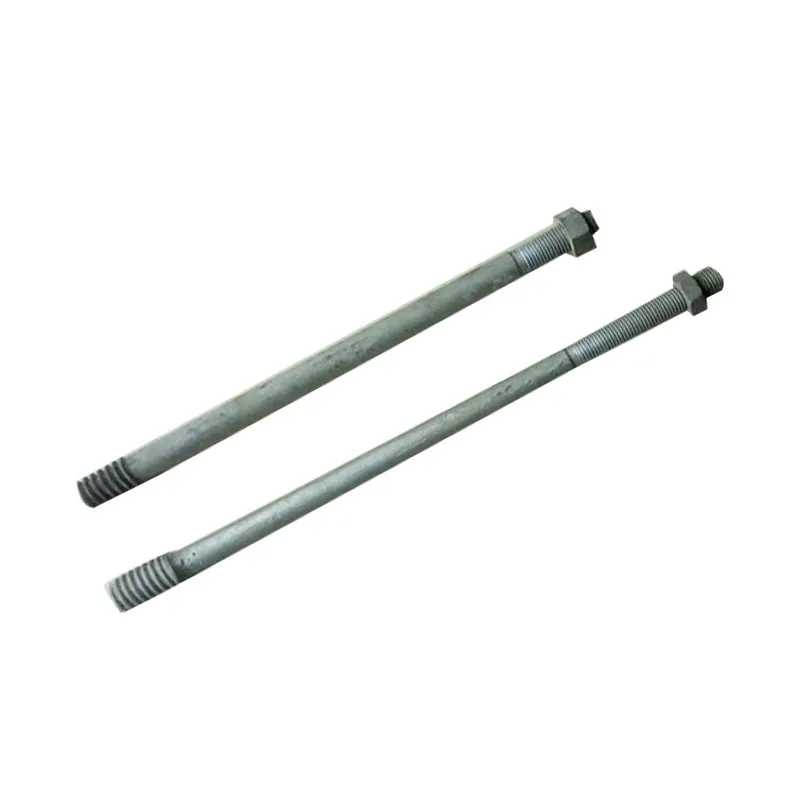
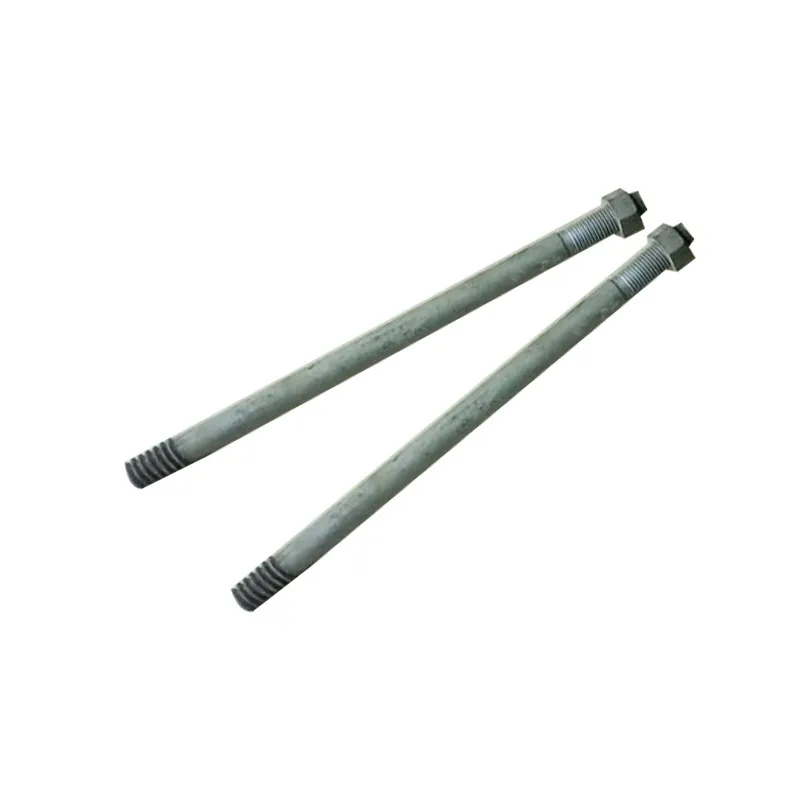
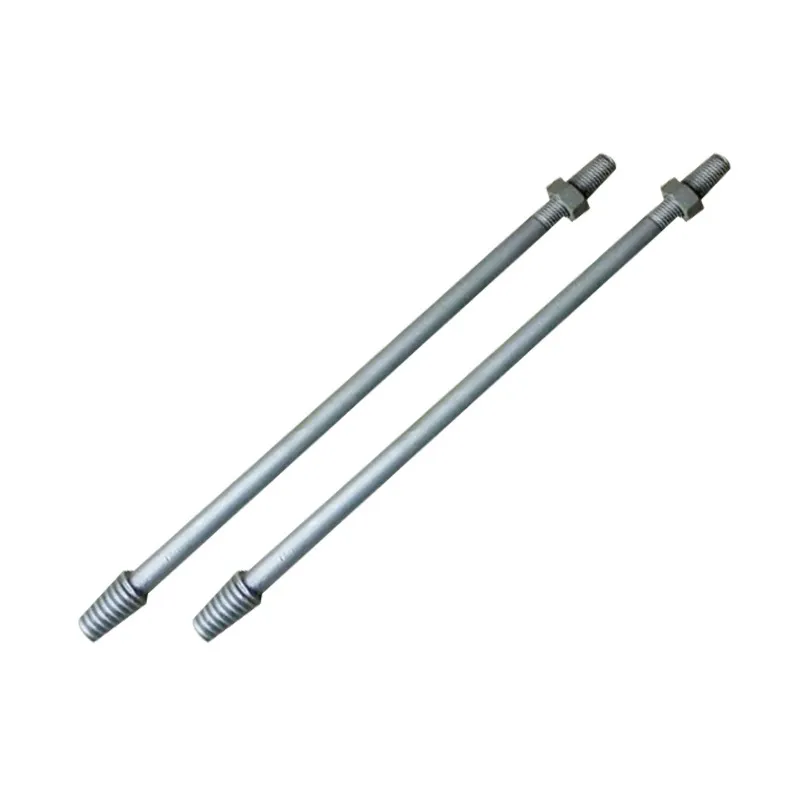
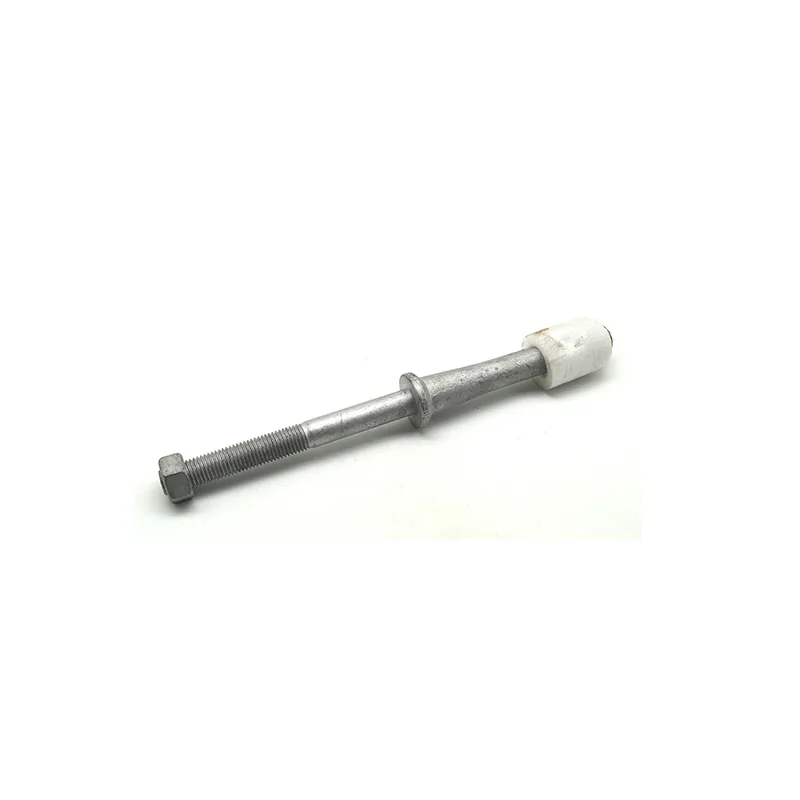
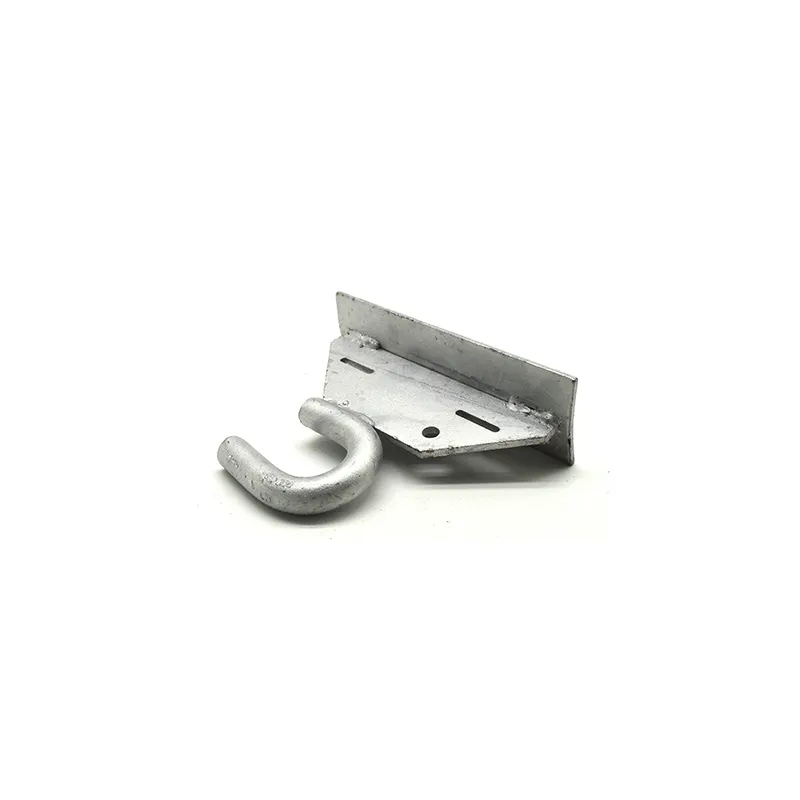
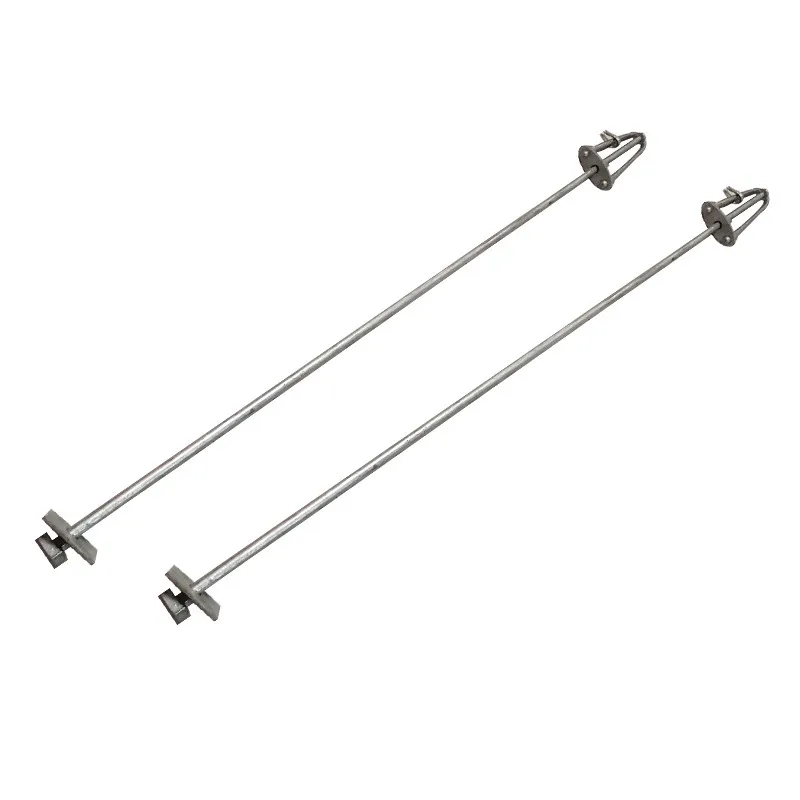
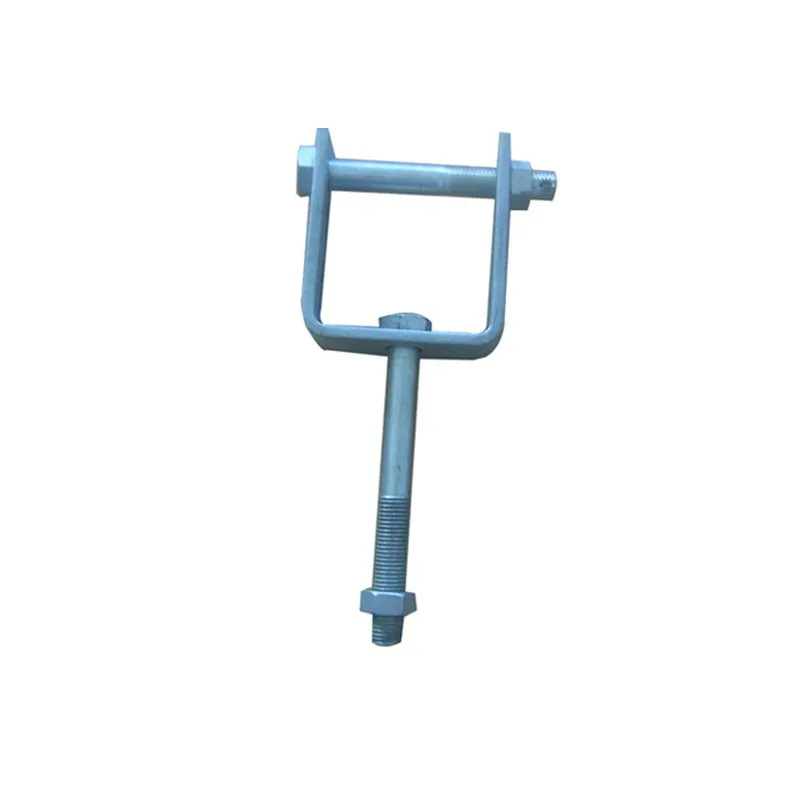
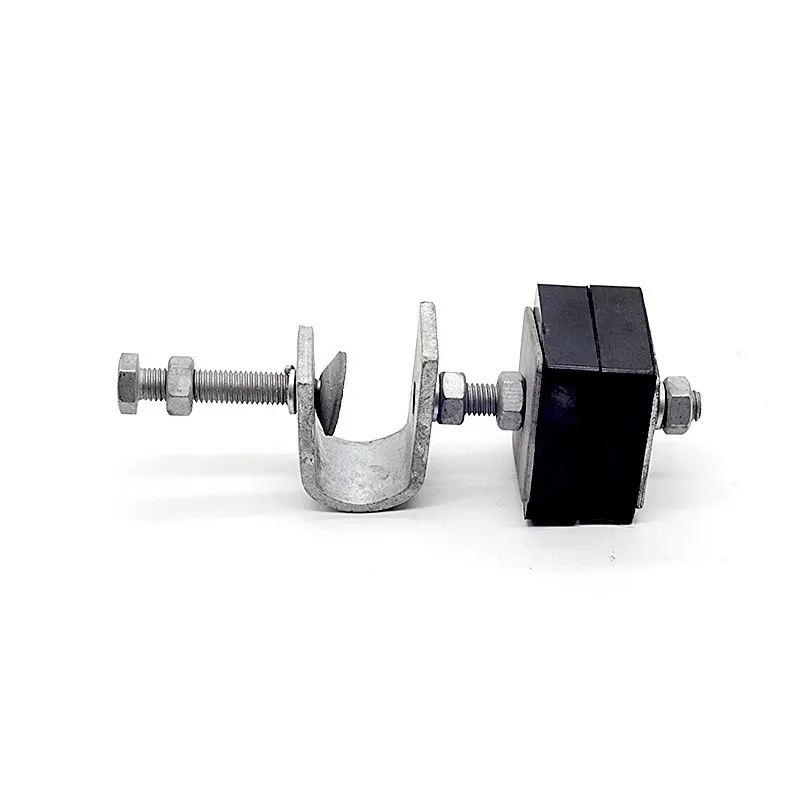
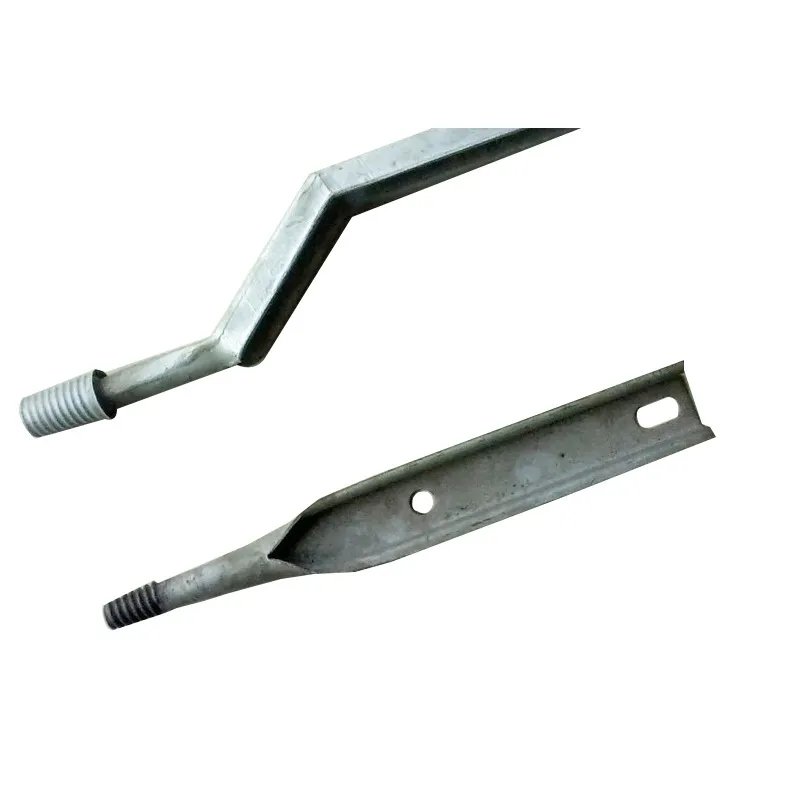
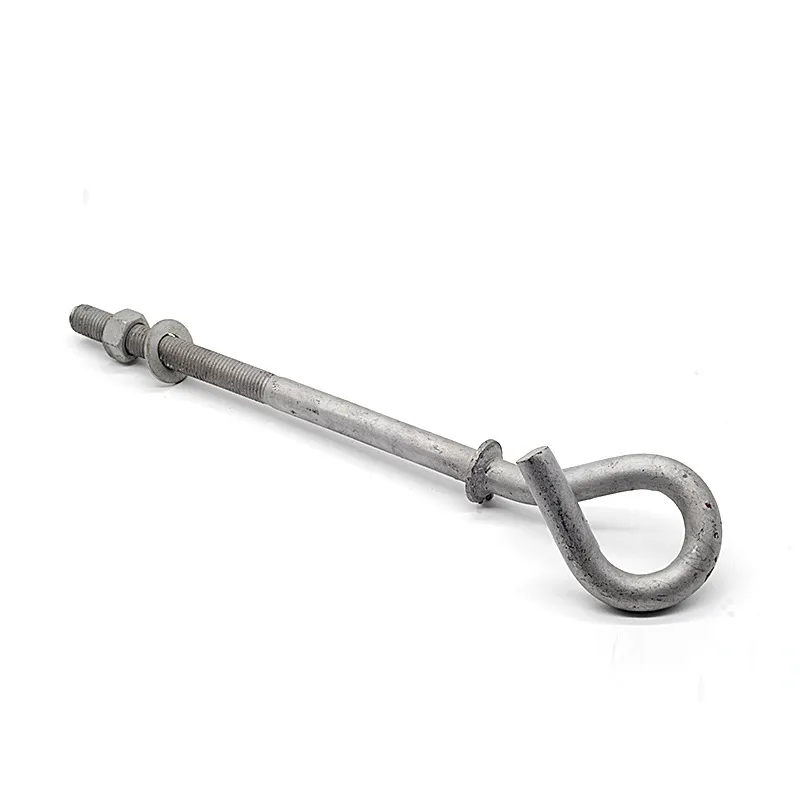
Straight steel brackets for insulators typically have a cylindrical shape. One end is cemented into the porcelain insulator body, while the other end is designed to connect to load-bearing