Products
Tallers
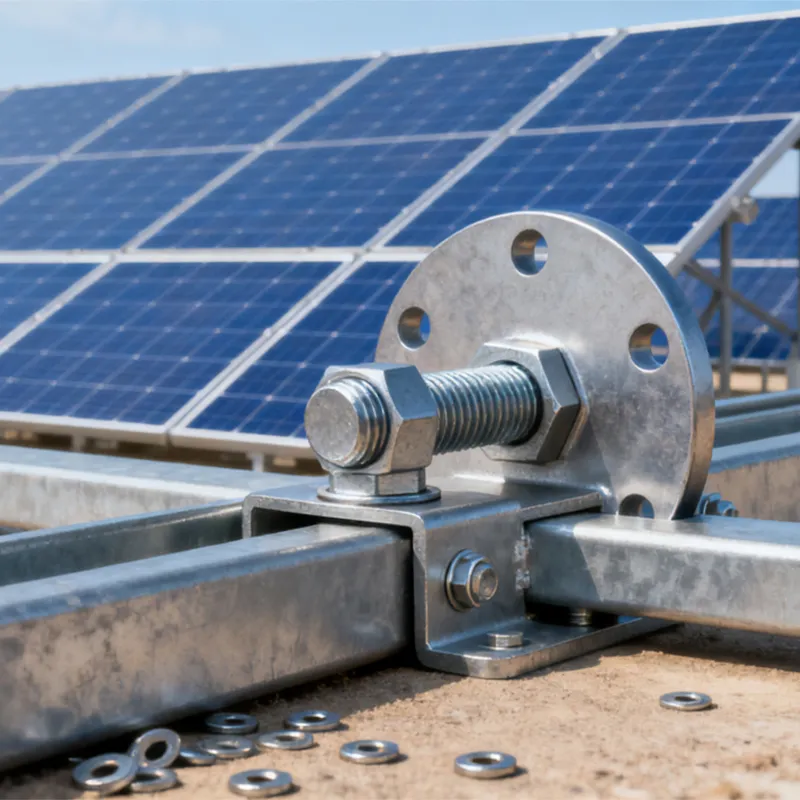
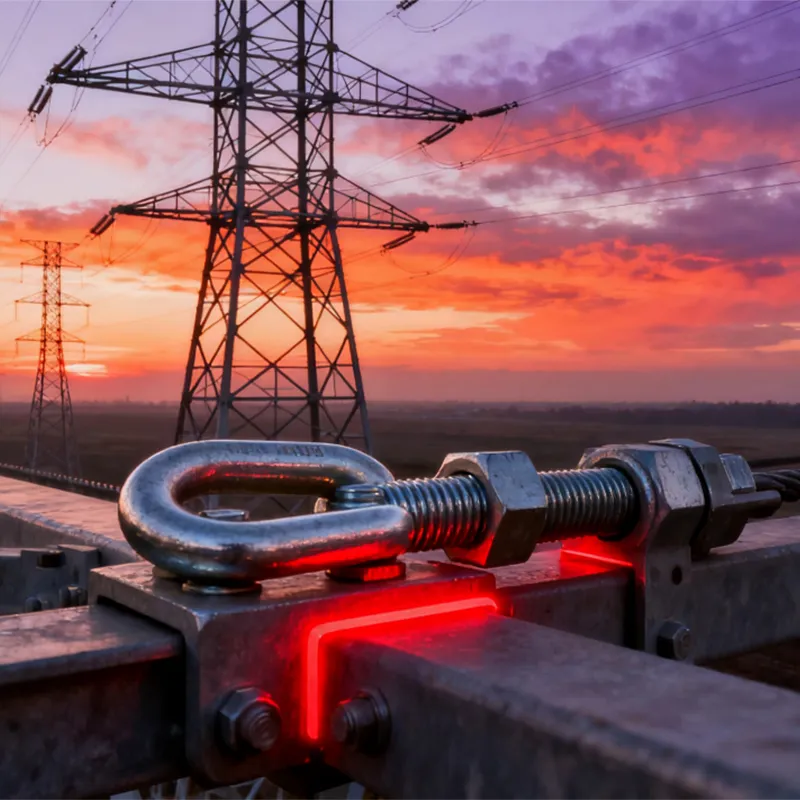
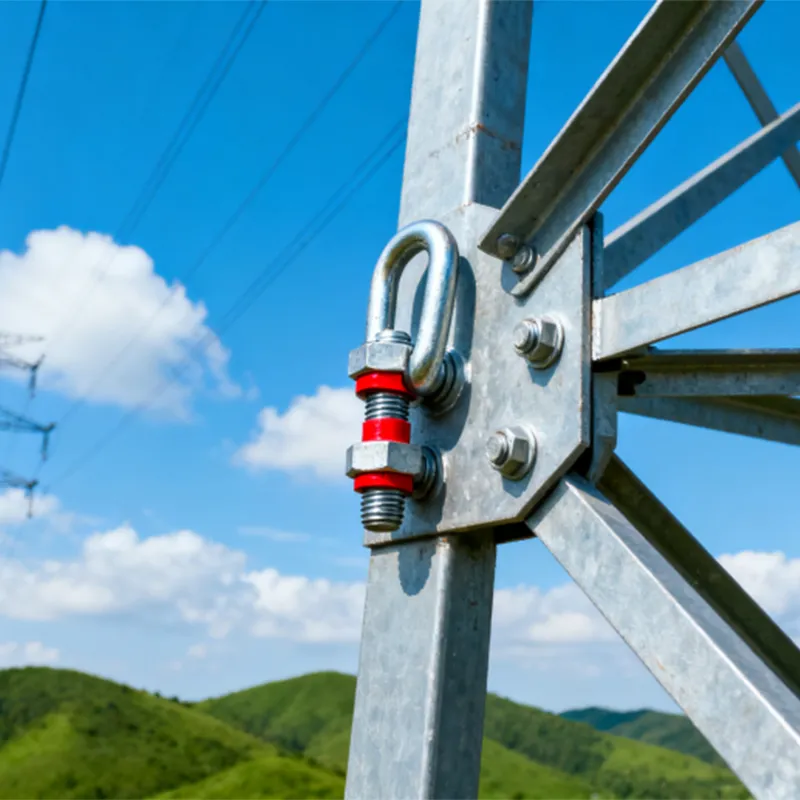
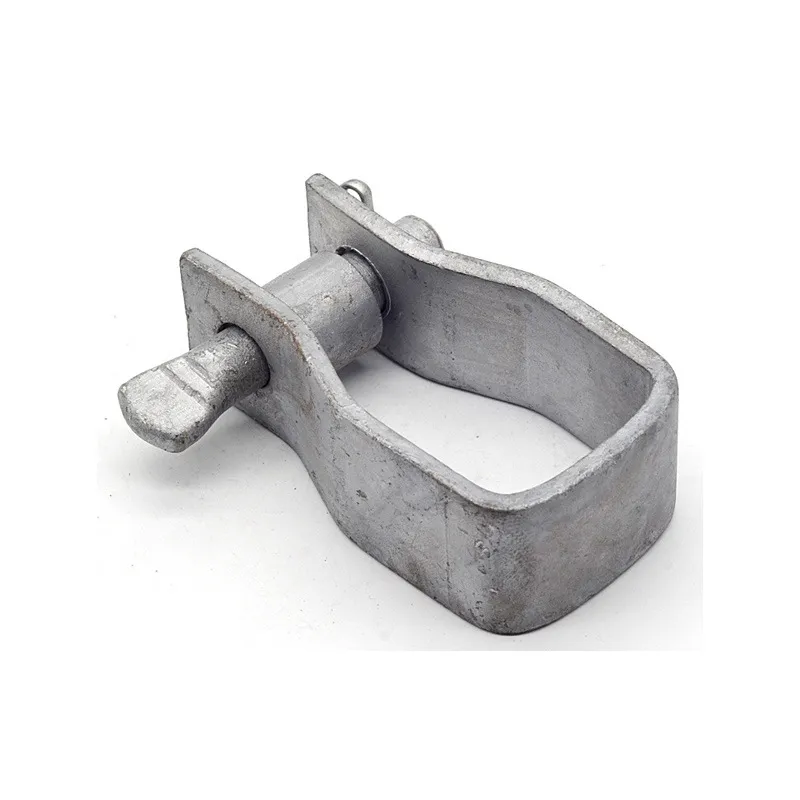
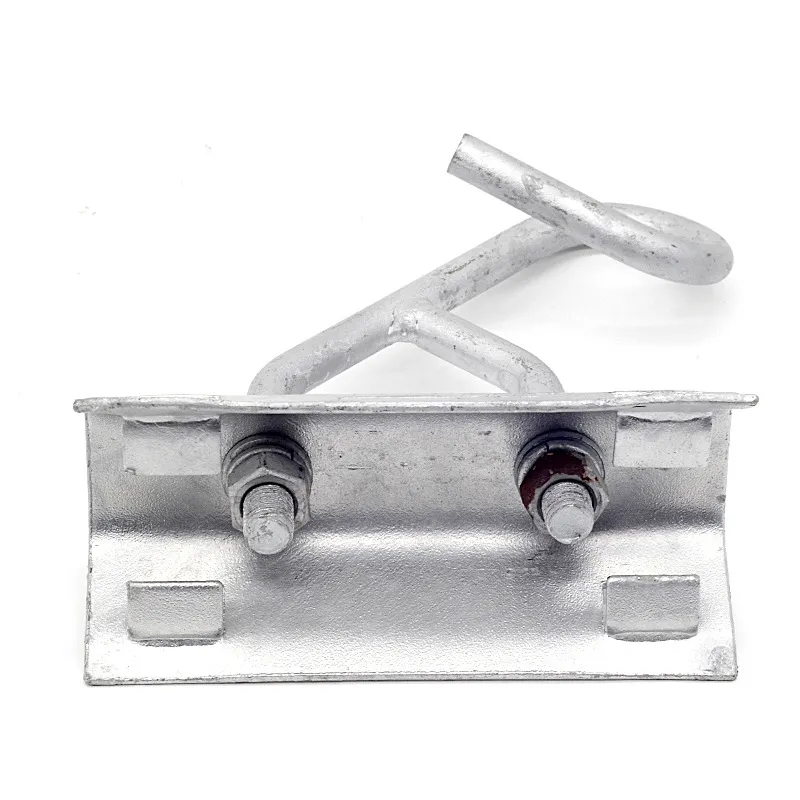
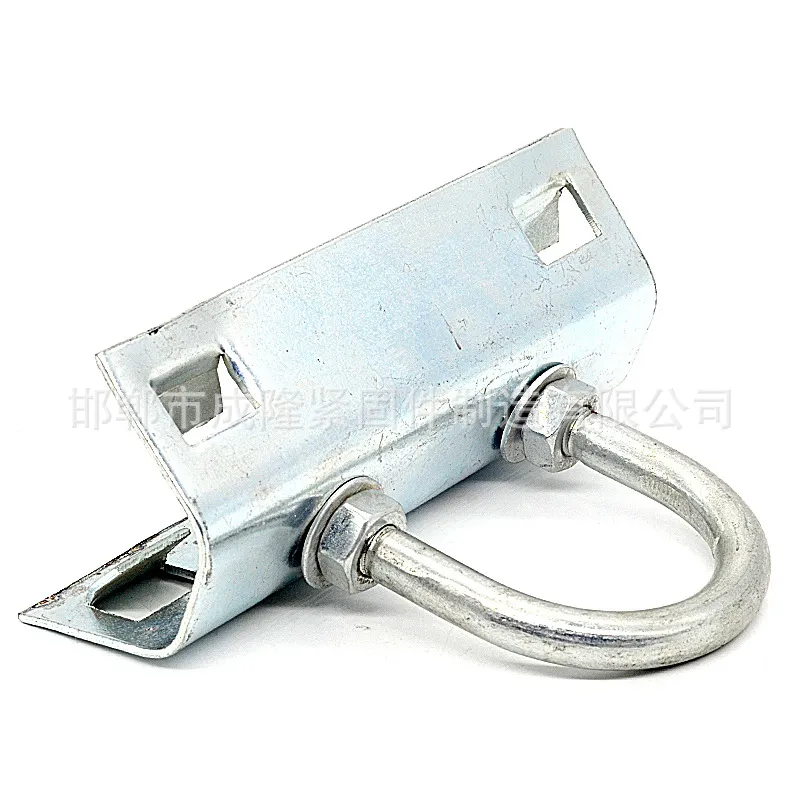
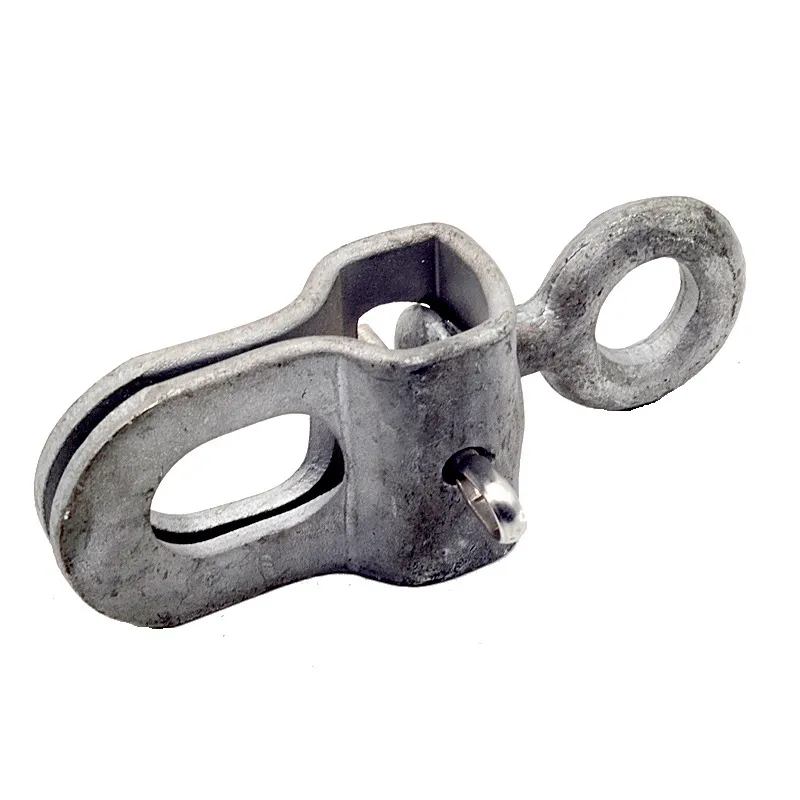
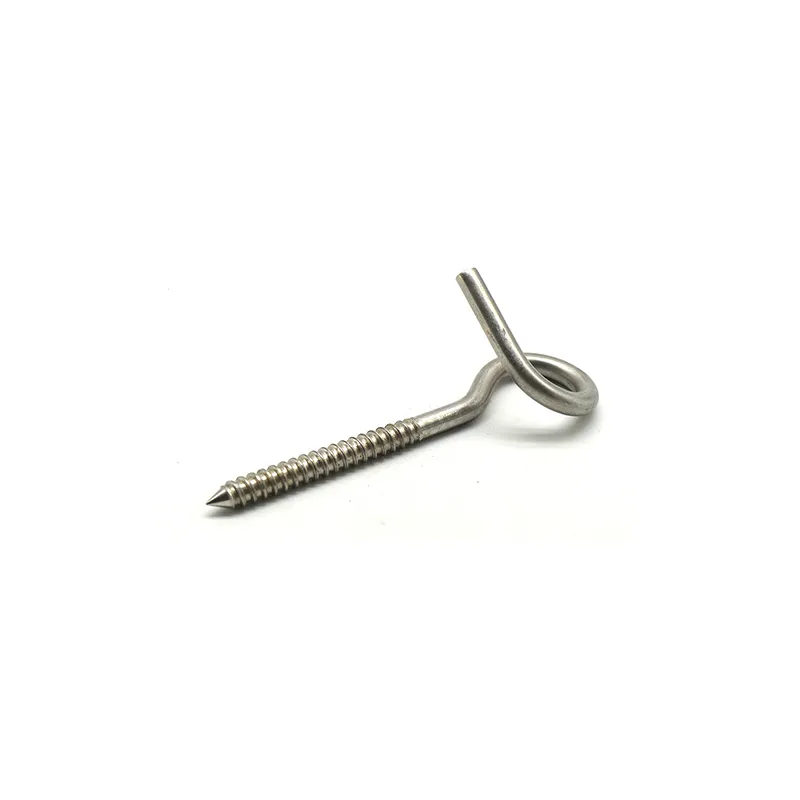
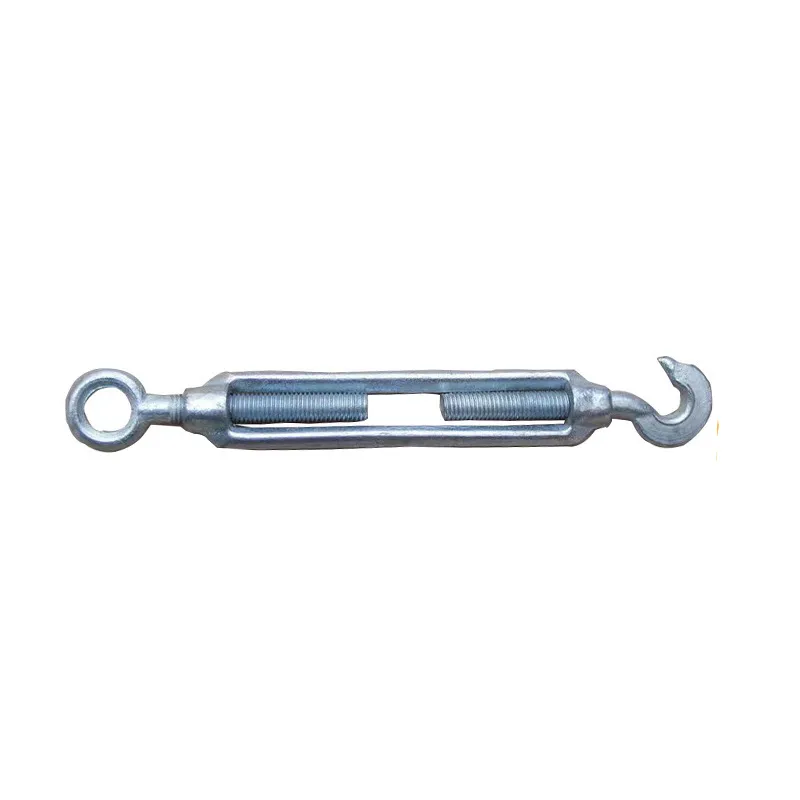
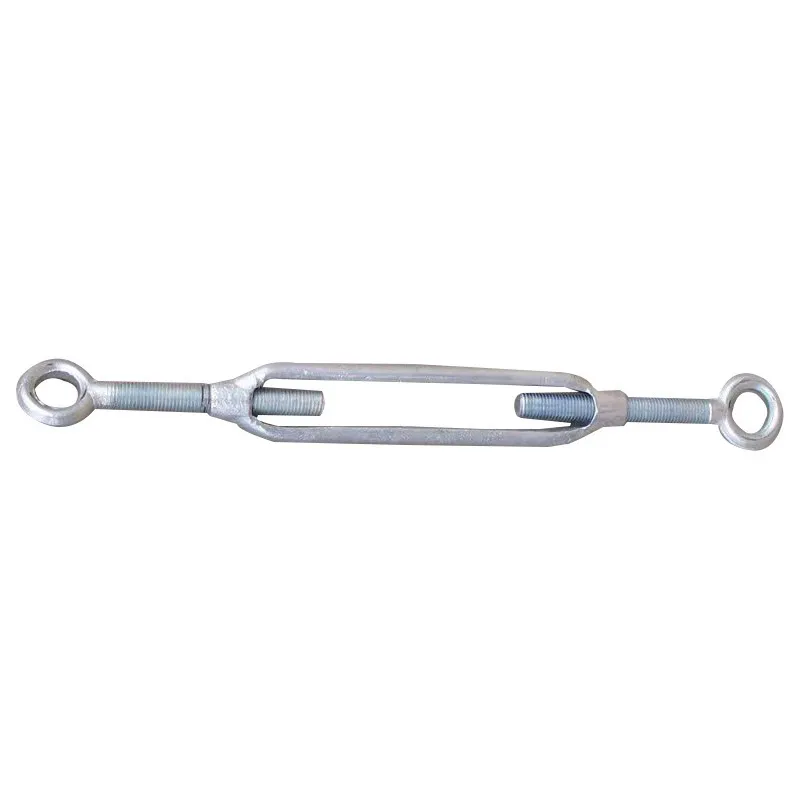
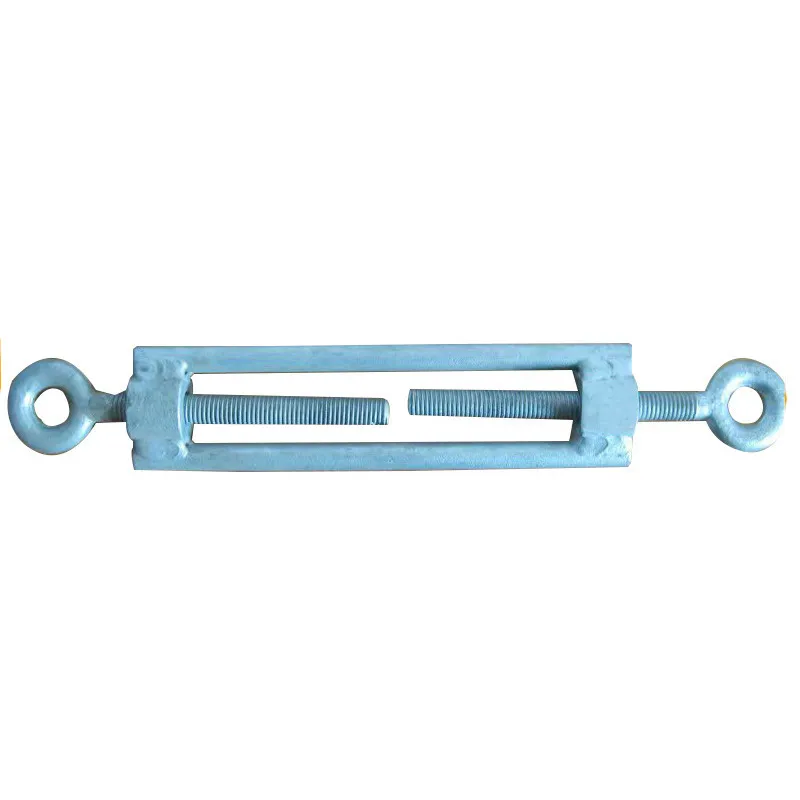
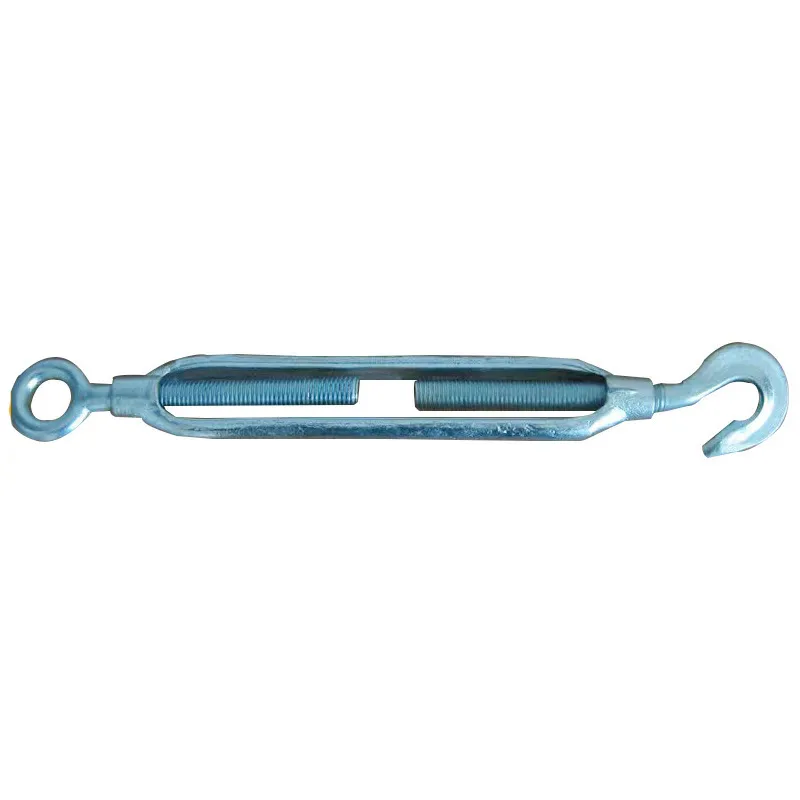
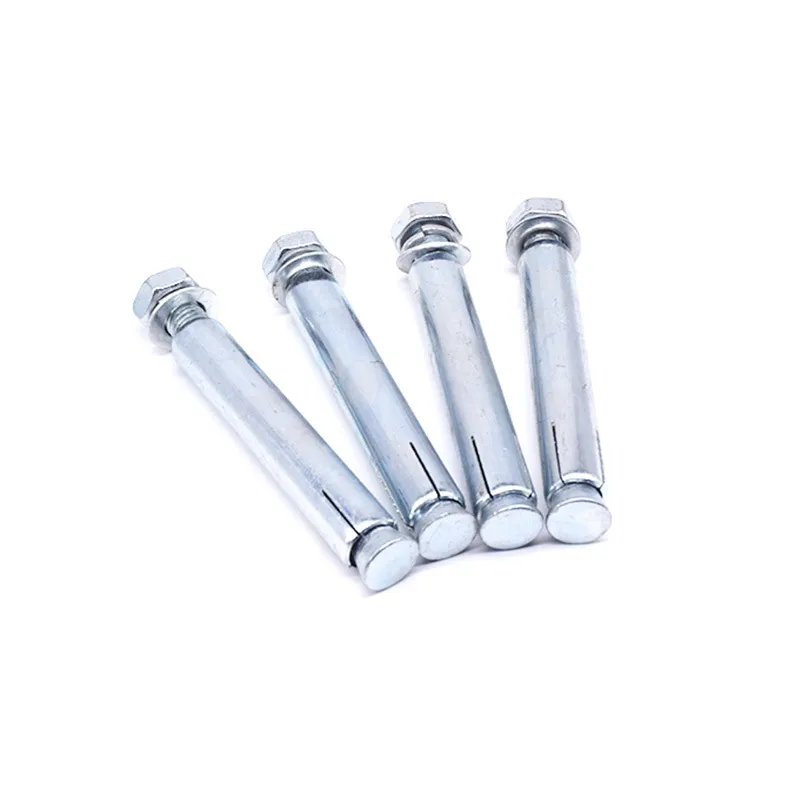
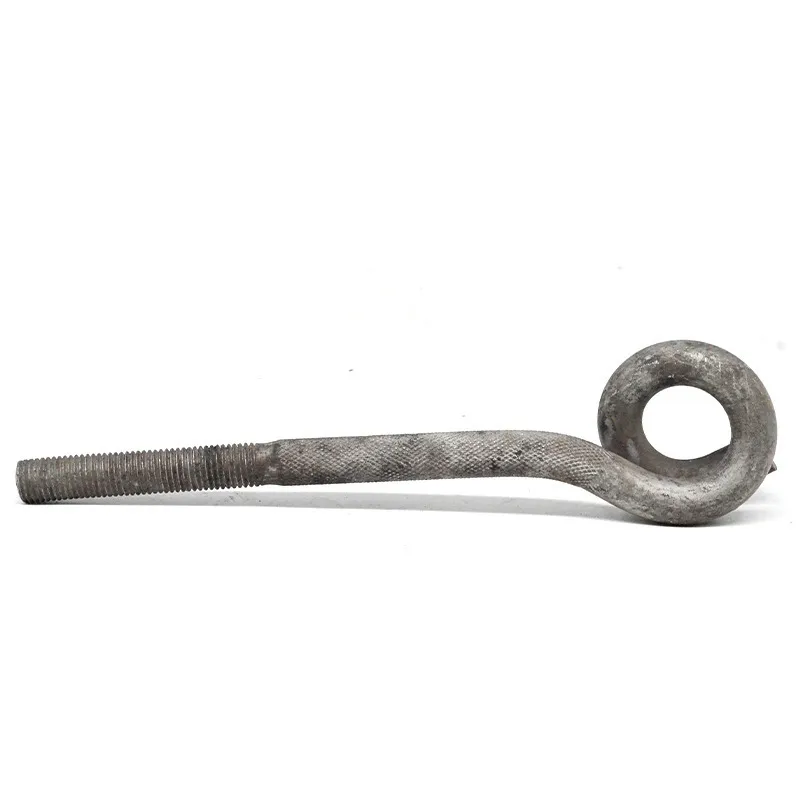
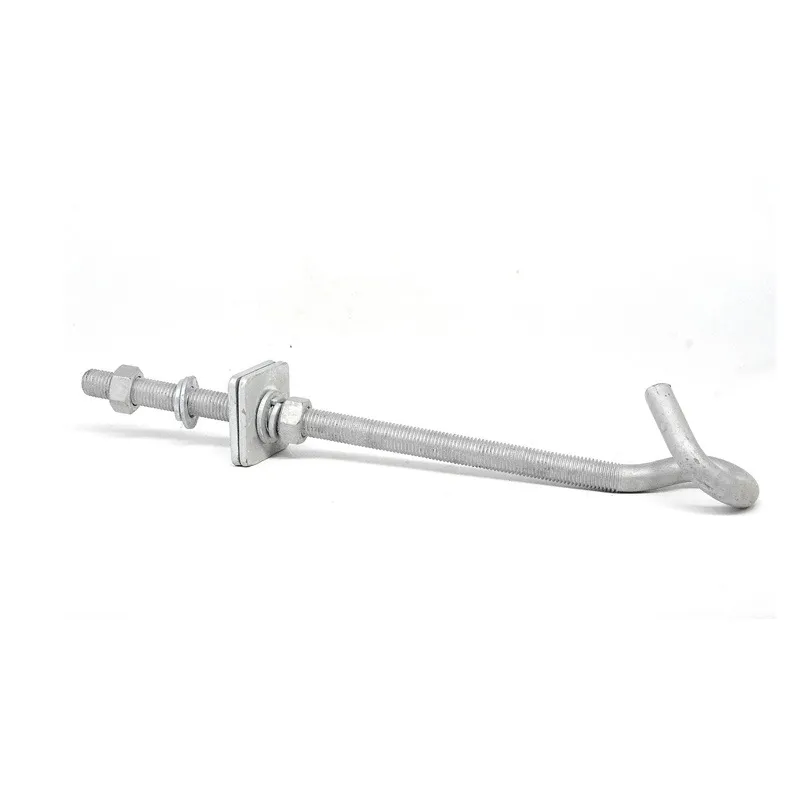