structures such as power poles. The section embedded in the porcelain component features deep grooves, which enhance connection strength and prevent loosening. An elastic gasket is placed between the upper part of the steel support and the porcelain; this gasket absorbs stresses caused by thermal expansion and contraction while ensuring a tight fit. This design prevents the ingress of moisture and contaminants, thereby avoiding degradation of insulating properties.
Material and Surface Treatment
Steel supports are usually made of steel to meet mechanical strength requirements. To improve corrosion resistance, they undergo hot-dip galvanizing. This coating effectively isolates the steel from external corrosive agents, ensuring long-term stable operation in harsh service conditions.
Technical Parameters and Standards
The technical characteristics and requirements for insulators with straight steel supports vary depending on the insulator type and application scenario. For example, insulators with straight steel supports for high-voltage lines—equipped with pin-type porcelain insulators—are classified into four categories based on rated voltage: 6 kV, 10 kV, 15 kV, and 20 kV. Each category is further divided into two subtypes according to the steel support type: those with straight supports on iron bases and those with straight supports on wooden bases. All new models have a rated voltage of 10 kV and are categorized into three types: standard type, enhanced insulation type 1, and enhanced insulation type 2.
Relevant standards specify the exact dimensions, material strength, mechanical properties, and electrical characteristics of the steel supports. The supports must possess sufficient tensile, bending, and shear strength to withstand conductor weight, wind loads, and potential electrodynamic forces from short circuits.
Function and Application
The primary function of straight steel insulator supports is to fasten insulators to poles or towers, bearing conductor tension and other external forces. This ensures stable insulating performance, supports and secures conductors, and guarantees the safe and reliable operation of power transmission lines. Widely used in overhead power transmission lines, these supports are a key component that ensures the safety of electrical energy transmission.















