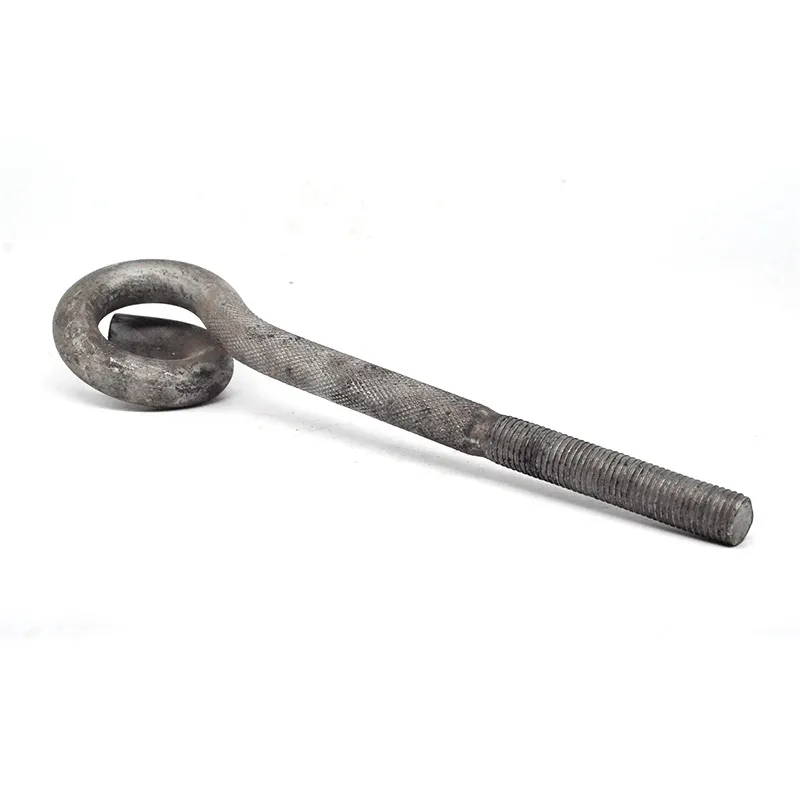
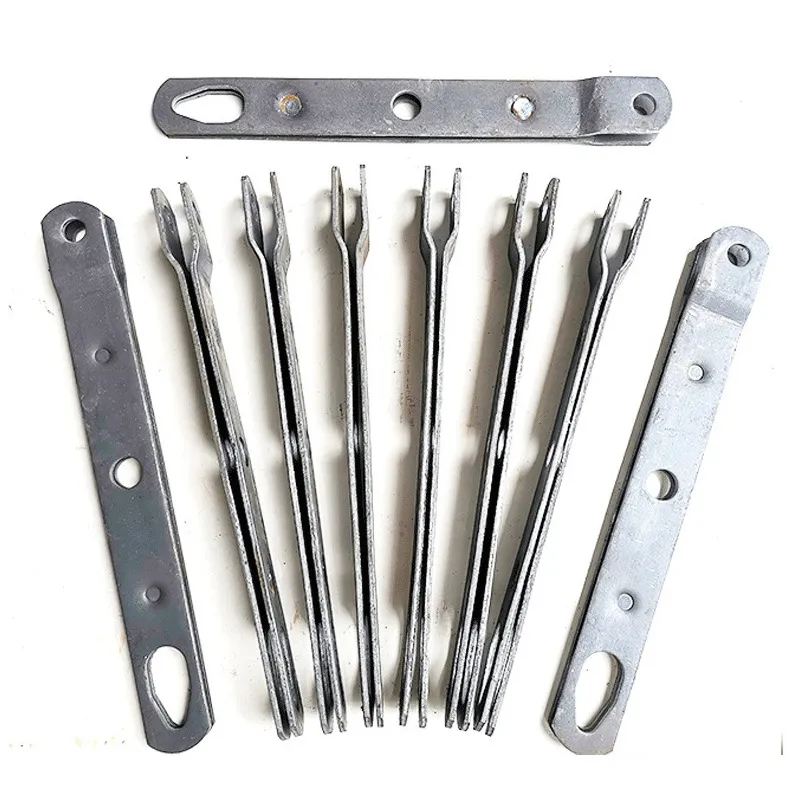
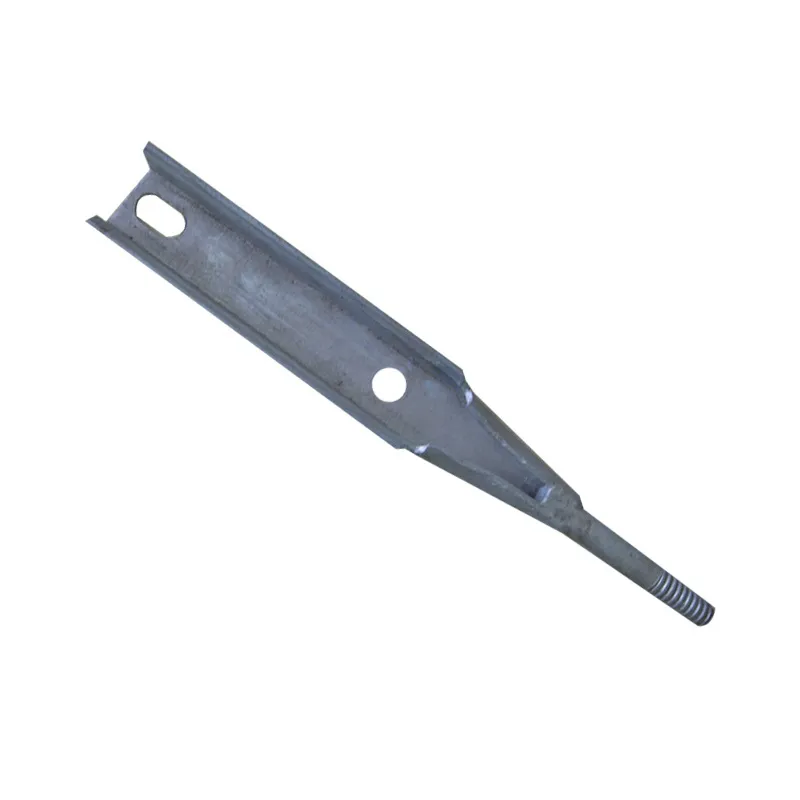
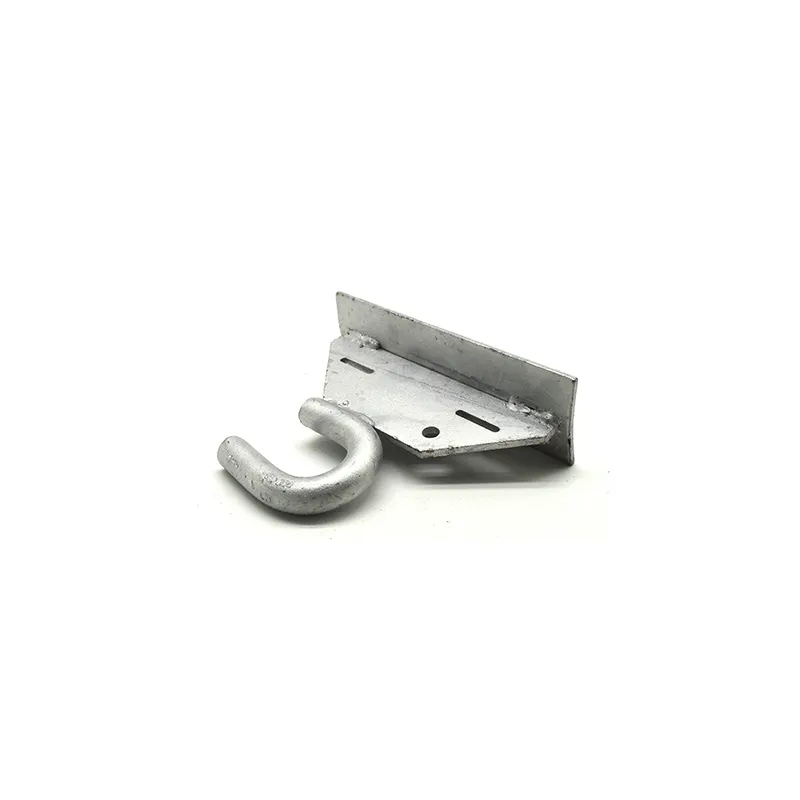
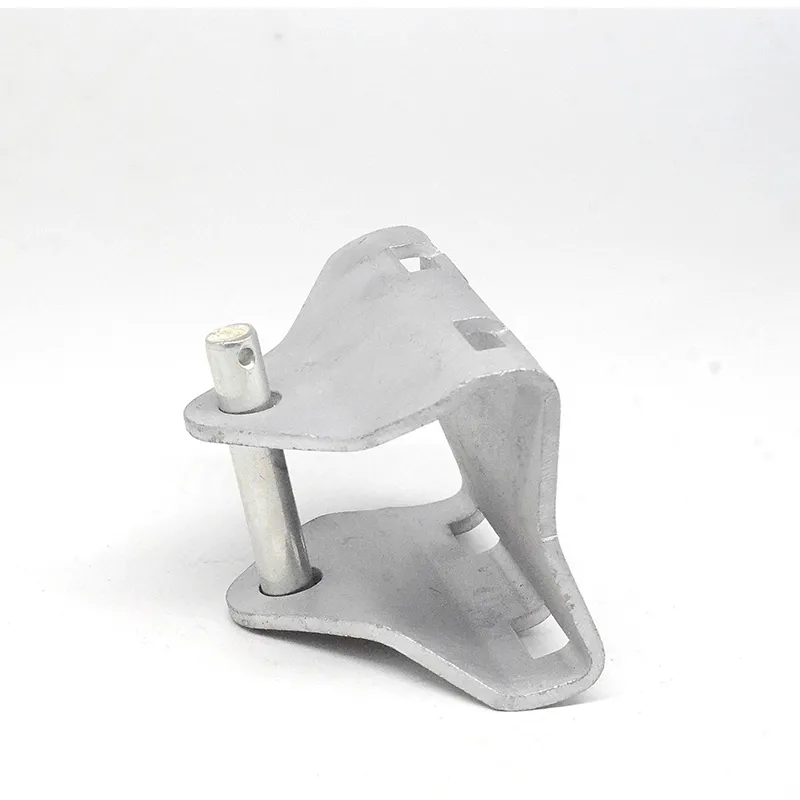
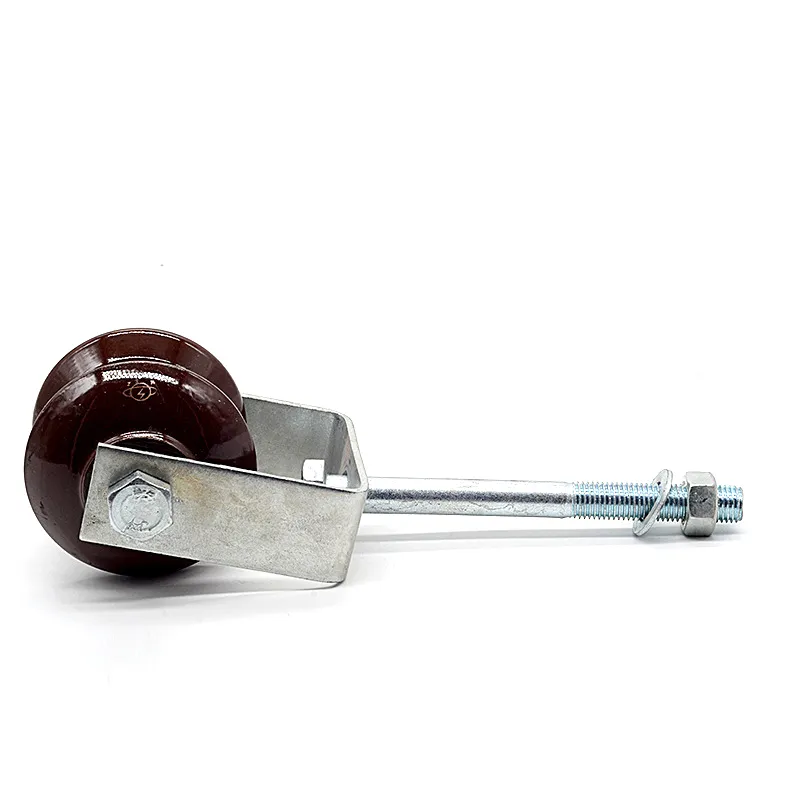
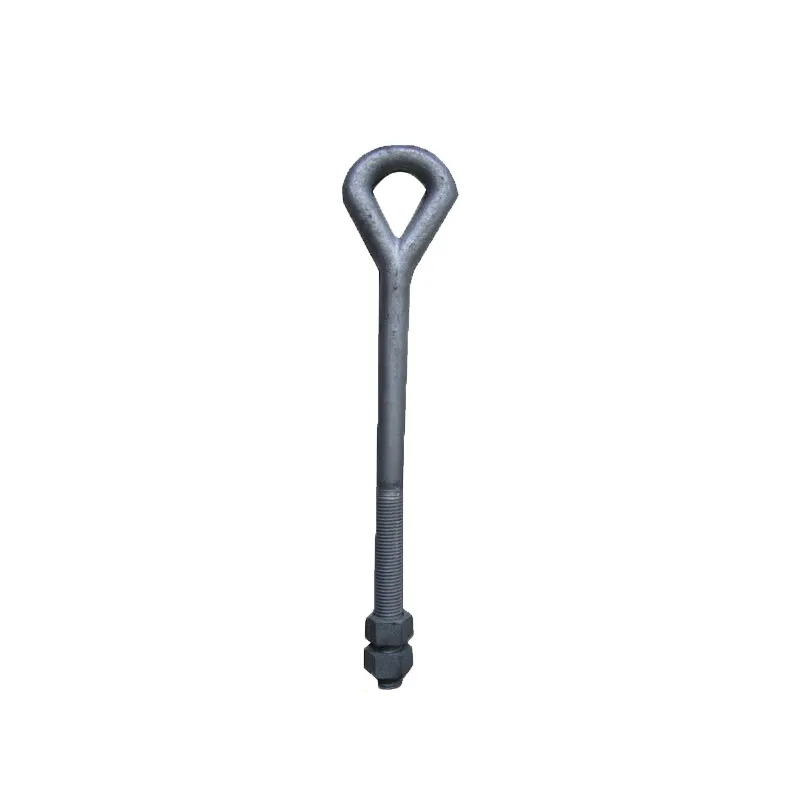
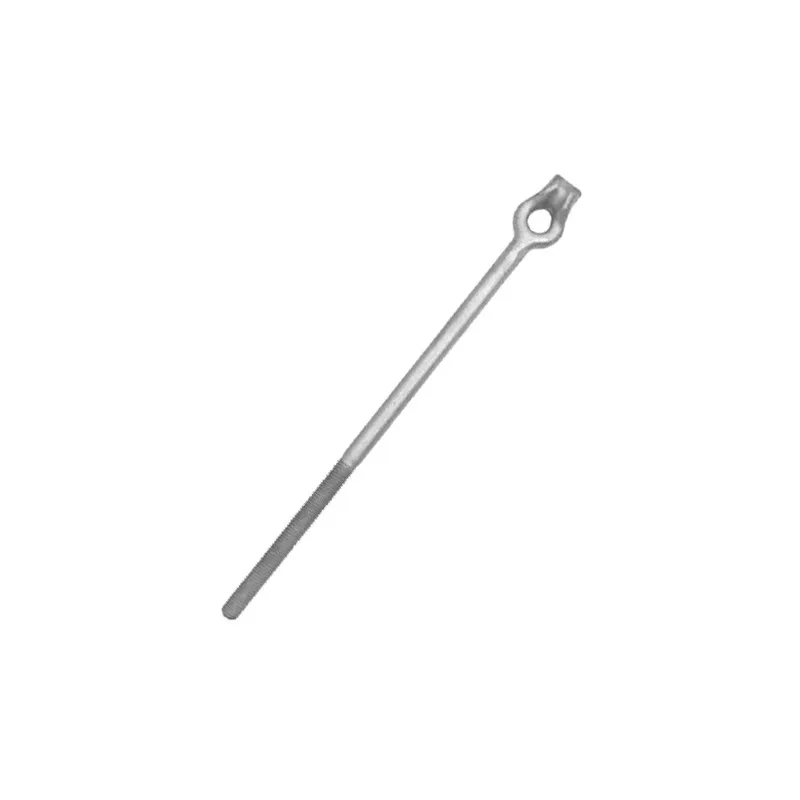
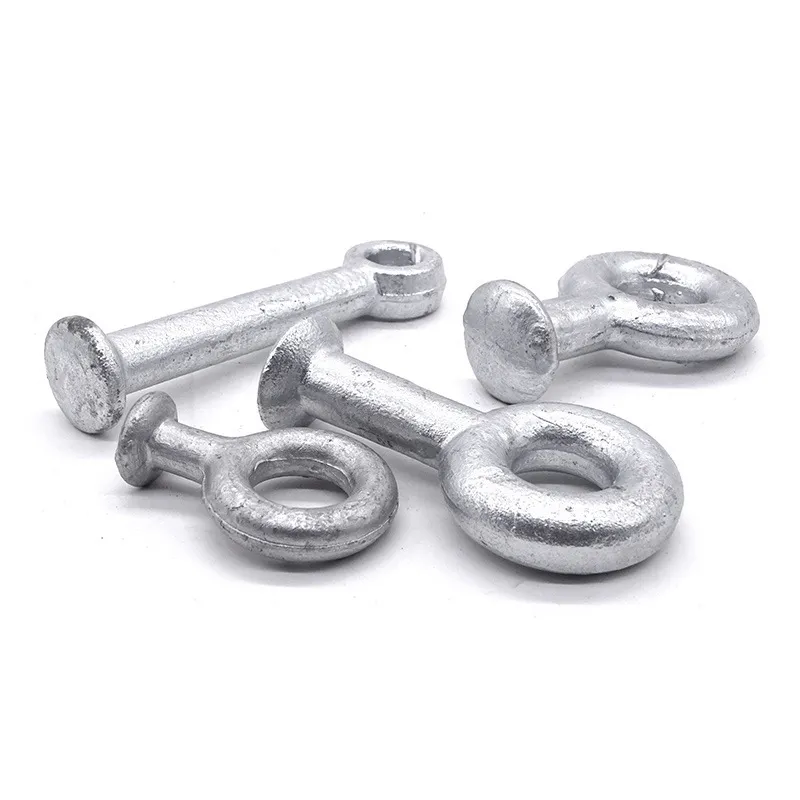
Product Description: Turnbuckles (also known as bolt turnbuckles or tensioners) are adjustable-length connecting elements. Their main mechanism extends or retracts the bolts at both ends by rotating the central nut, which is used to tension cables, ropes, or adjust the distance between com...
Description
marker
Product Description:
Turnbuckles (also known as bolt turnbuckles or tensioners) are adjustable-length connecting elements. Their main mechanism extends or retracts the bolts at both ends by rotating the central nut, which is used to tension cables, ropes, or adjust the distance between components. They are widely used in construction, transportation, and maritime navigation.
Main Structure and Operating Principle:
The structure of the turnbuckle is based on "bidirectional adjustment", which allows flexible changes to the overall length through simple operation and stable force transmission.
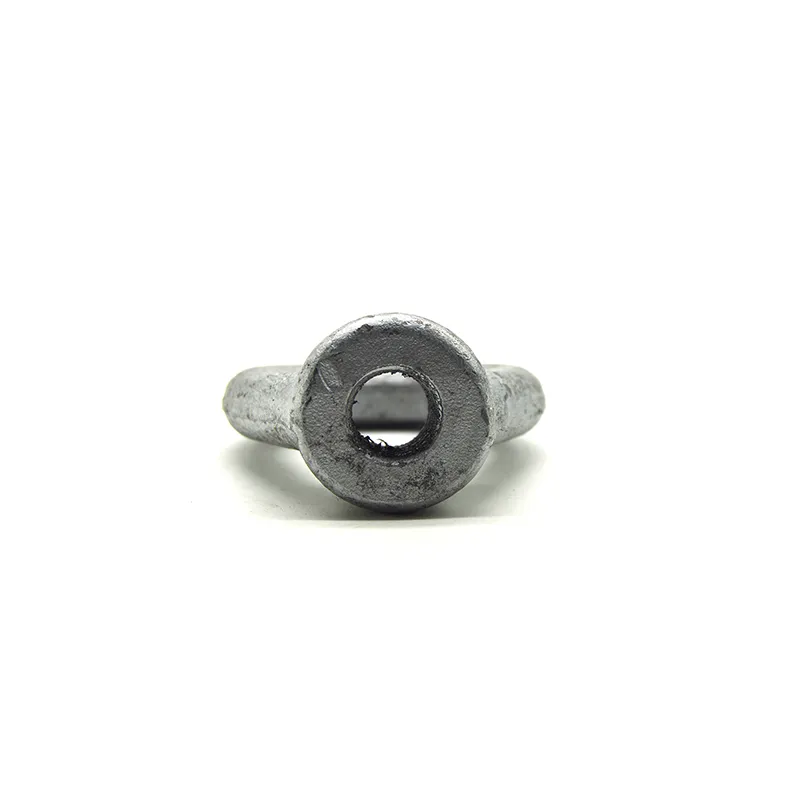
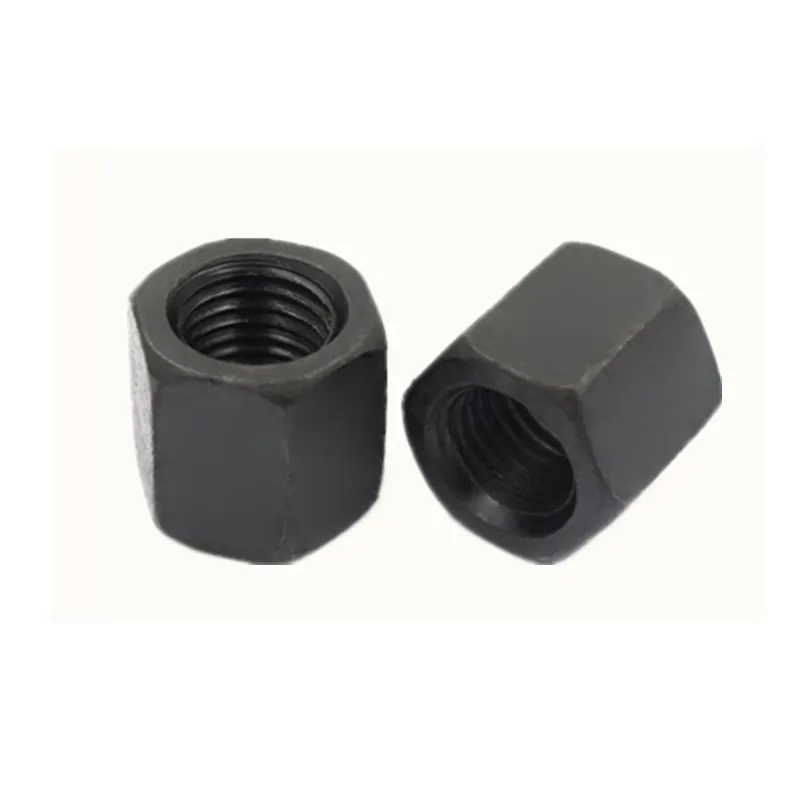
Main Structure
It consists of three parts:
- The central component is an "adjusting nut" with internal threads (usually hexagonal or round with anti-slip grooves).
- It connects to a "left threaded rod" at one end and a "right threaded rod" at the other.
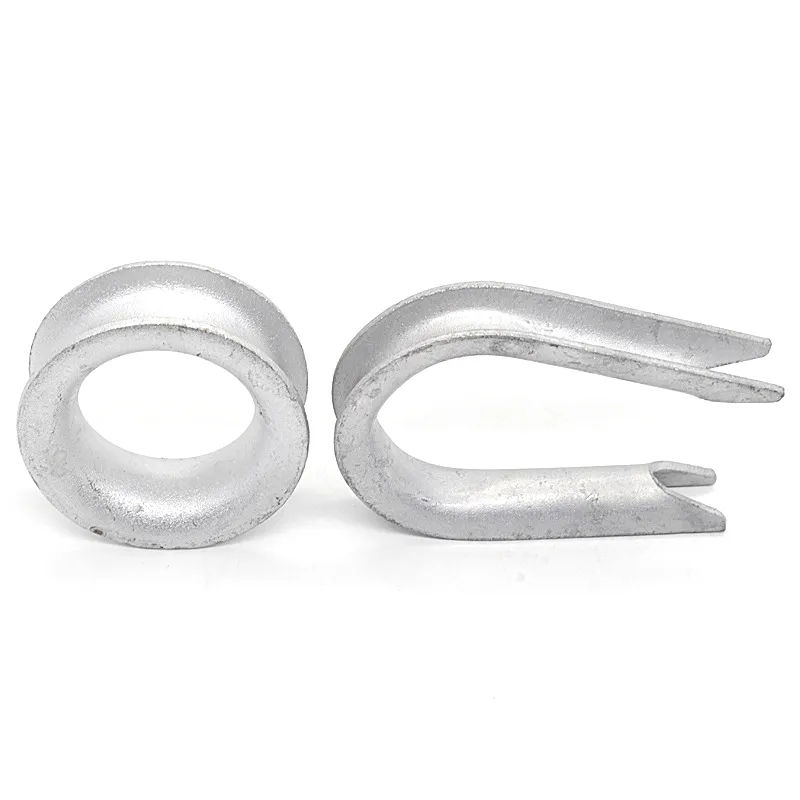
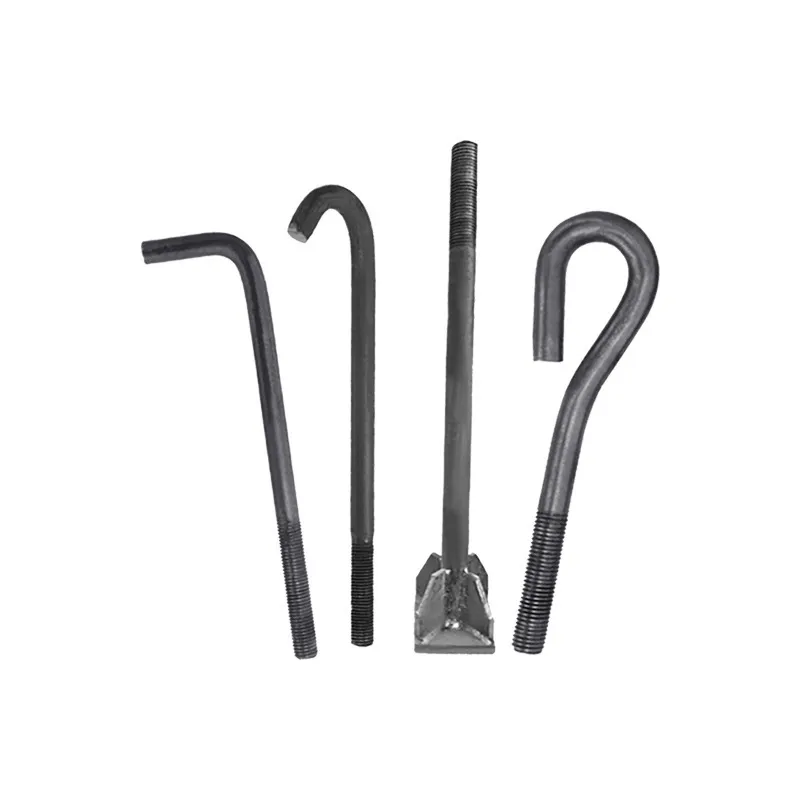
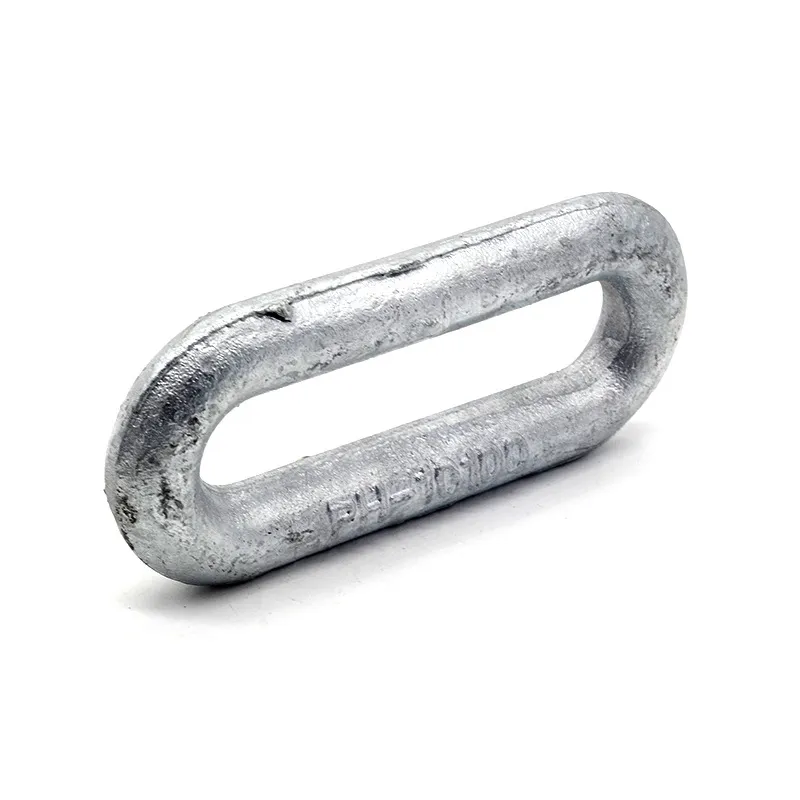
- The ends of the rods are typically equipped with hooks, rings, or forks for attaching cables or components.
Operating Principle
- The internal threads of opposite directions are processed inside the adjusting nut, connecting to the corresponding bolts at both ends.
- Rotating the adjusting nut clockwise pulls both bolts into the nut, reducing the overall length to tension cables or decrease the distance between components.
- Rotating the adjusting nut counterclockwise extends the two bolts outward, increasing the overall length to loosen cables or increase the distance.
- Quick adjustment can be achieved by rotating the nut without disassembling other components, making it suitable for dynamic loads.
Materials and Surface Treatment:
The choice of materials and surface treatment depends primarily on the corrosive activity of the working environment, load requirements, and whether the fitting will be exposed to external conditions.


















































